Critical Care and Hospitalist Medicine Made Ridiculously Simple
Also available on
Description
NEW 2024 EDITION!!!
***This new edition includes thoroughly revised and updated information regarding the latest medications, guidelines, and procedures when treating in the ICU and Emergency Department.***
Major highlights of the extensive edits since the previous edition:
- Extensive revisions to the POCUS chapter which now includes QR code access to ultrasound videos related to the text
- A new chapter on Acute Liver Failure
- Numerous edits to the ventilator chapter
- Hematologic emergencies
- Pain control
- Updates throughout ALL CHAPTERS related to new information and suggested reading references making the book the most current on the market
- Over 100 completely redrawn illustrations, charts, and tables
A fundamental and thorough guide to the treatment of hospitalized patients in critical care situations. Critical Care and Hospitalist Medicine Made Ridiculously Simple provides both introductory information as well as a complete base of knowledge that will be useful from medical student, to resident, to fellow, to practicing intensivist, hospitalist, internist, and specialists all charged with caring for patients in the ICU and Emergency Department, as well as the wards.
The current and practical content is organized in a logical, conceptual manner, using plain English for rapid assimilation of information, and focusing on critical care facts and approaches required to keep the critically ill patient alive and thriving.
Topics include: The Art of Patient Presentation, Approach to Acute Care Chest Radiology with the Top Ten X-ray Bad Guys, goals and findings of Point of Care Ultrasound, Sepsis and Resuscitation, Management of Tachyarrythmias, Running a Code, Hemodynamic Monitoring, Acute Coronary Syndromes, Acute Decompensated Heart Failure, High Systemic Arterial Blood Pressure, Pulmonary Thromboembolic Disease, Basic Airway Management, Acute Respiratory Failure, Mechanics of Respiratory Failure, Mechanical Ventilation, Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome, Obstructive Lung Disease and Respiratory Failure, Weaning From Mechanical Ventilation, Bleeding Clotting and Hematological Emergencies, Transfusion Medicine, Acute Kidney Injury, GI Bleeding, Acid-Base Disorders, Drug Overdose, and Neurologic Emergencies.
Author(s)
Michael Donahoe, M.D.
Michael Donahoe, M.D. is Professor of Medicine, division of Pulmonary, Allergy, and Critical Care Medicine at the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine and UPMC.
Mark T. Gladwin, M.D.
Mark T. Gladwin, M.D. is Jack D. Myers Professor and Chair of the Department of Medicine and Director, Pittsburgh Heart, Lung, Blood and Vascular Medicine Institute UPMC and the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine.
Details
Pages: 448
Publication: Edition 4 (May 15, 2024)
Language: English
ISBN: 9781962445030 eISBN: 9781962445047
Table of contents
Introduction
Contributors
The Illustrator
The Consultant for Point of Care Ultrasound (POCUS)
Chapter 1 The Art of the Patient Presentation
1.1 Welcome to Acute Hospital Medicine
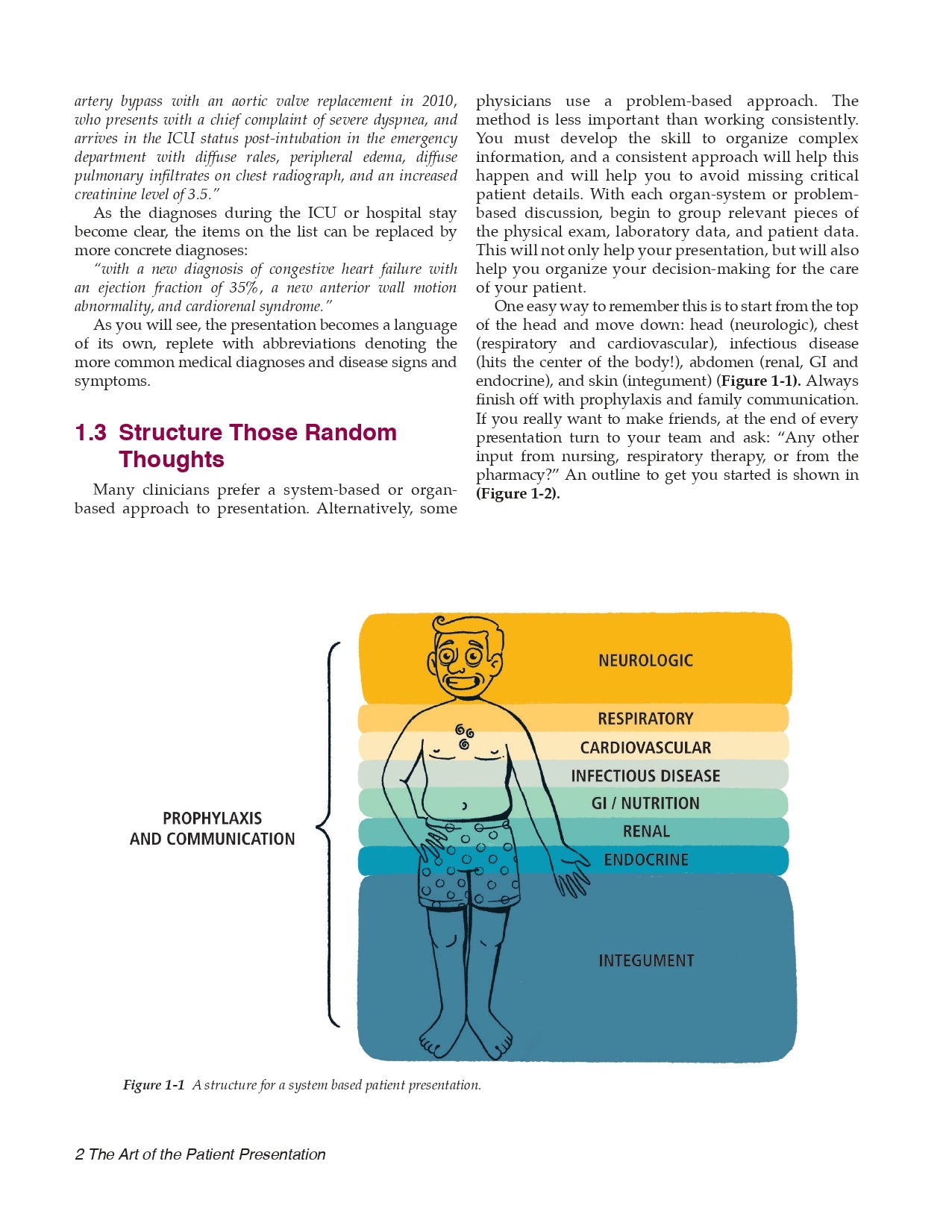
1.2 How to Summarize Your Patient
1.3 Structure Those Random Thoughts
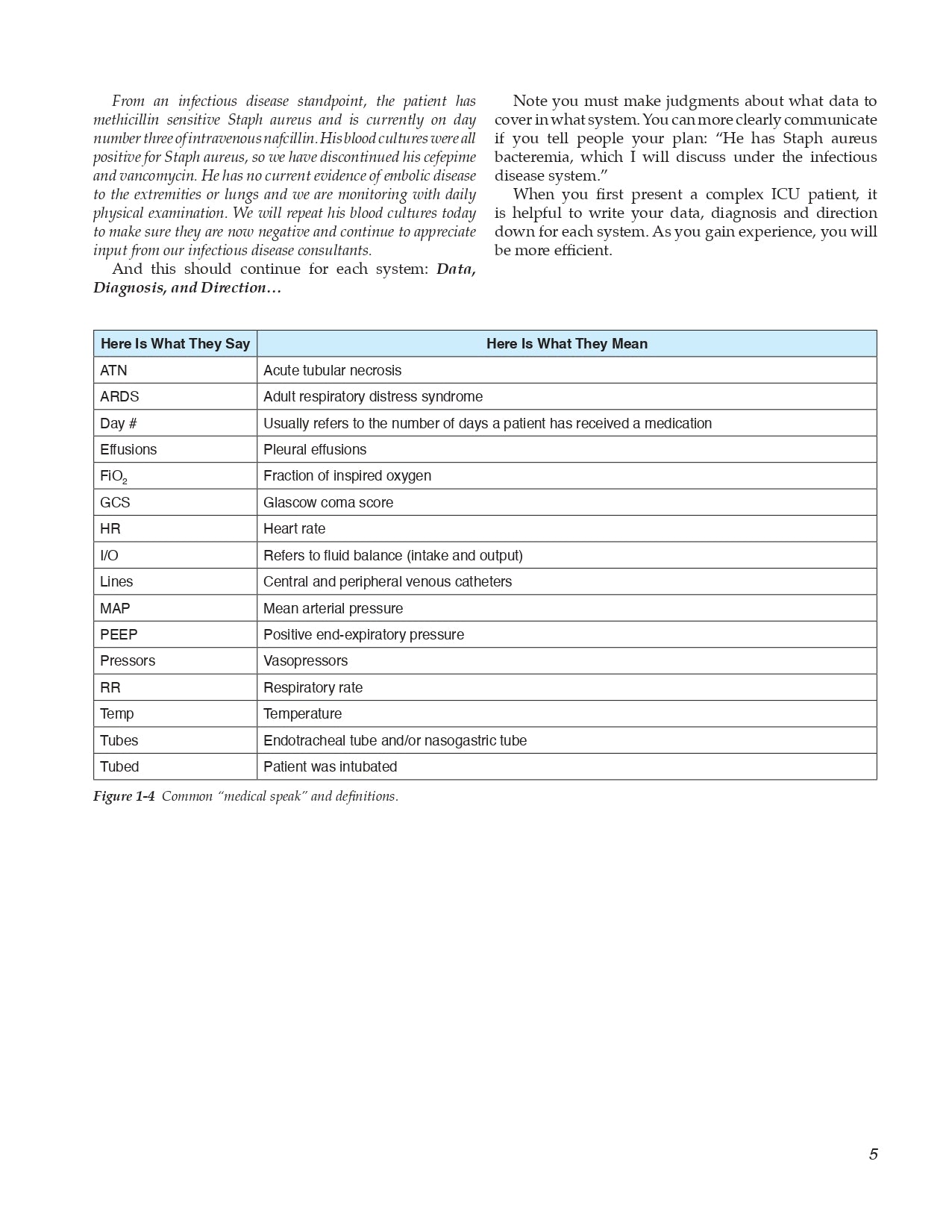
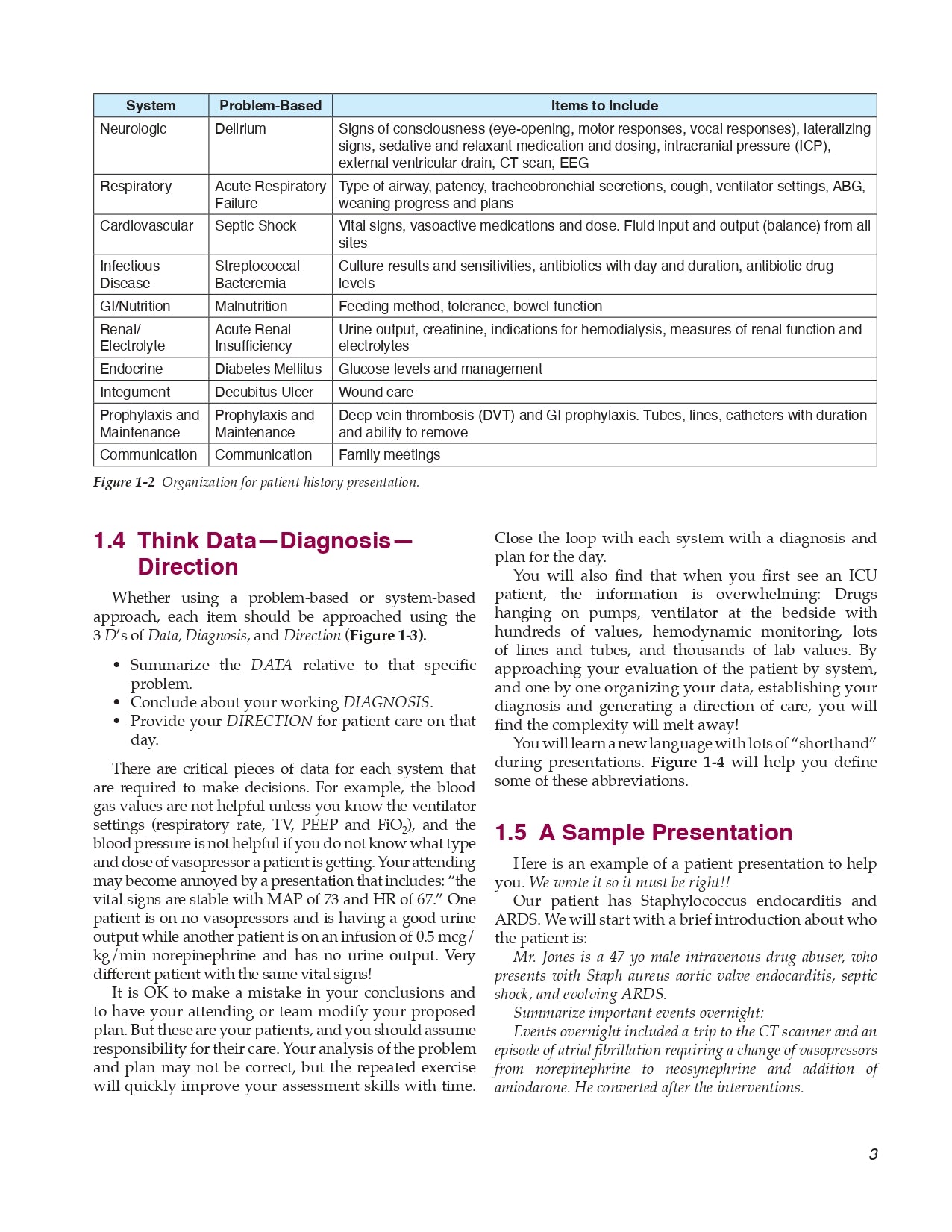
1.4 Think DataDiagnosisDirection
1.5 A Sample Presentation
Chapter 2 Acute Care Chest Radiology
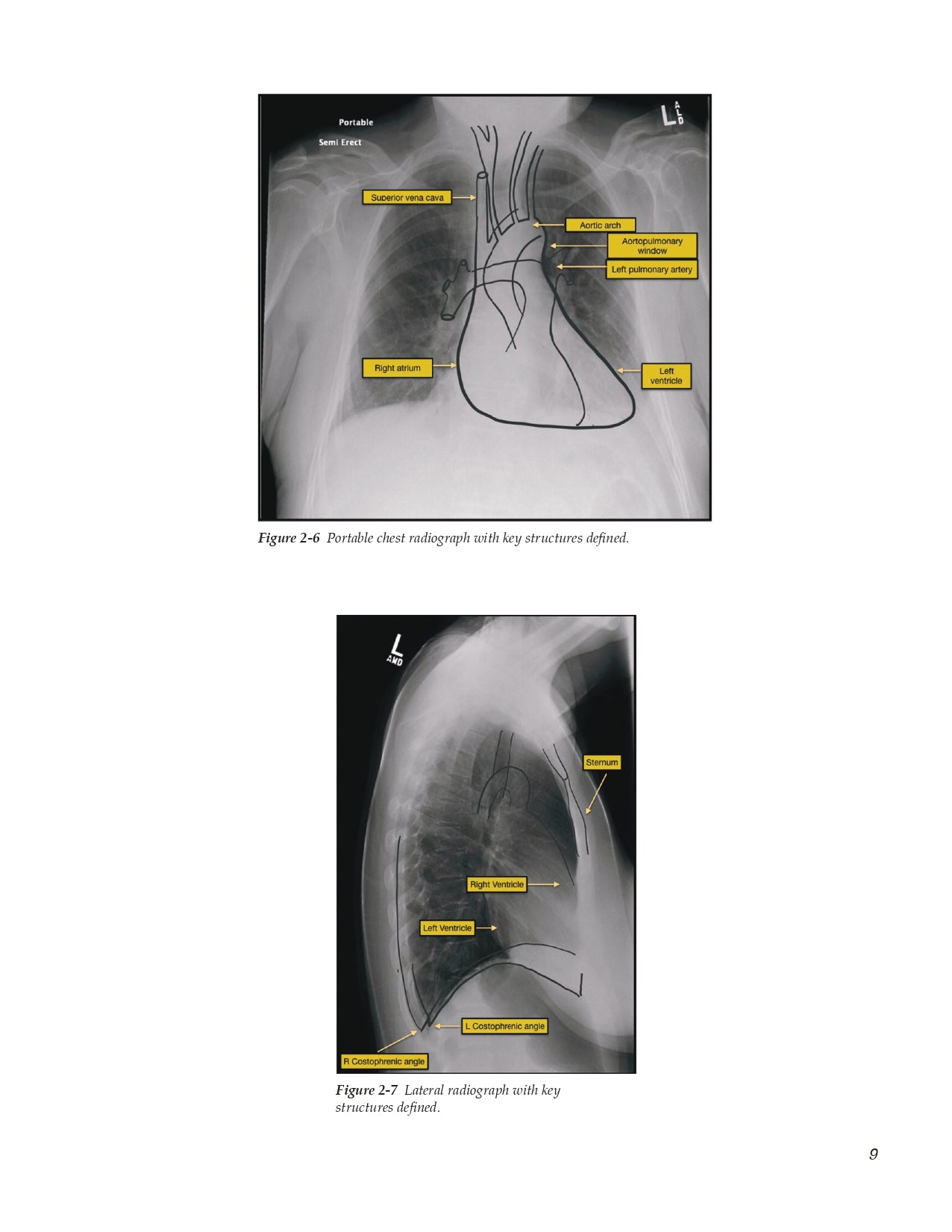
2.1 Basics of Reading Portable Chest Radiographs
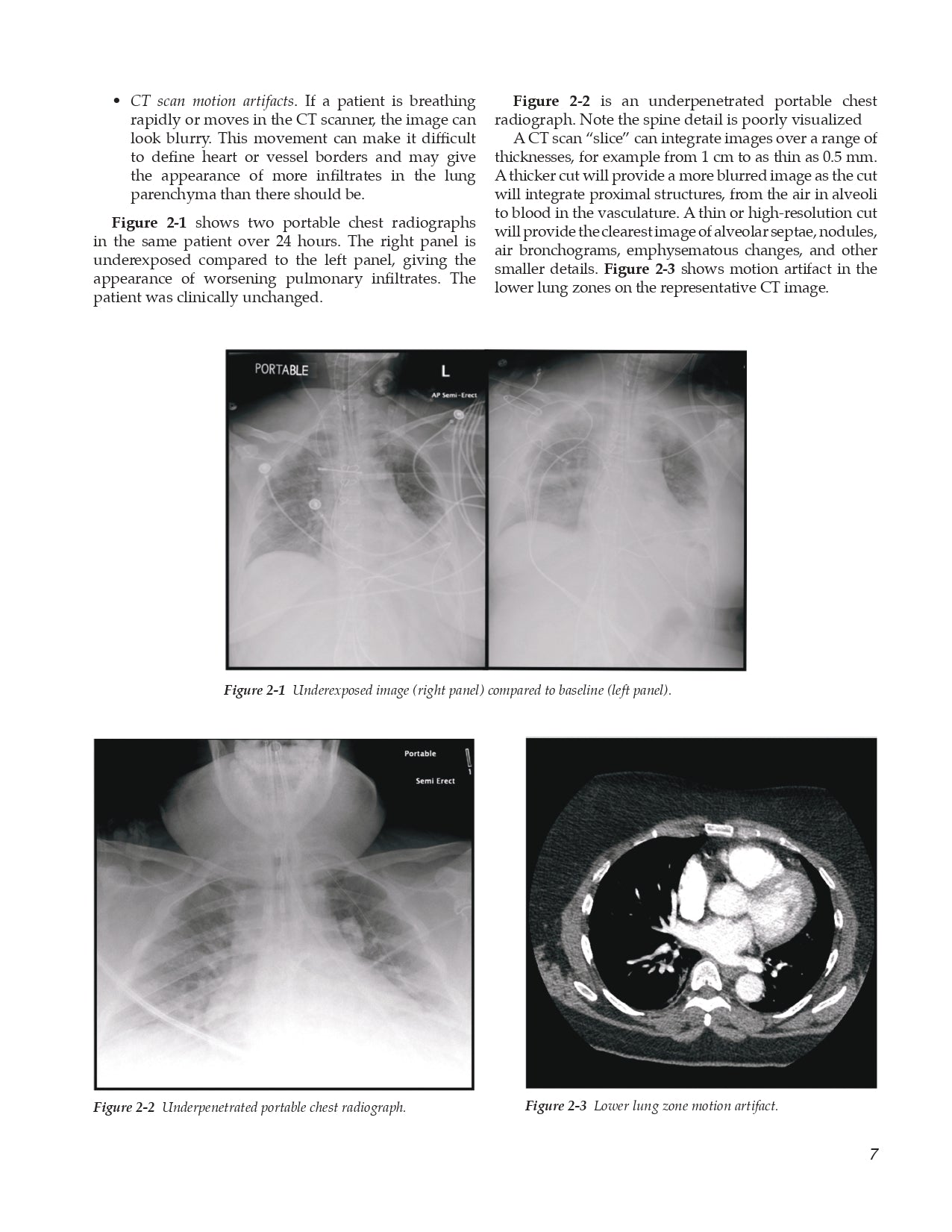
- Is the Radiograph Worth Reading?
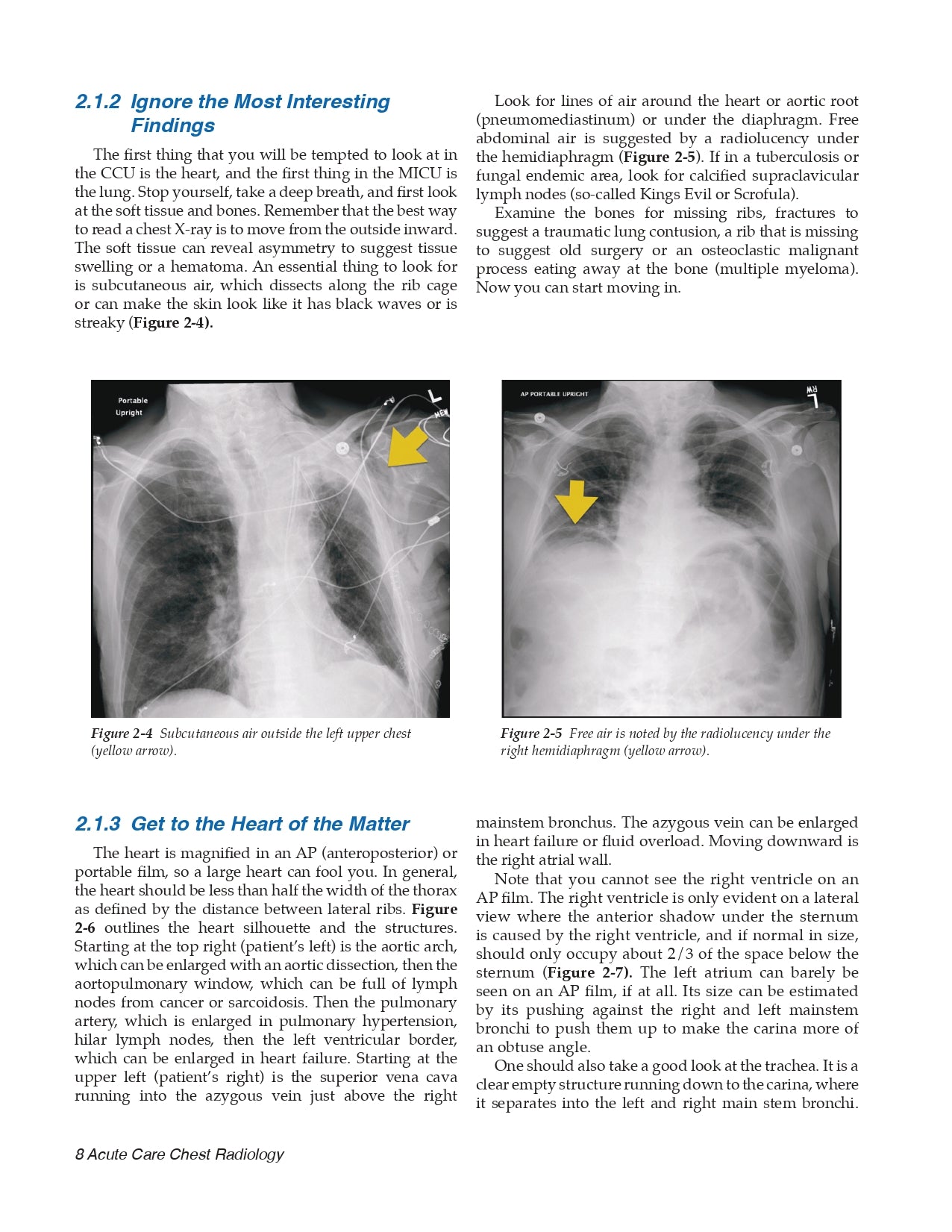
- Ignore the Most Interesting Findings
- Get to the Heart of the Matter
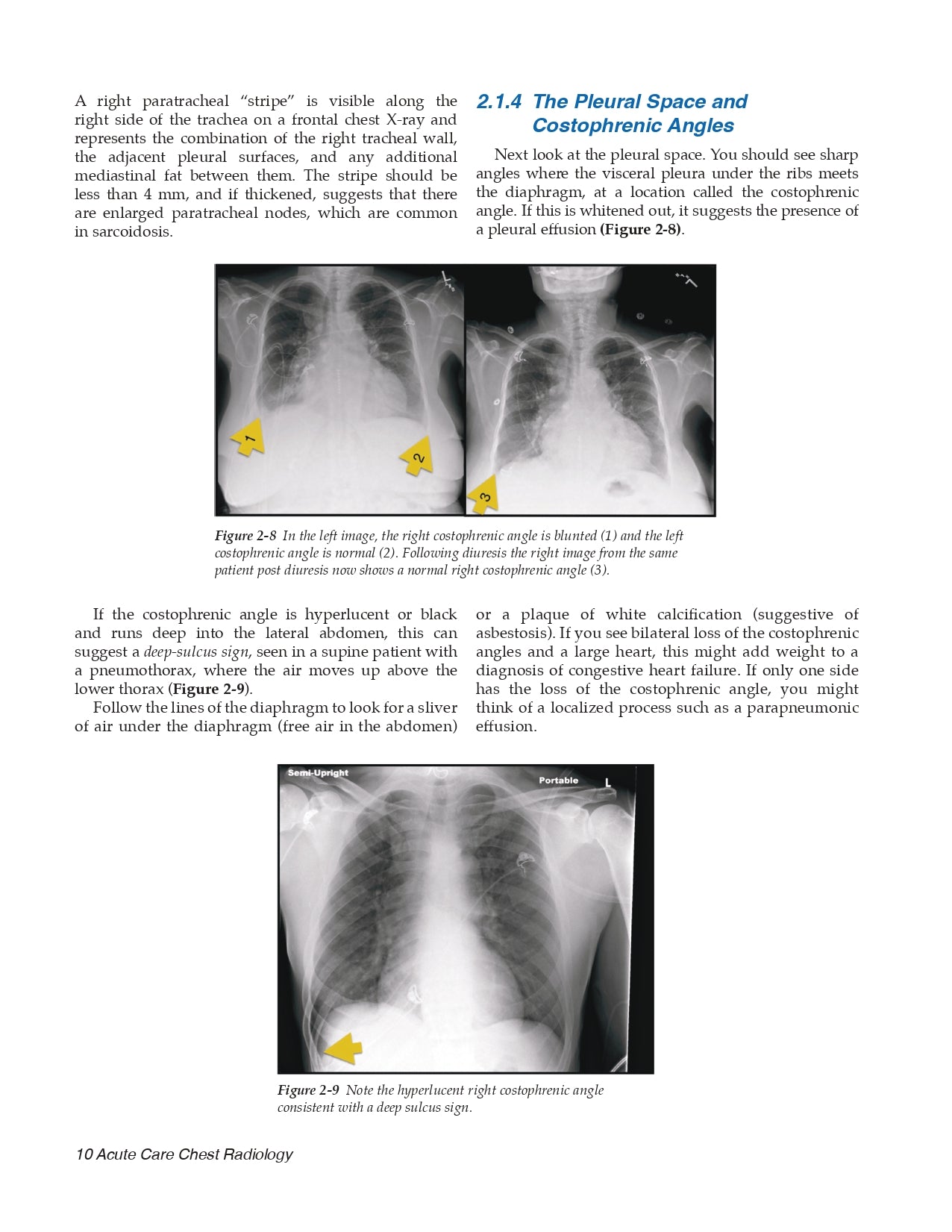
- The Pleural Space and Costophrenic Angles
- Finally, the Lungs!
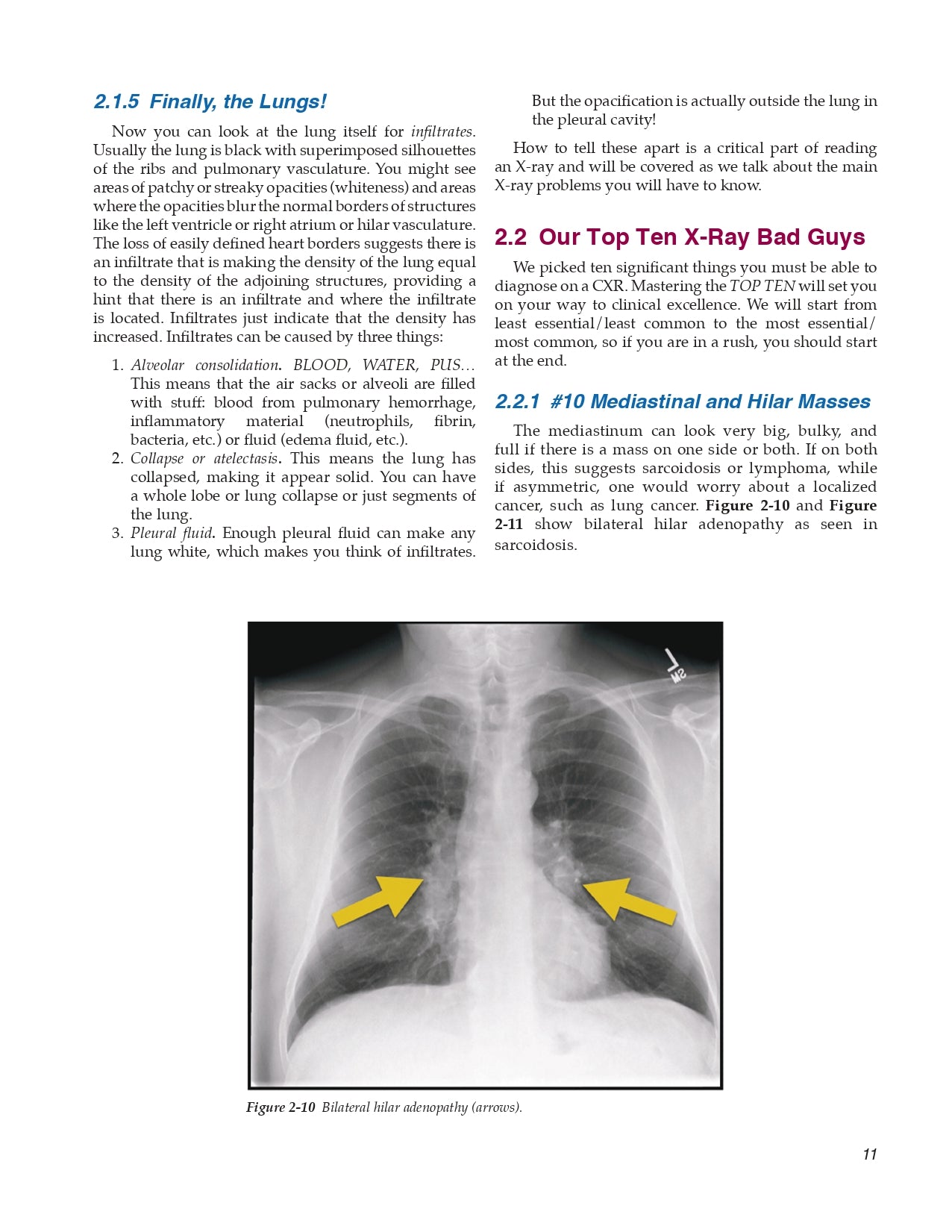
2.2 Our Top Ten X-Ray Bad Guys
- #10 Mediastinal and Hilar Masses
- #9 Pericardial Effusion and Tamponade
- #8 Pulmonary Hypertension and Pulmonary Emboli
- #7 Tube Mishaps
- #6 Pneumothorax and Barotrauma
- #5 Effusions, Empyema, and Hemothorax
- #4 Atelectasis and Lobar Collapse
- #3 Congestive Heart Failure
- #2 Pneumonia
- #1 Adult Respiratory Distress Syndrome
-- Suggested Reading
Chapter 3 Point of Care Ultrasound (Pocus)
3.1 The Three Goals of POCUS
- Procedural Guidance
- Diagnosis
- Shock Management
3.2 POCUS Lingo
3.3 Our Top Ten POCUS Findings in the ICU
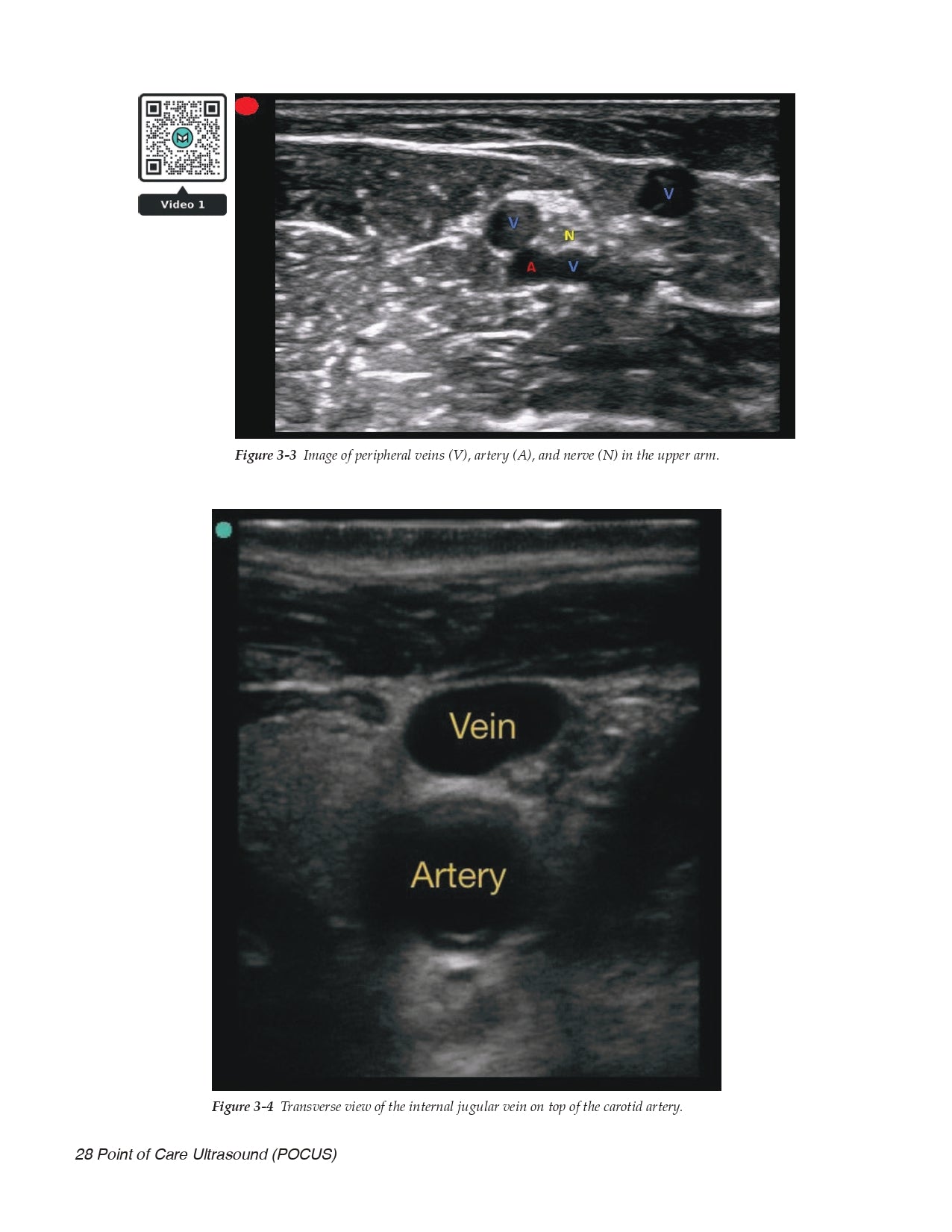
- Vessel Location for Catheter Placement
- Pneumothorax
- Pleural Fluid
- Lung Patterns
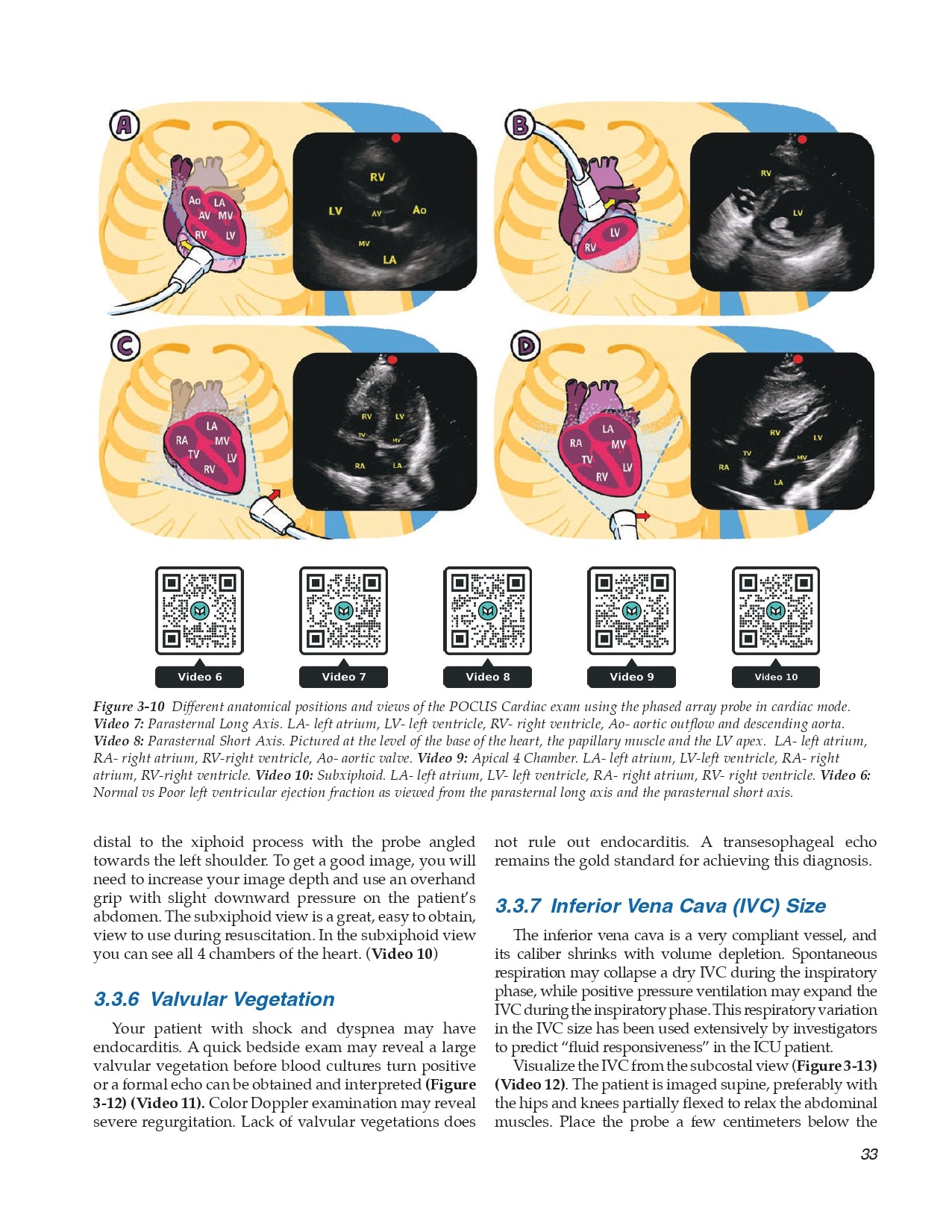
- Left Ventricle and Right Ventricle Dysfunction
- Valvular Vegetation
- Inferior Vena Cava (IVC) Size
- Distended Bladder
- Peritoneal Fluid
- Deep Venous Thrombosis (DVT)
3.4 POCUS Focus
Chapter 4 Sepsis and Resuscitation
4.1 Sepsis Defined
4.2 Sepsis and Shock
4.3 Initial Sepsis Management
- Reverse Hypoxemia and Limited Ventilation
- Reverse Hypotension and Support Organ Perfusion
4.4 Fluid Administration in Sepsis
- Crystalloids vs. Colloids
4.5 Vasopressors and Inotropes
4.6 Assessment of Tissue Oxygenation
- Mixed Venous Oxygen Saturation
- Blood Lactate
4.7 Hydrocortisone and Septic Shock
4.8 Antibiotics and Source Control
- Suggested Reading
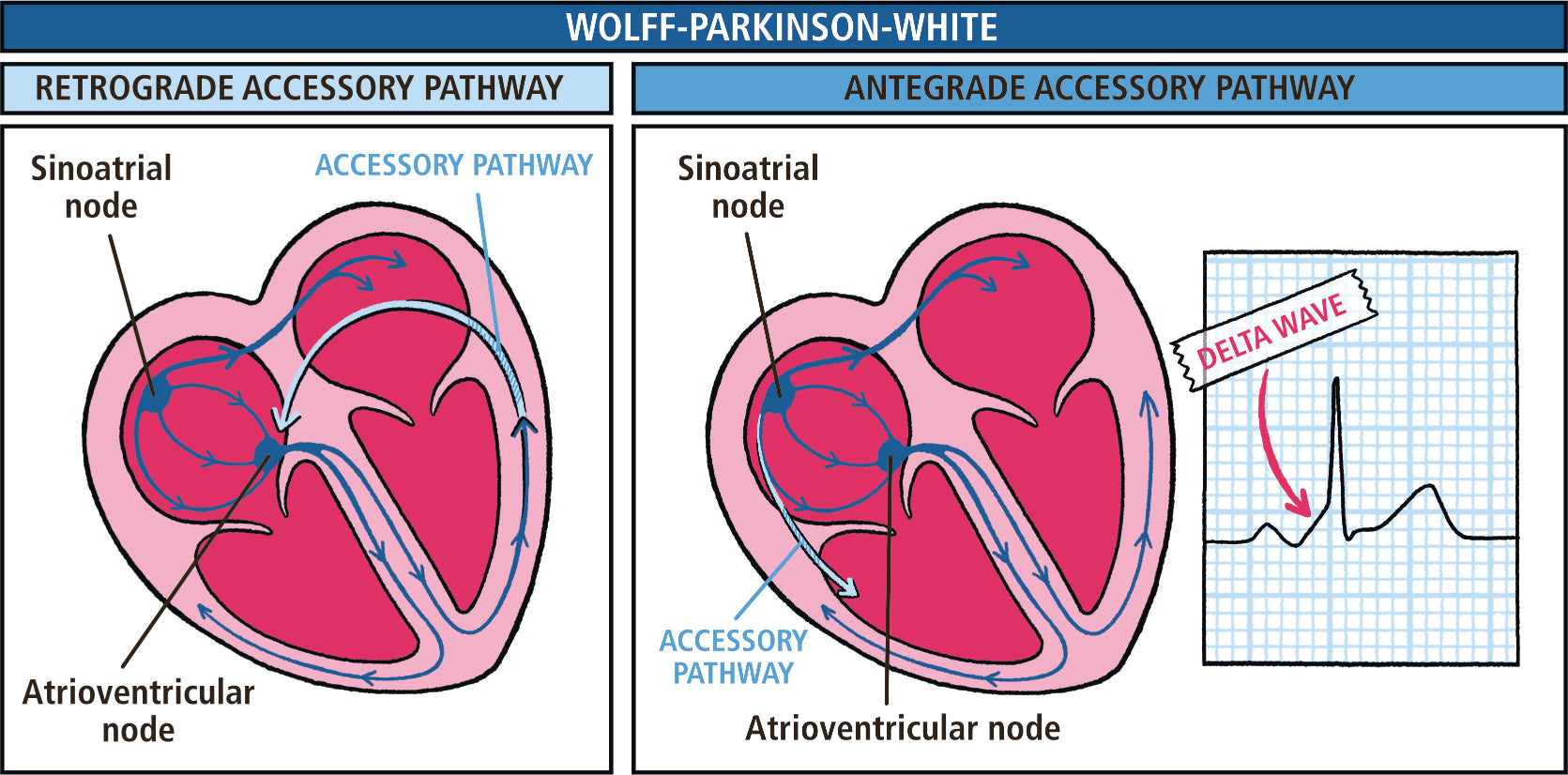
Chapter 5 Management of Tachyarrythmias
5.1 Do I Have Time to Think?
5.2 What is the Diagnosis?
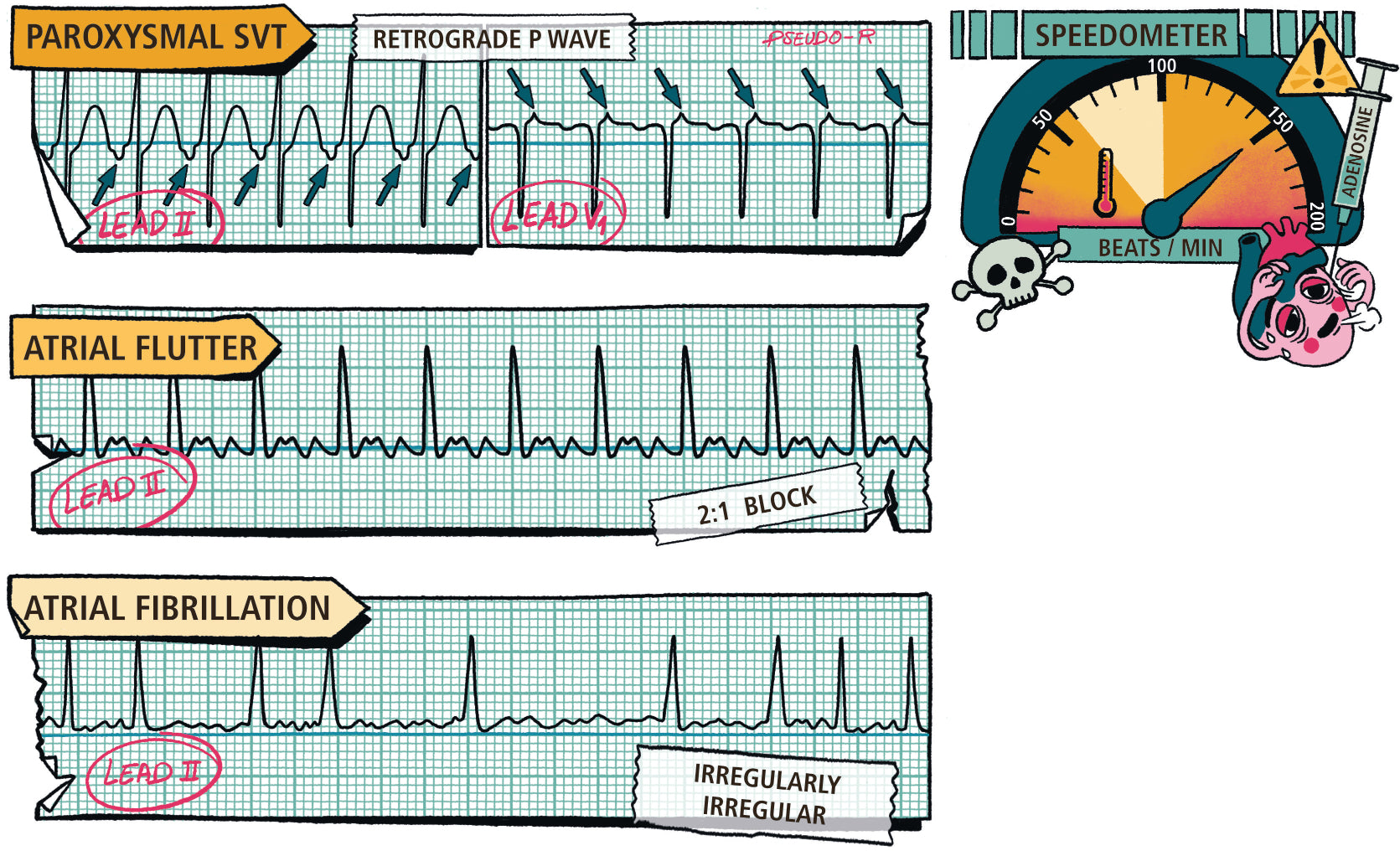
- Narrow Complex Tachycardia
- Wide Complex Tachycardia
5.3 How Do I Stop the Arrhythmia?
- Sinus Tachycardia
- Atrial Fibrillation and Flutter
- Multi-focal Atrial Tachycardia
- Paroxysmal Supraventricular Tachycardia (PSVT)
- Ventricular Tachycardia
5.4 What is the Rhythm Trying to Tell Me?
5.5 Do I Need to Anticoagulate?
- Suggested Reading
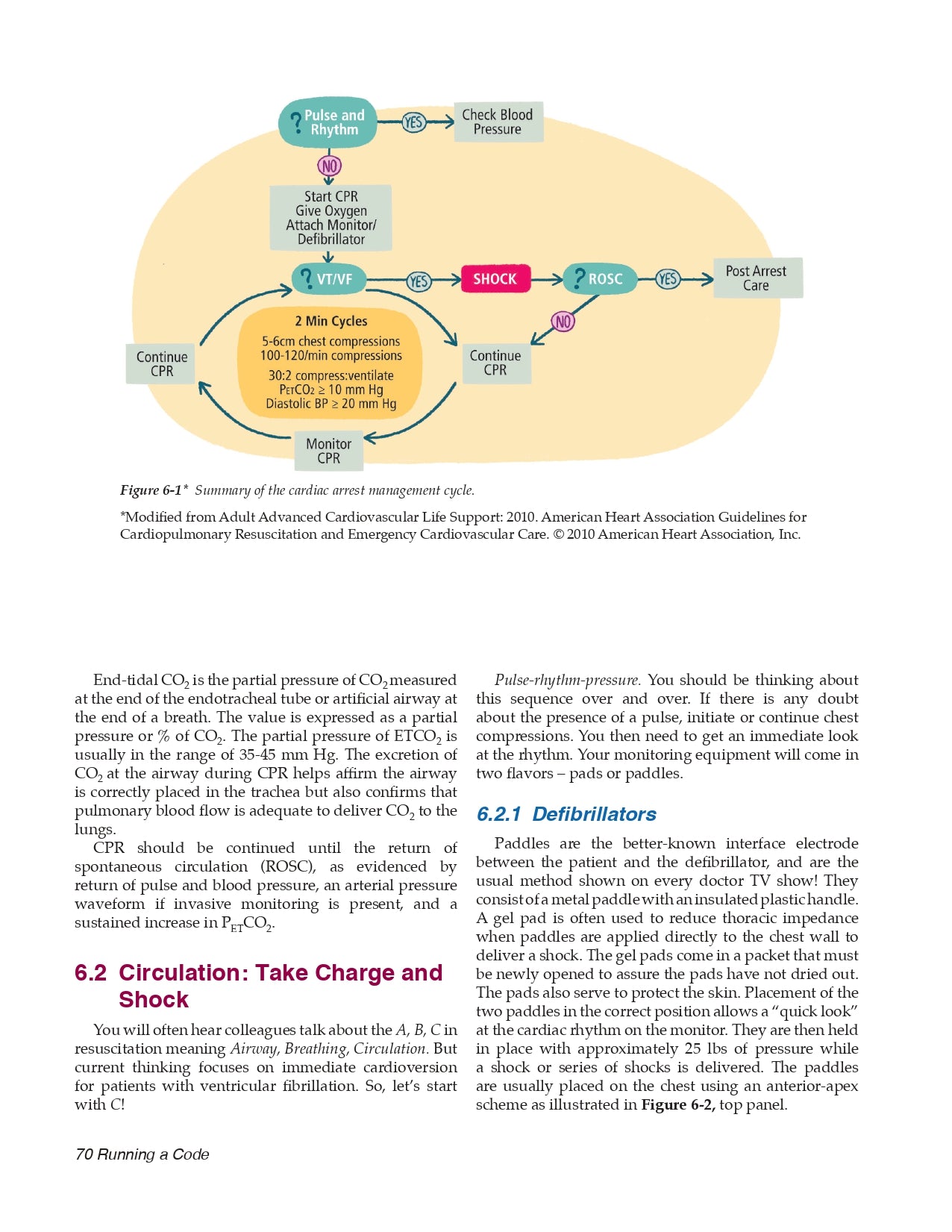
Chapter 6 Running a Code
6.1 Chest Compressions
6.2 Circulation: Take Charge and Shock
- Defibrillators
- Pulseless and a Shockable Rhythm
- Pulseless Electrical Activity (PEA)
- Pulseless and Asystole (Flat Line)
6.3 Breathing and Airway
6.4 Post-Arrest Care
- Suggested Reading
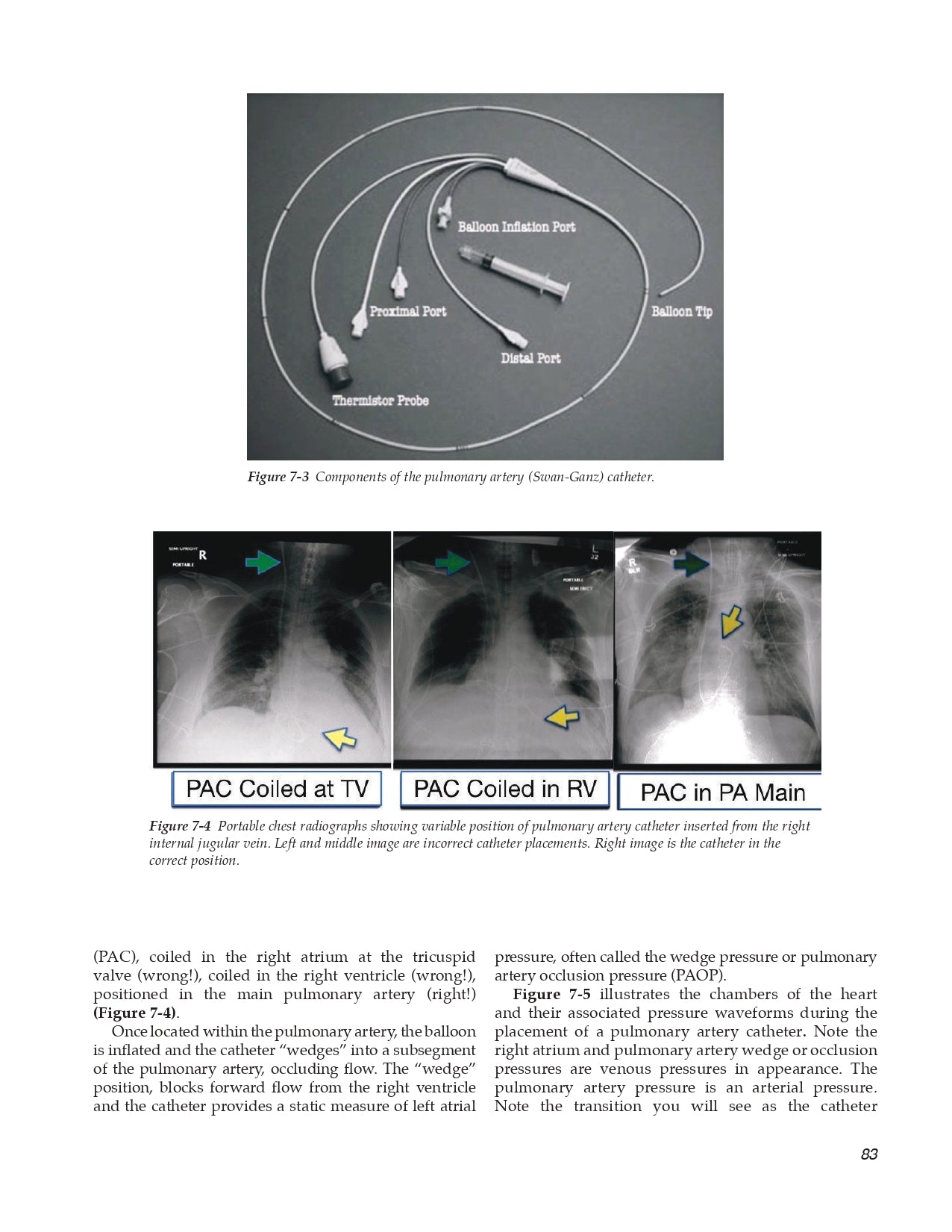
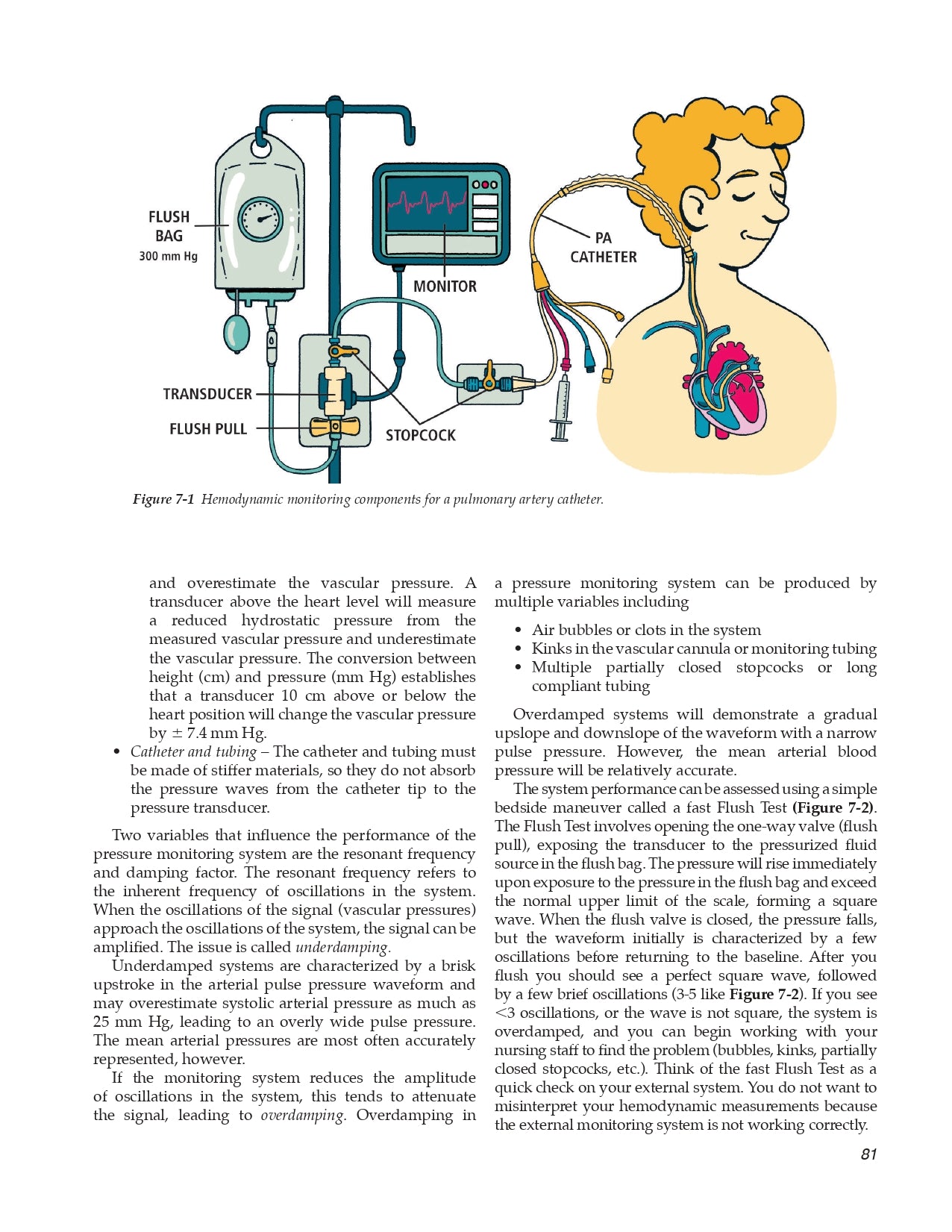
Chapter 7 Hemodynamic Monitoring
7.1 Arterial Blood Pressure
- The Arterial Catheter
7.2 Pressure Transducers
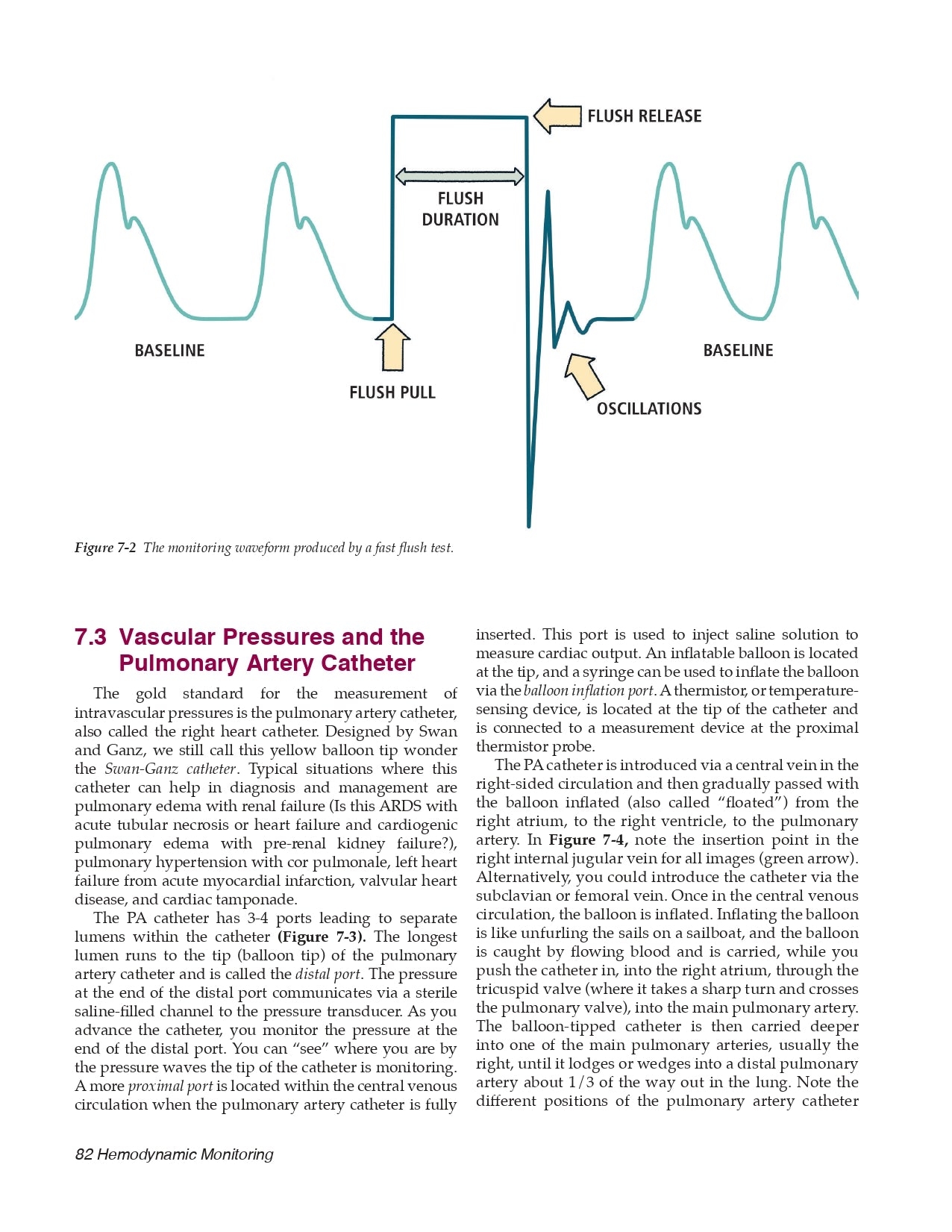
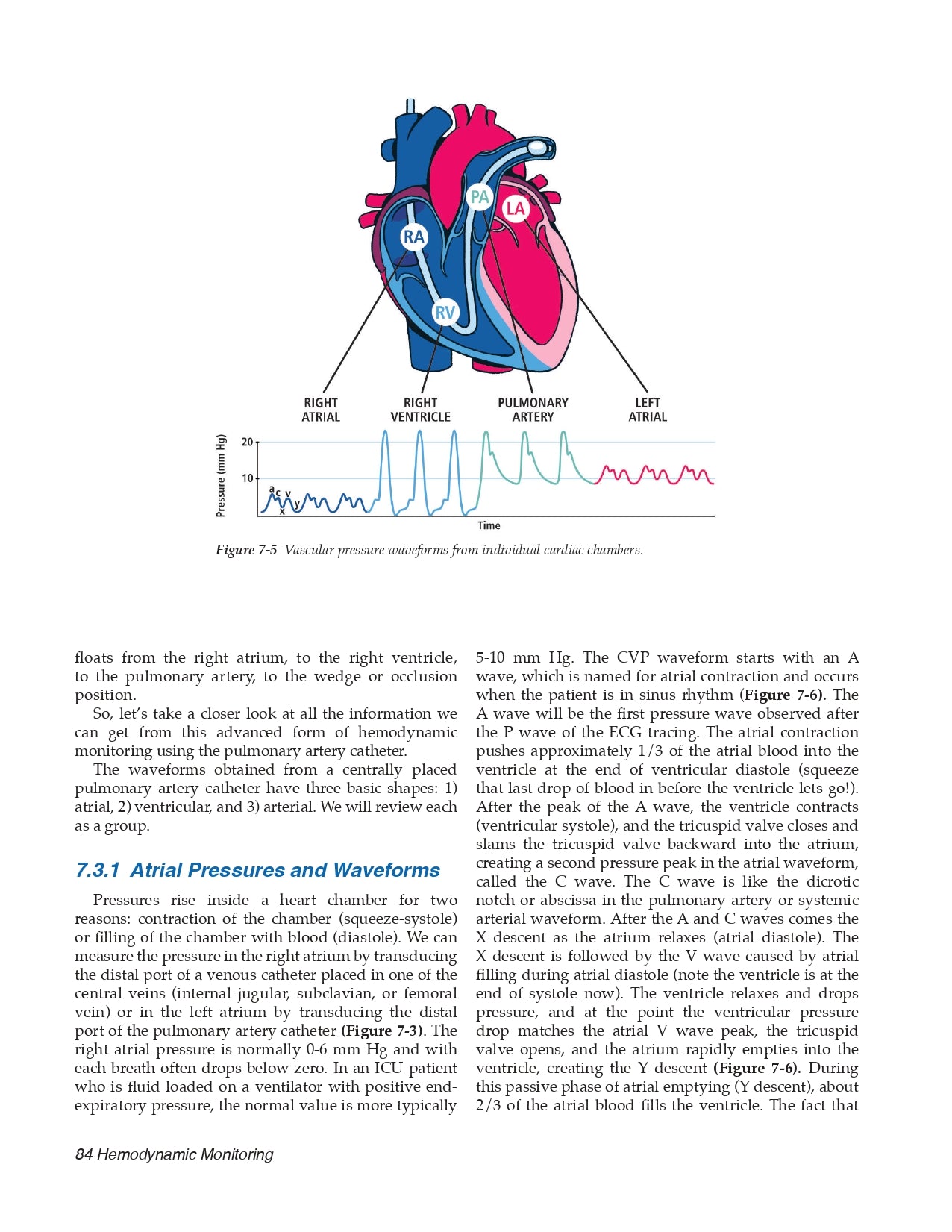
7.3 Vascular Pressures and the Pulmonary Artery Catheter
- Atrial Pressures and Waveforms
- Ventricular Pressures and Waveforms
- Pulmonary Artery Pressure and Waveforms
7.4 Cardiac Chamber Pressures and Pericardial Disease
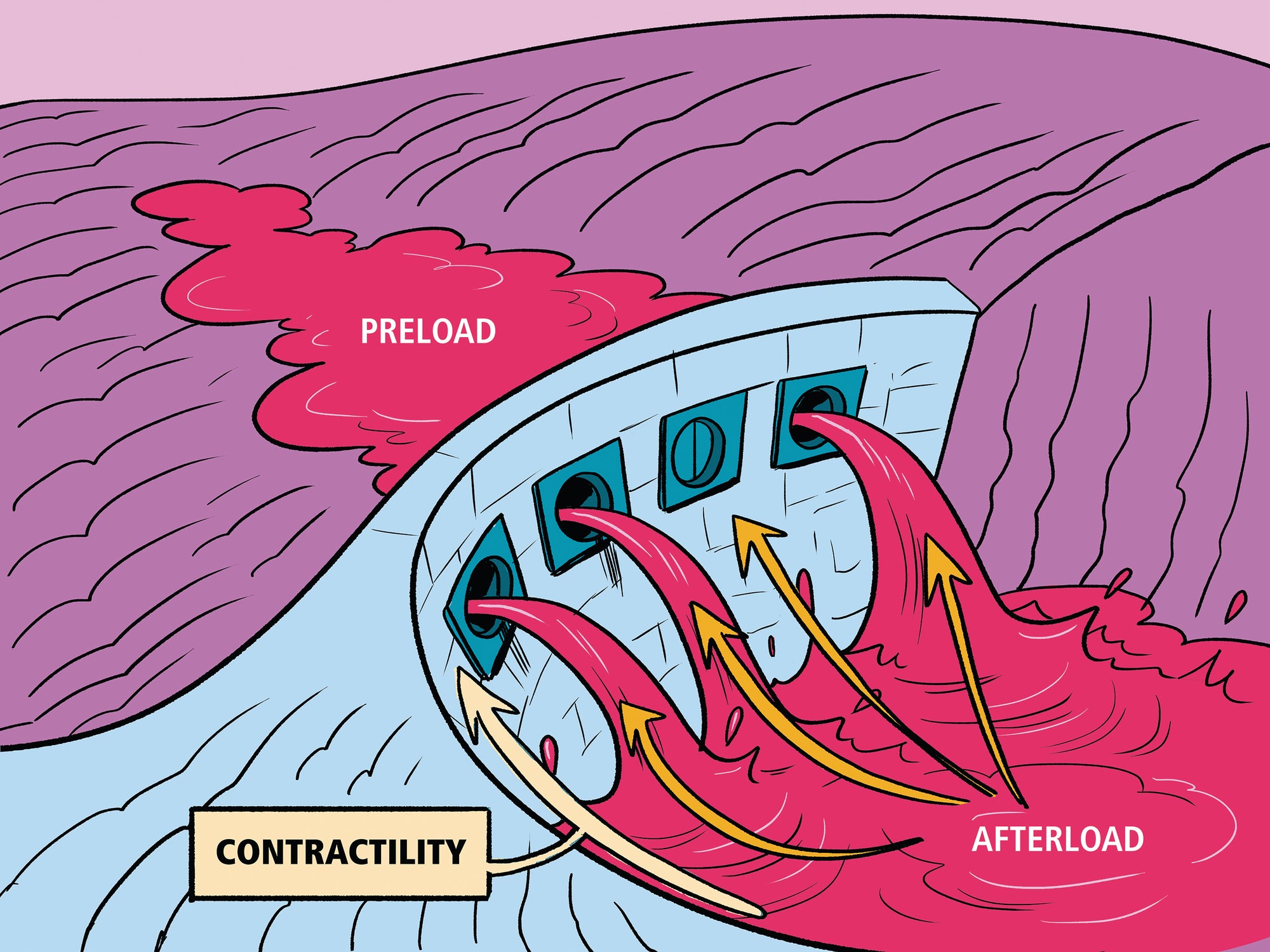
7.5 Cardiac Output
7.6 Vascular Resistance
7.7 Shock and Hemodynamic Assessment
- Hypovolemic Shock
- Cardiogenic Shock
- Distributive Shock
7.8 Limitations of the Pulmonary Artery (PA) Catheter
7.9 Hemodynamic Assessment without the PA Catheter
- Techniques to Change Preload
- Techniques to Assess Stroke Volume
- Inferior Vena Cava Diameter
- Miscellaneous Methods for Preload Assessment
7.10 Hemodynamic Approach to Your ICU Patient
- Suggested Reading
Chapter 8 Acute coronary syndromes
8.1 Step 1: Cool down the Heart
8.2 Step 2: Classify the ACS Syndrome (STEMI, Unstable Angina, NSTEMI)
- The ECG
- Cardiac Biomarkers
- ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction (STEMI)
- Non-ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction (NSTEMI) and Unstable Angina (UA)
8.3 Step 3: Crush the Platelets
8.4 Step 4: Bash the Coagulation System for UA and NSTEMI
8.5 Step 5: Blast Open the Obstruction for STEMI and High-Risk NSTEMI
- Treatment at a PCI-Capable Hospital
- Pharmacologic Therapy for Non-PCI-Capable Hospital
- Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG)
8.6 Wrapping it up
- Suggested Reading
Chapter 9 Acute Decompensated Heart Failure
9.1 Diagnosis of Decompensated Left Heart Failure
- Imaging
- Brain Natriuretic Peptide
- Echocardiography
9.2 Treatment of Acute Decompensated Left Heart Failure
- Reduce Left Ventricular Filling Pressure (Preload)
- Reduce Systemic Vascular Resistance (Afterload)
- Fix the Broken Heart (Dam)Increase Cardiac Output
- Find the Cause
- Arrythmia Management
- Hypertension Management
9.3 Diagnosis of Pulmonary Hypertension and Right Heart Failure
- Pulmonary Hypertension Classification
- Pulmonary Hypertension Diagnosis
- Why Pulmonary Hypertension Matters
9.4 Treatment of Pulmonary Hypertension in the Hospital
- Nitric Oxide
- Endothelin A and B Receptor Blockers
- Prostanoids
- Inotropes
- Heroics
9.5 Pulmonary Hypertension with Shock
- Suggested Reading
Chapter 10 High Systemic Arterial Blood Pressure
10.1 Pathophysiology of Hypertensive Urgency
10.2 Patient Assessment
10.3 Drug Therapy
- Calcium Channel Blockers
- Nitric Oxide Vasodilators
- Beta-Blockers
- Miscellaneous Medications
10.4 Hypertensive Emergency Clinical Syndromes
- Cardiovascular Disease
- Cerebrovascular Disease
- Subarachnoid Hemorrhage (SAH)
- Renovascular Disease
- Excess Catecholamine States
- Miscellaneous Conditions
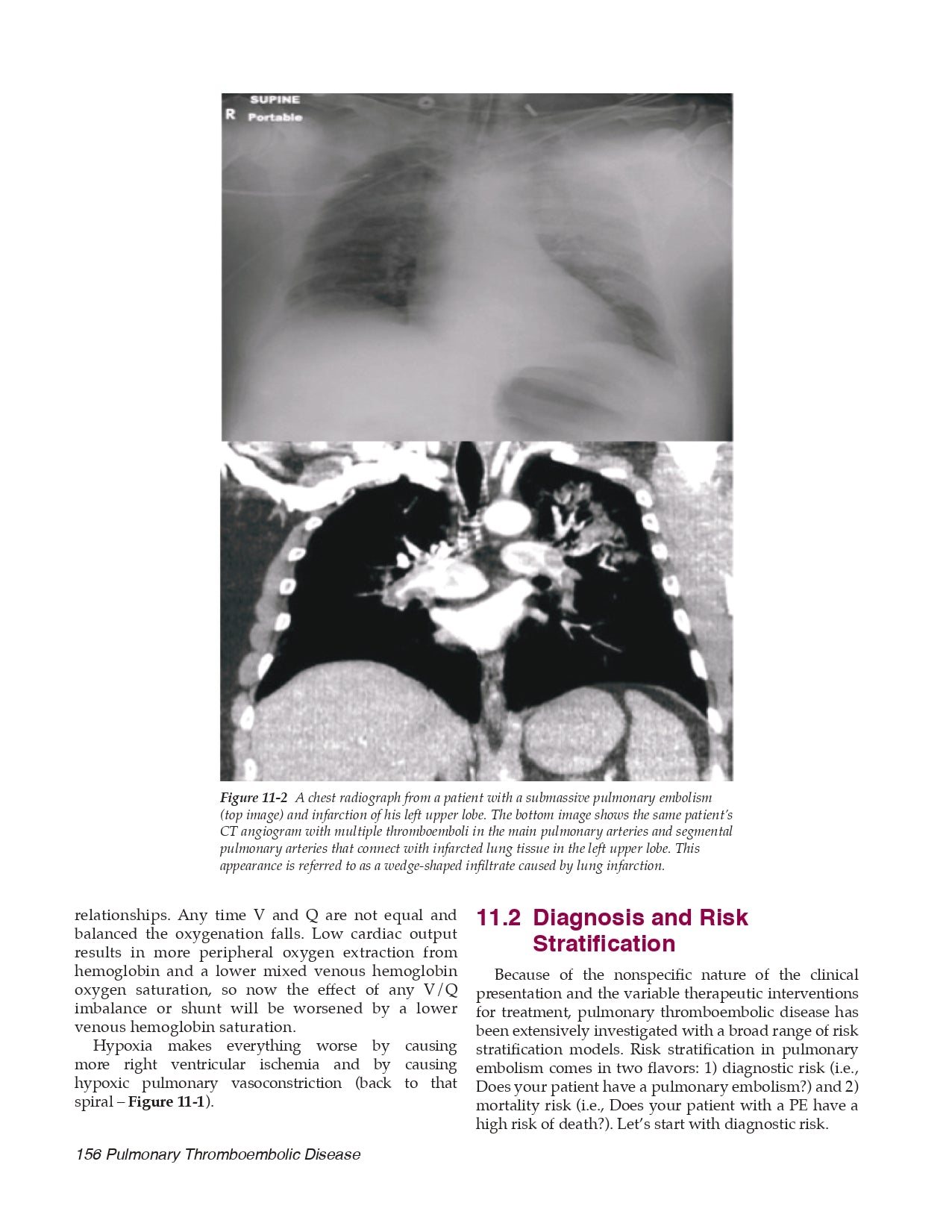
Chapter 11 Pulmonary Thromboembolic Disease
11.1 Pathophysiology
- Right Heart Failure in PE
- Gas Exchange in PE
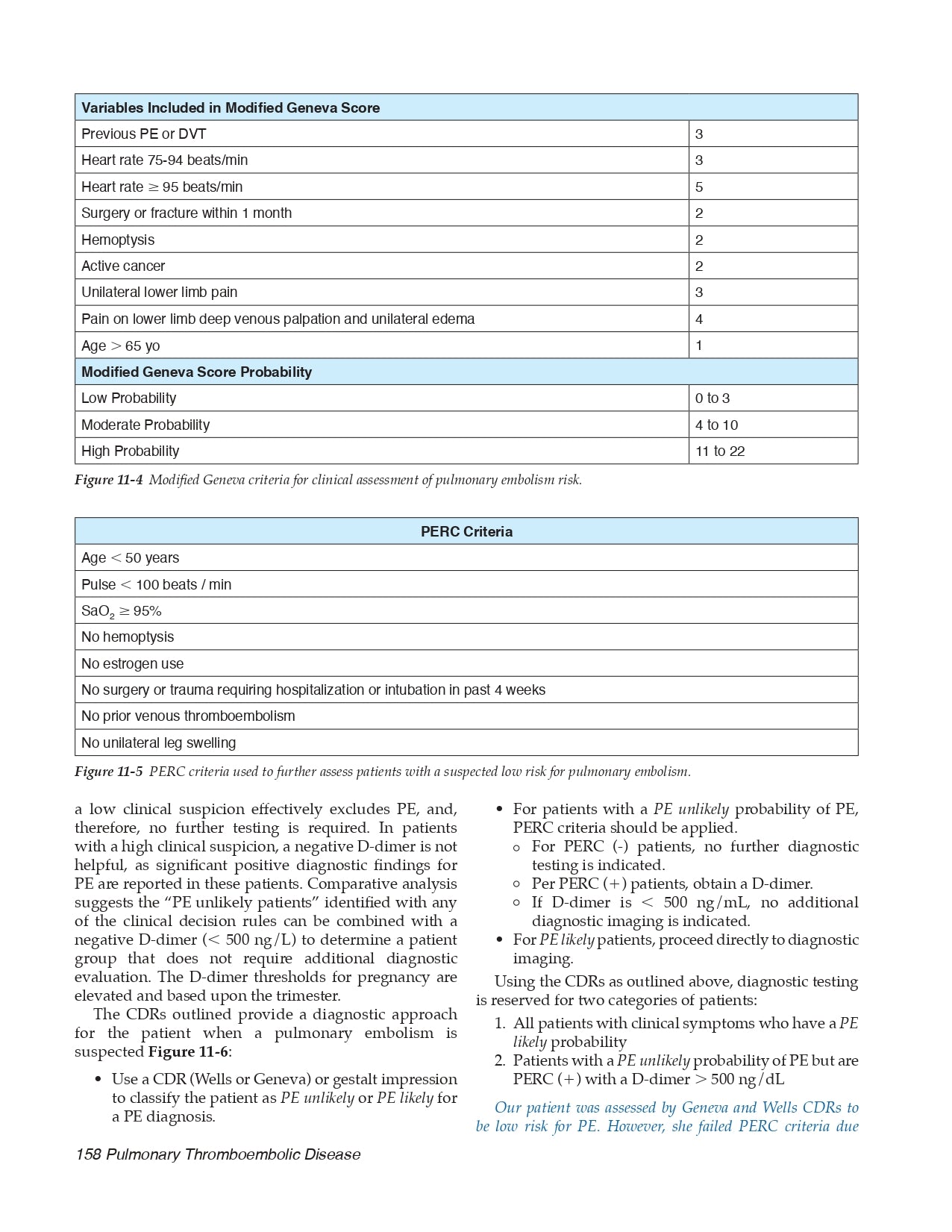
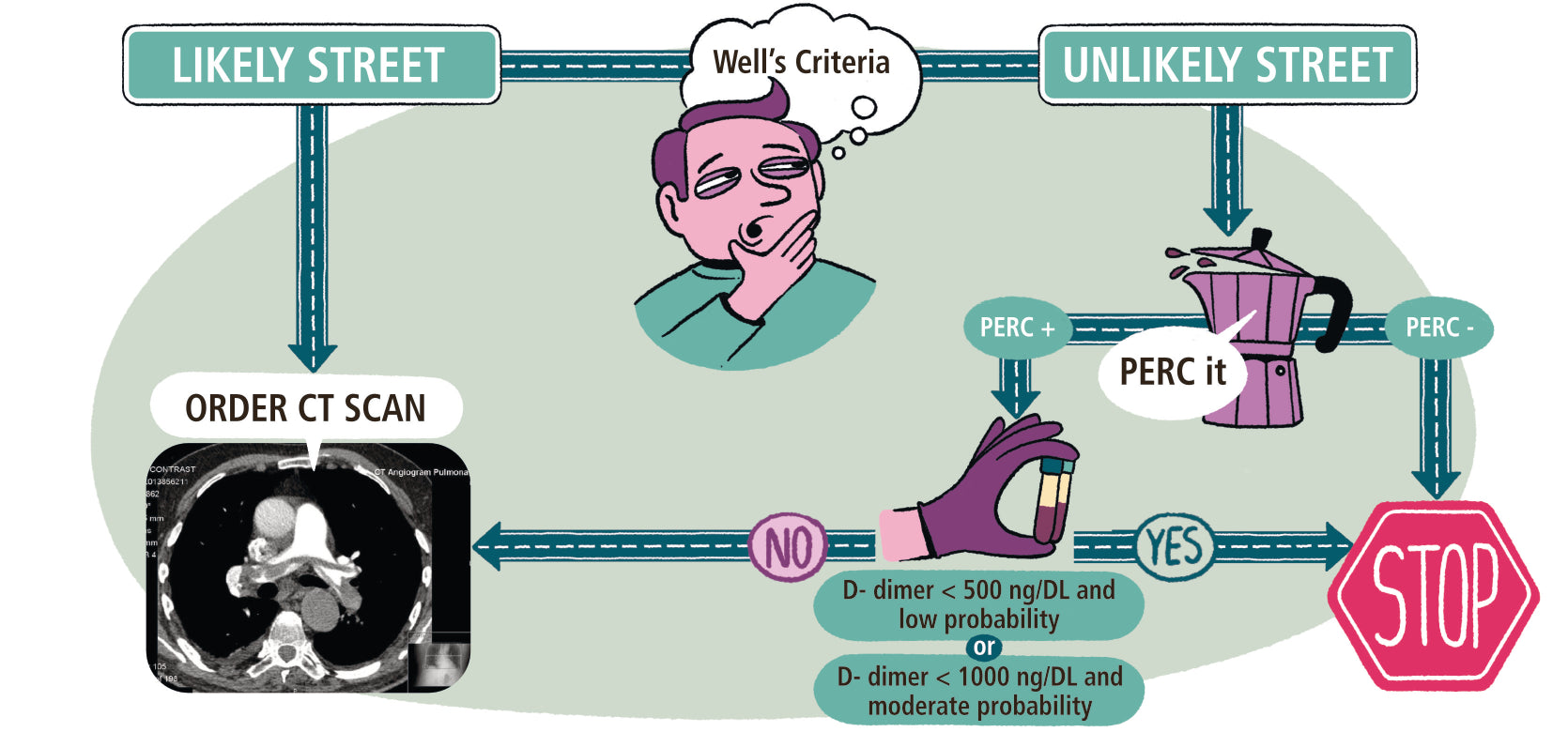
11.2 Diagnosis and Risk Stratification
- Diagnostic Risk PE Clinical Decision Rules
- Mortality Risk
11.3 Treatment of Massive PE
- Oxygenate and Ventilate
- Optimize RV Cardiac Output
- Reduce RV Afterload with Anticoagulation
- To Lyse or Not to Lyse
11.4 Treatment of Submassive PE
- Suggested Reading
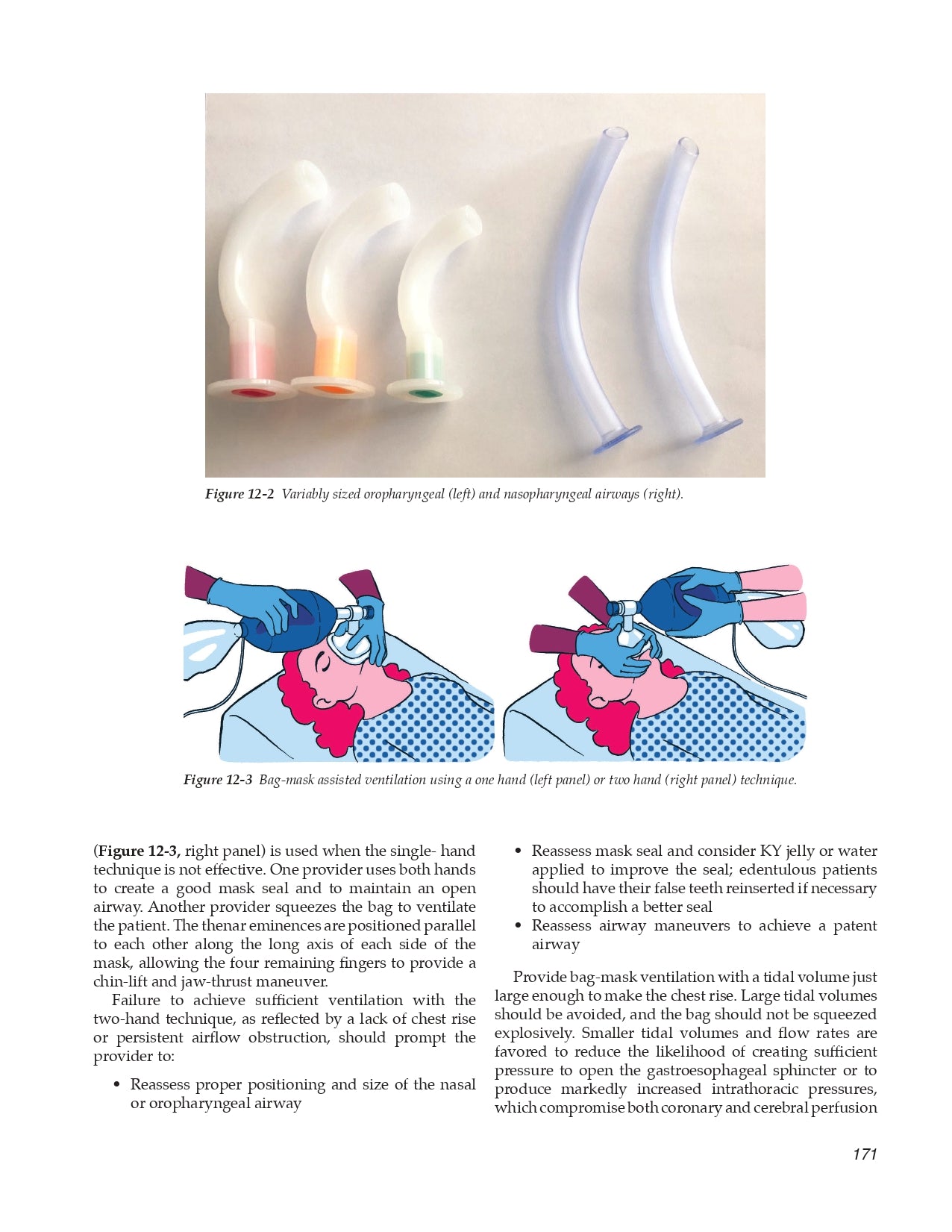
Chapter 12 Basic Airway Management
12.1 Establish a Patent Airway with Ventilation
12.2 Clinical Clues for a Difficult Intubation
12.3 Key Steps to a Successful Airway
12.4 Endotracheal Intubation
- The Tools
- Pre-oxygenation
- Intubation Pharmacology
- Post-intubation Hemodynamics
12.5 The Difficult Airway
12.6 Changing the Endotracheal Tube
- Suggested Reading
Chapter 13 Acute Respiratory Failure
13.1 Assessment of Arterial Blood Oxygenation
- Partial Pressure of Oxygen (PaO2)
- Pathophysiology of Hypoxemia
- Non-invasive Oxygen Saturation (SpO2)
- Assessment of Tissue Oxygen Delivery (DO2)
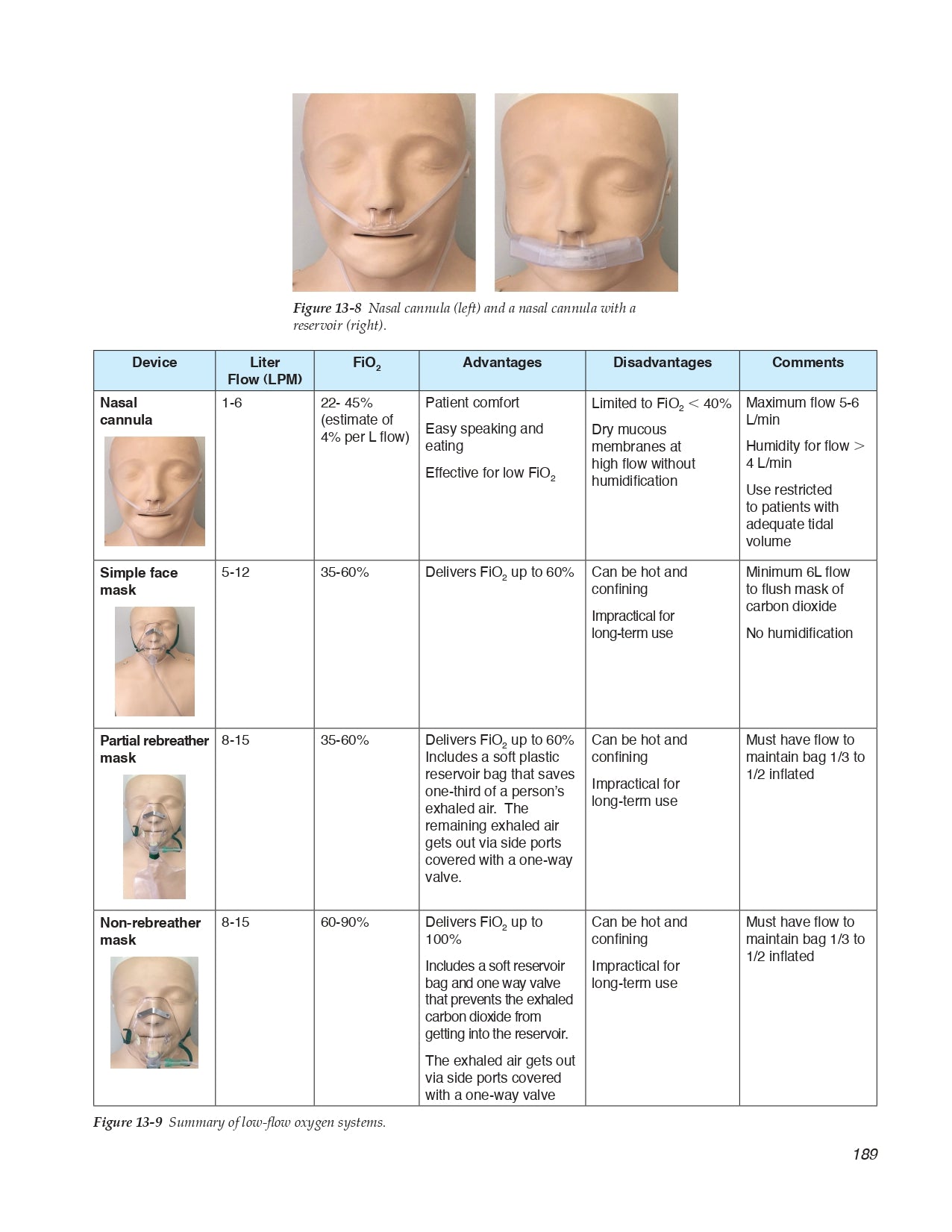
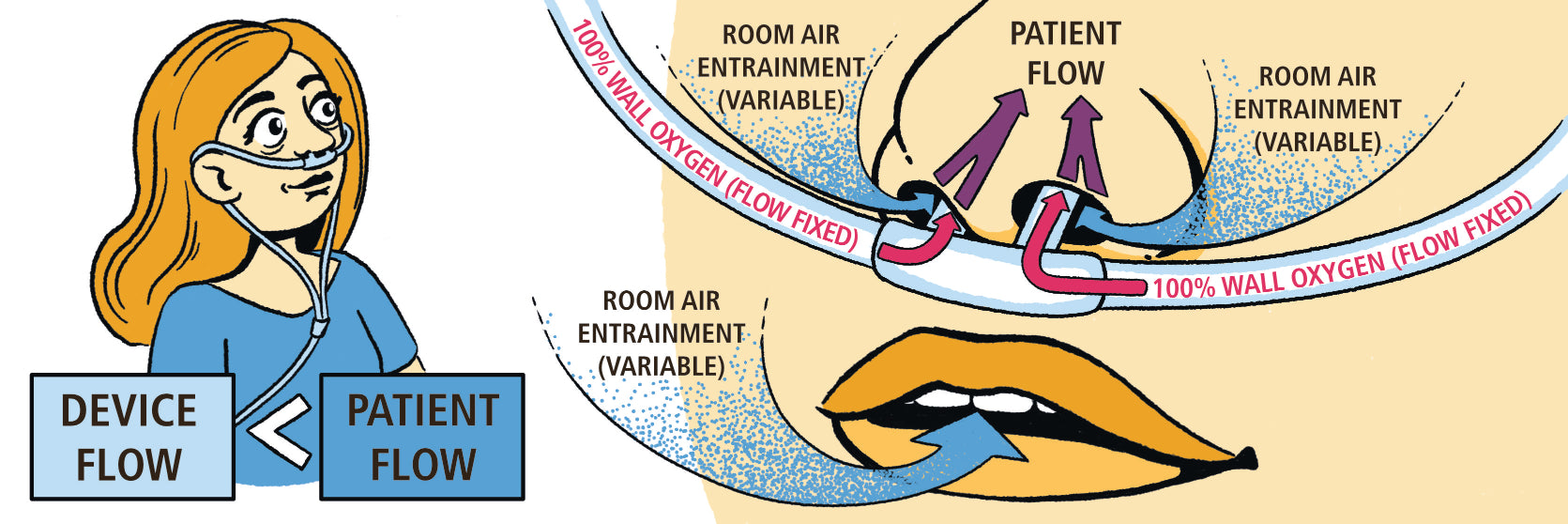
13.2 Supplemental Oxygen and Hypoxemic Respiratory Failure
- Low-Flow Oxygen Systems
- High-Flow Oxygen Systems
- High-Flow Nasal Cannula
- Fixing Hypoxemia
13.3 Assessment of Ventilation (PaCO2)
- Non-Invasive Assessment of Carbon Dioxide
13.4 Hypercapnic Respiratory Failure
- Primary and Secondary Compensation
- Etiology of Ventilation Disorders in the ICU
- Suggested Reading
Chapter 14 Mechanics of Respiratory Failure
14.1 Simple Mechanics of Lung Inflation the EOM
14.2 Compliance/Elastance and Pleural Pressure
- Measurement of Compliance
14.3 Resistance and Time Constants
- Measurement of Airways Resistance
14.4 Lets Put it Together
- Suggested Reading
Chapter 15 Mechanical Ventilation
15.1 Ventilator Components
15.2 Setting the Breath Rate (Triggering)
- Pressure-Based Triggering
- Flow-Based Triggering
15.3 Setting the Breath Type
- Control Breaths
- Support Breaths
15.4 Modes of Mechanical VentilationThe Full Monty
- Control (Assist Control) Ventilation
- Intermittent Mandatory Ventilation (IMV)
- Spontaneous Mode of Ventilation
- APRV and BiLevel Ventilation
15.5 Mode summary
15.6 Positive End-Expiratory PressurePEEP, CPAP, and EPAP
- Adverse Effects of End-Expiratory Pressure
15.7 How to Set Your Best PEEP on the Ventilator
15.8 Extrinsic vs. Intrinsic PEEP
15.9 Mean Airway Pressure and Oxygenation
- Suggested Reading
Chapter 16 Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (Ards)
16.1 ARDS Ridiculously Simple Overview
16.2 Berlin Definition
16.3 Causes of ARDS
16.4 Pathophysiology of ARDS
- ARDS as a Heterogeneous Lung Disease
16.5 Airway Management in ARDS
16.6 ARDS and the Ventilator First Do No Harm
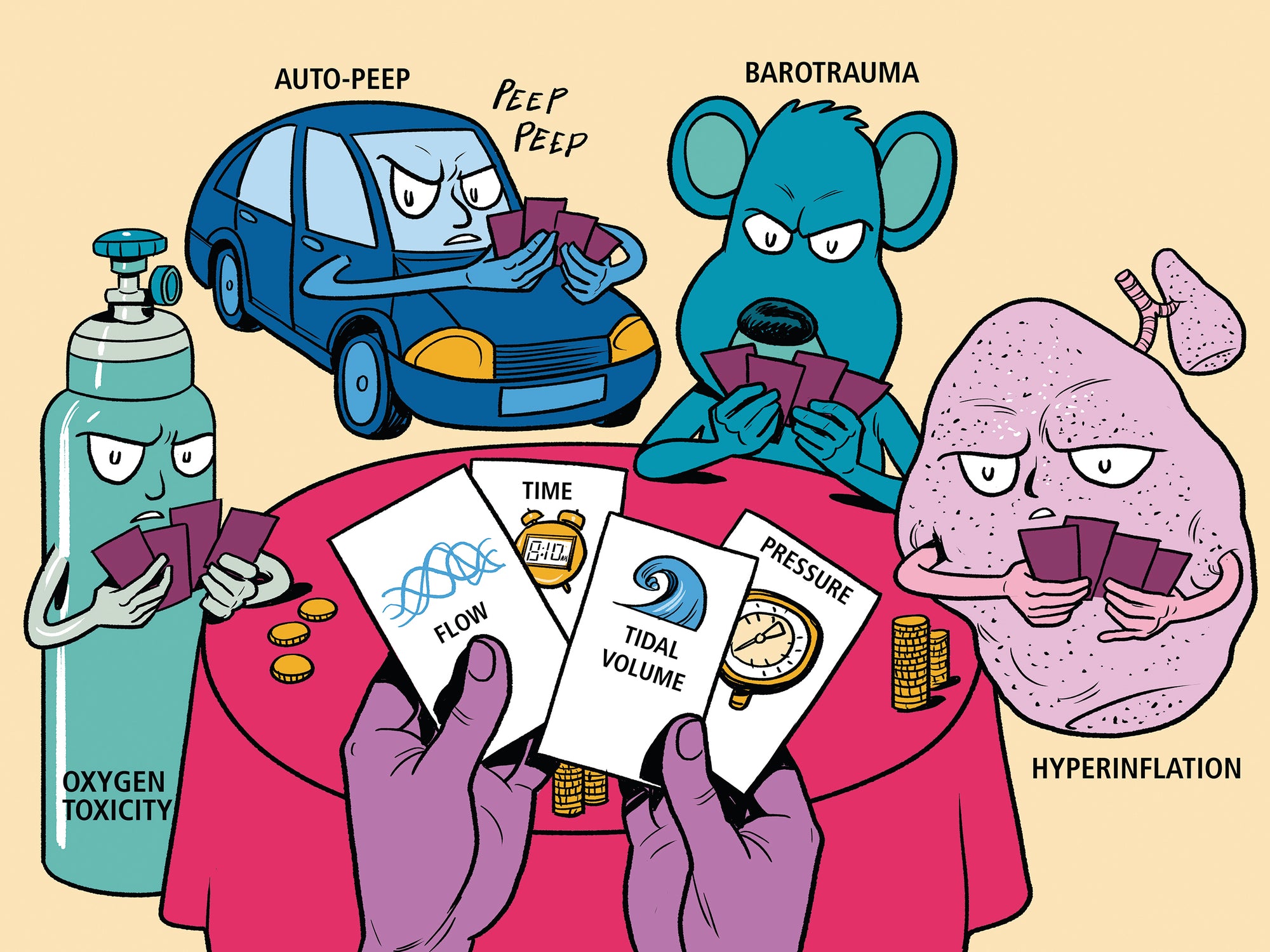
- Oxygen Toxicity: Hyperoxic Lung Injury
- BarotraumaNo Pressure!
- Volutrauma Turn Down the Volume!
- Atelectrauma The Elusive Best Peep!
16.7 Mechanical Ventilation in ARDS
- Control Breaths
- PEEP Management
- Alveolar Recruitment Maneuvers
16.8 Fluid Management in ARDSWet or dry?
16.9 Approach to Intractable Hypoxemia in ARDS
- Pharmacologic Paralysis
- Prone Ventilation
- Inhaled Vasodilators
- High-frequency Oscillation
- APRV and Bilevel Ventilation
- Extracorporeal Support
- Hypoxemia Overview
16.10 The Little Things
16.11 Prognosis
- Suggested Reading
Chapter 17 Obstructive Lung Disease (Old) and Respiratory Failure
17.1 Pathophysiology of Airflow Obstruction
17.2 Intrinsic PEEP (PEEPi) in OLD
- Intrinsic PEEP Assessment
- Complications of Intrinsic PEEP
- Limiting Intrinsic PEEP in OLD
17.3 Mechanical Ventilation in OLD
- Non-Invasive Mechanical Ventilation in OLD
- Invasive Mechanical Ventilation in OLD
- Ventilator Management in OLD
17.4 Drug Therapy in OLD
- Antibiotics
- Bronchodilators
- Corticosteroids
- Miscellaneous Interventions
17.5 Patient Outcome
- Suggested Reading
Chapter 18 Weaning From Mechanical Ventilation
18.1 Control That SOB
18.2 Spontaneous Breathing Trial (SBT)
- Spontaneous Breathing Trial Intolerance
- Removing the Tube
18.3 Non-invasive Ventilation (NIV) and Weaning
18.4 Alternatives to the SBT Trial
18.5 Beyond the SBT Trial Pain, Sedation, and Delirium
- Sedation Management: Less Is More
- Pain Management
- Delirium
- Early Mobility in the ICU
18.6 Coordination of Ventilator Care Know Your Alphabet?
18.7 When Is a Tracheostomy Indicated?
- Timing and Technique of Tracheostomy
- Type and Size of the Tracheotomy Tube
- Care of the Tracheotomy Tube
- Swallowing
- Decannulation
- Suggested Reading
Chapter 19 Bleeding, Clotting and Hematological Emergencies
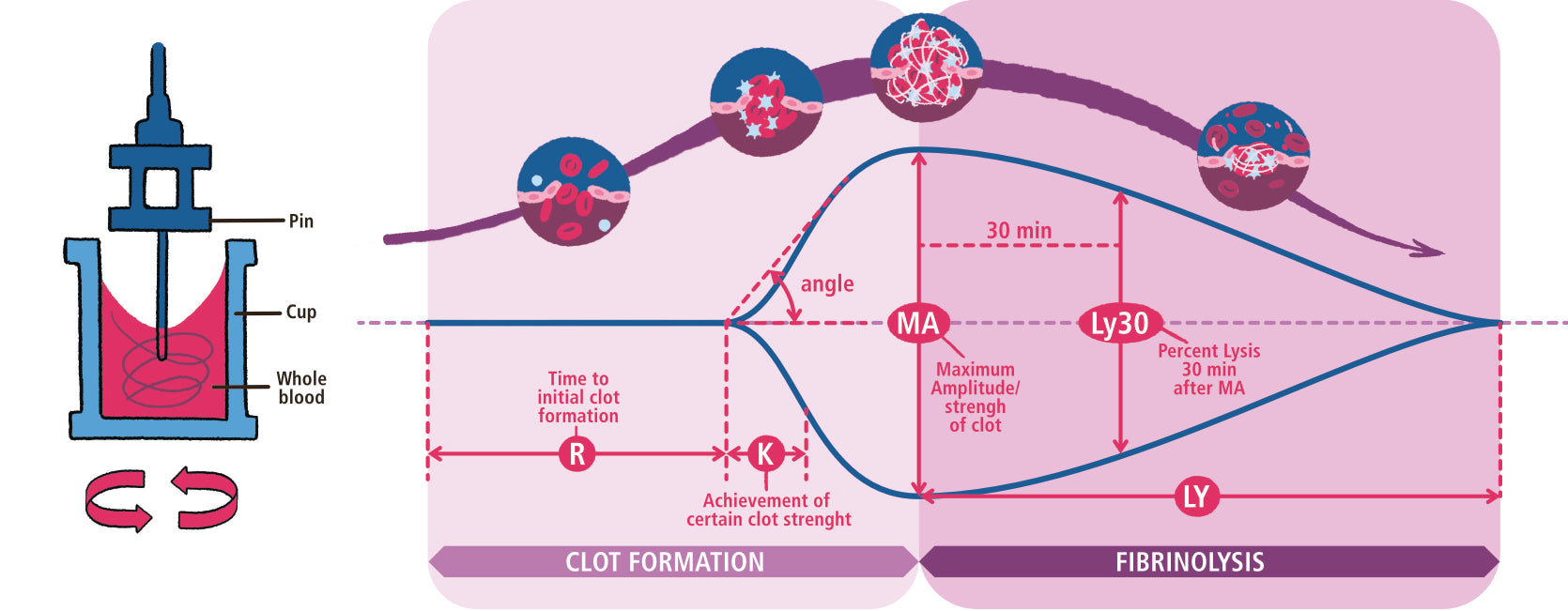
19.1 Clotting Cascade: Help Me Memorize! ! !
- Extrinsic or Tissue Factor Pathway
- Intrinsic or Contact (collagen) Activation Pathway
- Anti-Clotting Pathways
19.2 Overview of Bleeding and Clotting disorders
- Things that Elevate the PT-INR
- Things that Elevate the PTT
- Things that Elevate both PT-INR and PTT
19.3 Top four Bad Boys of ICU Hematology
- Public Enemy #1: Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia (HIT)
- Public Enemy #2: Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC)
- Public Enemy #3: Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura (and HELLP! and HUS! )
- Public Enemy #4: Catastrophic Antiphospholipid Antibody Syndrome (CAPS)
- Suggested Reading
Chapter 20 Transfusion Medicine
20.1 Quick-Thinking Rapid Transfusion
20.2 Red Blood Cell Transfusions
- When to Transfuse?
- Complications of Red Blood Cell Transfusion
20.3 Platelets
20.4 Fresh Frozen Plasma (FFP)
20.5 Cryoprecipitate
20.6 Recombinant Factor VIIa (Novo-Seven)
20.7 Four-Factor Prothrombin Complex Concentrate
- Suggested Reading
Chapter 21 Acute Kidney Injury
21.1 Classification of Acute Kidney Injury
21.2 Drug-induced Acute Kidney Injury
21.3 Prevention of Acute Kidney Injury
- Hypoperfusion
- Contrast-Induced AKI
- Aminoglycoside Nephropathy
21.4 Management of Acute Kidney Injury
- Diuretic Use in AKI
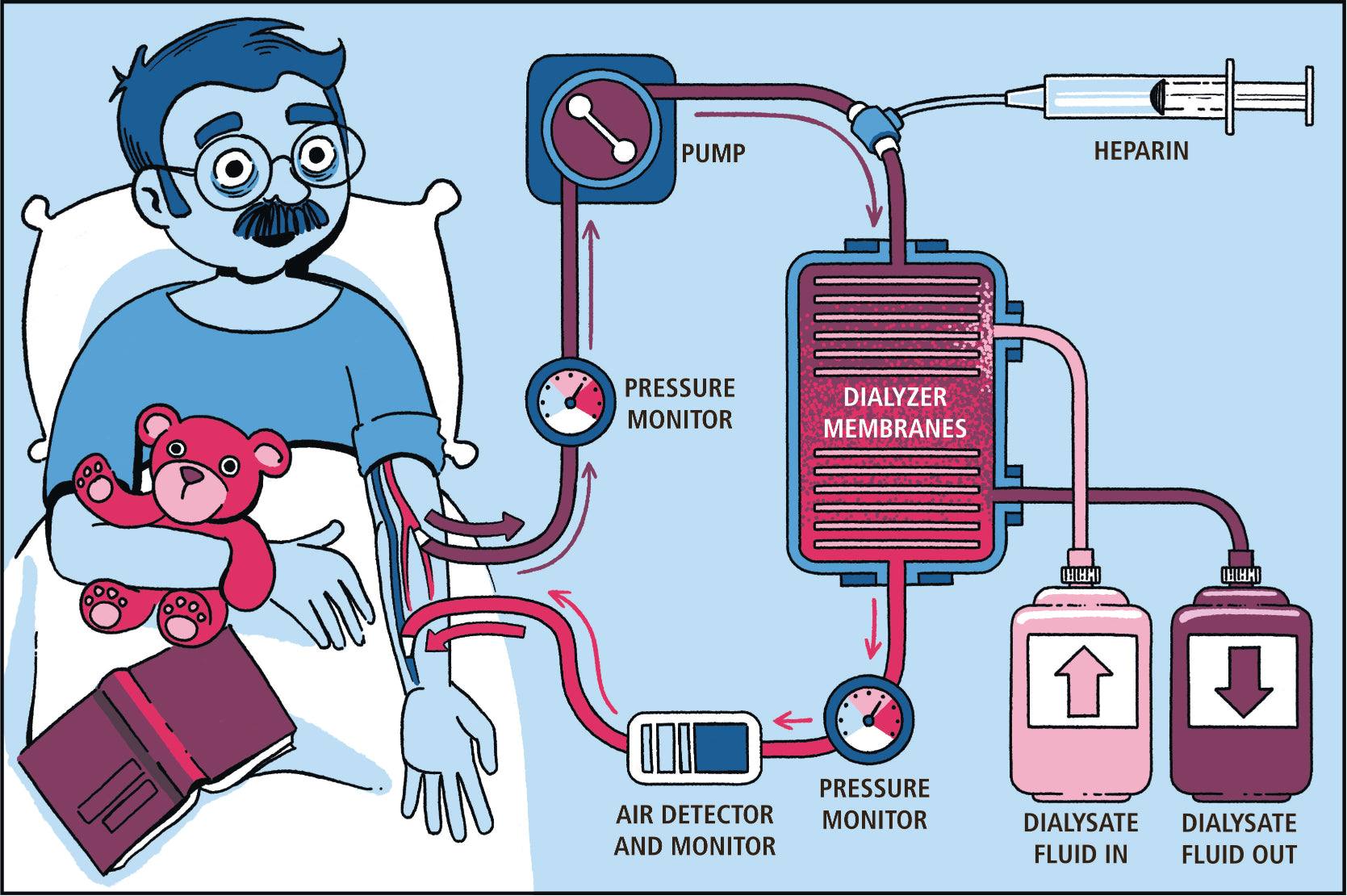
- Dialysis Therapy
- Dialysis Methods
- Dialysis Dose
- Suggested Reading
Chapter 22 Gastrointestinal Bleeding
22.1 ABCs (and D) of GI Bleeding
- Access
- Blood and Blood Products
- Call for Help
- Diagnose the Bleeding Source
- Suggested Reading
Chapter 23 Acid-Base Disorders
23.1 Simple Acid-Base
23.2 Primary Disturbance and Secondary Compensation
23.3 The Four Steps of Acid-Base Analysis
- STEP 1: Define the Primary Disorder
- STEP 2: Assess the Compensation
- STEP 3: Calculate the Anion Gap
- STEP 4: Calculate the Delta Gap
23.4 Respiratory Acid-Base Disorders
- Respiratory Acidosis
- Respiratory Alkalosis
23.5 Metabolic Acid-Base Disorders
- Metabolic Acidosis and the Anion Gap
- Metabolic Acidosis and the Osmolar Gap
- Anion Gap Metabolic Acidosis and Management
- Non-Anion Gap Acidosis
23.6 Metabolic Alkalosis
- Contraction Alkalosis
- Post-Hypercapnic Metabolic Alkalosis
- Mineralocorticoid Excess
- Suggested Reading
Chapter 24 Drug Overdose
24.1 The Basics
- Resuscitate and Stabilize
- Confirm Diagnosis and Toxin
- Antidotes and Toxin Elimination
- The Overdose Booby Traps
24.2 Specific Overdoses
- Acetaminophen
- Alcohols
- Benzodiazepines
- Slow it Down: Beta Blockers and Calcium Channel Blockers
- Speed it Up: Cocaine and Cathinones
- Hypoglycemia Secondary to Insulin and Oral Hypoglycemic Agents
- Antidepressants and the Abnormal ECG
- Salicylates and the Pseudosepsis Syndrome
- Serotonin Syndrome
- Opioids
- Suggested Reading
Chapter 25 Neurologic Emergencies
25.1 Acute Ischemic Stroke
25.2 Acute Intracerebral Hemorrhage
- Blood Pressure Control
- Reversal of Coagulopathy
- Elevated Intracranial Pressure
25.3 Status Epilepticus
25.4 Acute Myasthenic Crisis
Chapter 26 SARS-CoV-2 Infection and COVID-19 Disease
26.1 Epidemiology of the Pandemic
26.2 SARS-CoV-2 Virus
- SARS-CoV-2 Infectivity
26.3 COVID-19: Clinical Features
- COVID-19 Clinical Phenotypes
- COVID-19 Timeline
- COVID-19 Risk factors
26.4 The Diagnosis of COVID-19
- Laboratory Testing in COVID-19
- Radiology Findings in COVID-19
- PCR and Antibody Testing
- Pre-Test Probability and PCR Testing
26.5 Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
26.6 The Clinical Management of COVID-19
- Hypoxemic Respiratory Failure in the Non-Intubated Patient
- Airway Management
- Hypoxemic Respiratory Failure in the Intubated Patient
- Cardiovascular Management of the Patient with COVID-19
- Cytokine Release Syndrome (CRS)
- Coagulation Disorders
- Gastrointestinal Manifestations of COVID-19
- Renal Manifestations of COVID-19
26.7 Treatment of COVID-19
- Empiric Antibiotics for Secondary Infection
- Antiviral therapy
- Corticosteroid Therapy
- Convalescent plasma (CP)
- Monoclonal Antibody Therapy
- Anticoagulant and antiplatelet therapy
- Anti-inflammatory therapy
- Treatment for Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19
26.8 Vaccine for COVID-19
26.9 Goals of Care and Resource Limitations
- Suggested Reading
References
Index