Endocrinology Made Ridiculously Simple
Also available on
Description
NEW RELEASE!!!
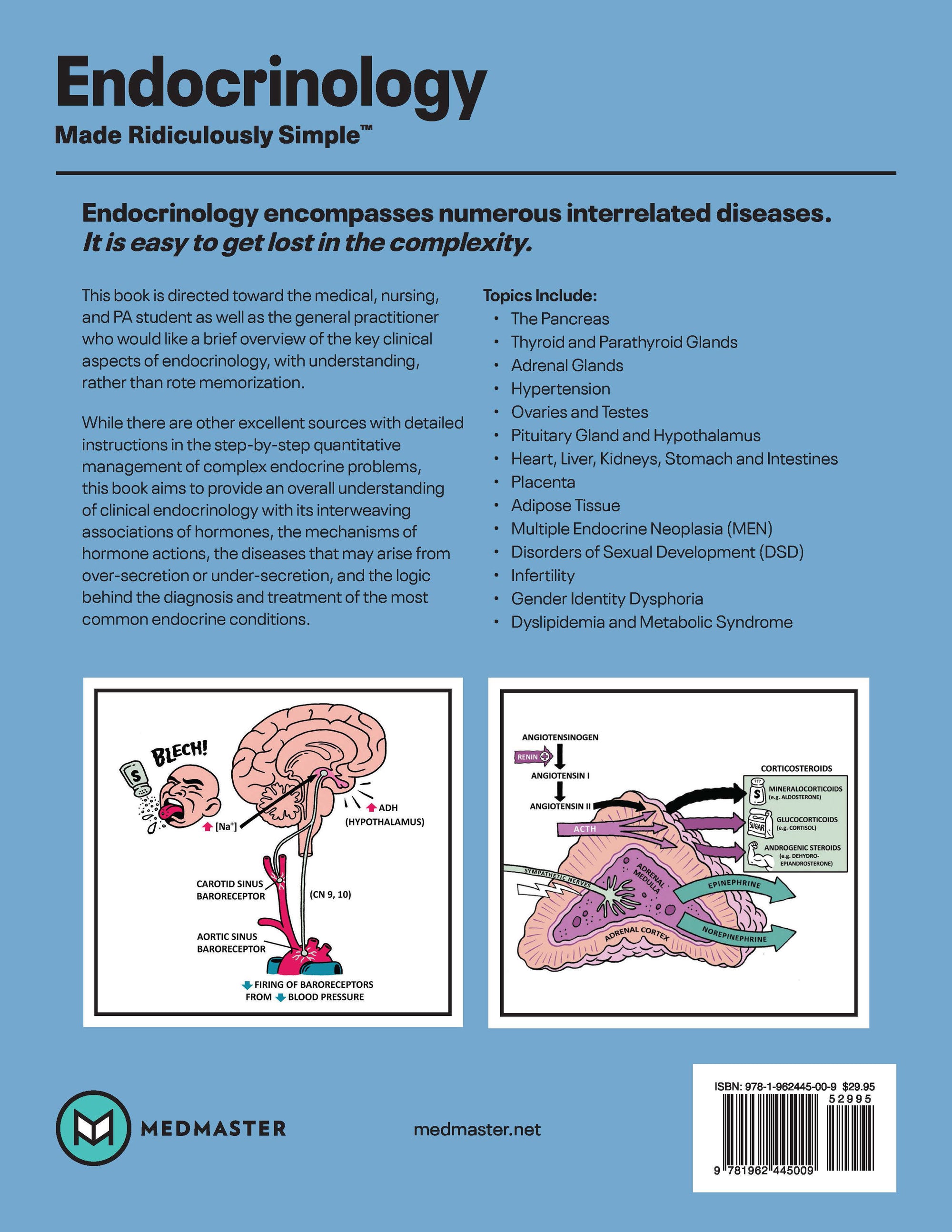
Endocrinology encompasses numerous interrelated diseases. It is easy to get lost in the complexity. This book is directed toward the medical, nursing, and PA student as well as the general practitioner who would like a brief overview of the key clinical aspects of endocrinology, with understanding, rather than rote memorization.
While there are other excellent sources with detailed instructions in the step-by-step quantitative management of complex endocrine problems, this book aims to provide an overall understanding of clinical endocrinology with its interweaving associations of hormones, the mechanisms of hormone actions, the diseases that may arise from over-secretion or under-secretion, and the logic behind the diagnosis and treatment of the most common endocrine conditions.
Topics Include:
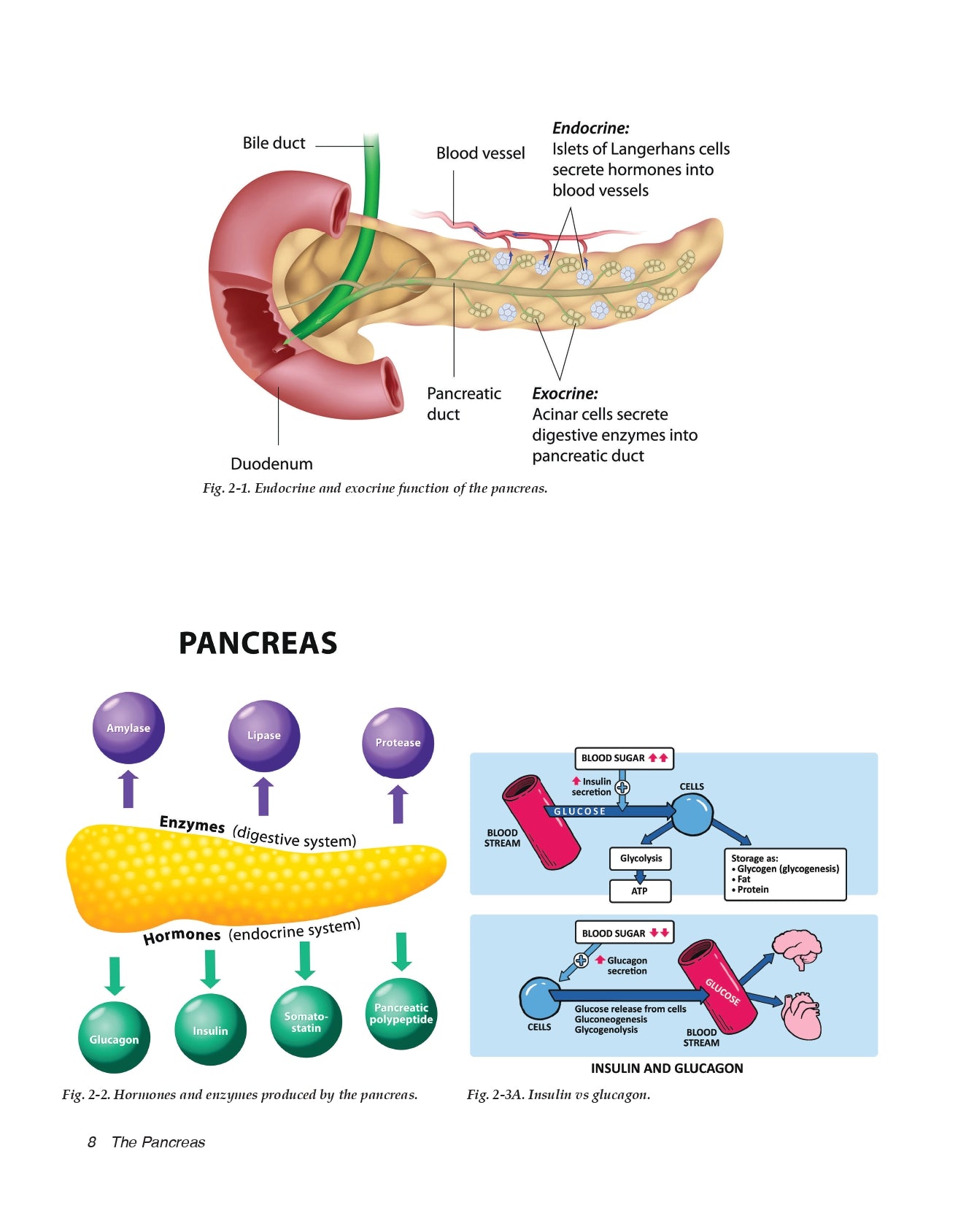
- The Pancreas
- Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands
- Adrenal Glands
- Hypertension
- Ovaries and Testes
- Pituitary Gland and Hypothalamus
- Heart, Liver, Kindeys, Stomach and Intestines
- Placenta
- Adipose Tissue
- Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia (MEN)
- Disorders of Sexual Development (DSD)
- Infertility
- Gender Identity Dysphoria
- Dyslipidemia and Metabolic Syndrome
Author(s)
Stephen Goldberg, M.D.
Stephen Goldberg, M.D., a graduate of the Albert Einstein College of Medicine, is a researcher, physician, teacher, computer programmer, writer, musician/composer, and past President of the Medmaster Publishing Company for 40 years. Dr. Goldberg has published numerous medical and scientific papers through research at the Albert Einstein College of Medicine, National Institutes of Health, New York Medical College and the University of Miami School of Medicine. He has authored 20 books in a diversity of medical areas, including textbooks of Anatomy, Physiology, Biochemistry, Genetics, Biostatistics and Epidemiology, Neurology, Consciousness, Ophthalmology, Hematology, and Computer Programming, as well as many interactive computer programs on various medical topics, including Atlas of Microbiology and Atlas of Human Diseases. He is Professor Emeritus at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine, where he taught medical students for 25 years. His reputation is that of an educator who can simplify complex topics. He received the George Paff Most Outstanding Professor Teaching Award11 times at the U of M and was invited in 2004 to be the keynote speaker at the medical school graduation commencement at the Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis for his work in medical education. He is currently Editor-in-Chief of the Medmaster Publishing Company.
Details
Pages: 130
Publication: Edition 1 (February 15, 2024)
Language: English
ISBN: 9781962445009 eISBN: 9781962445016
Table of contents
Chapter 1. Introduction
The Hormones
Endocrine Diagnosis and Treatment
Chapter 2 . The Pancreas
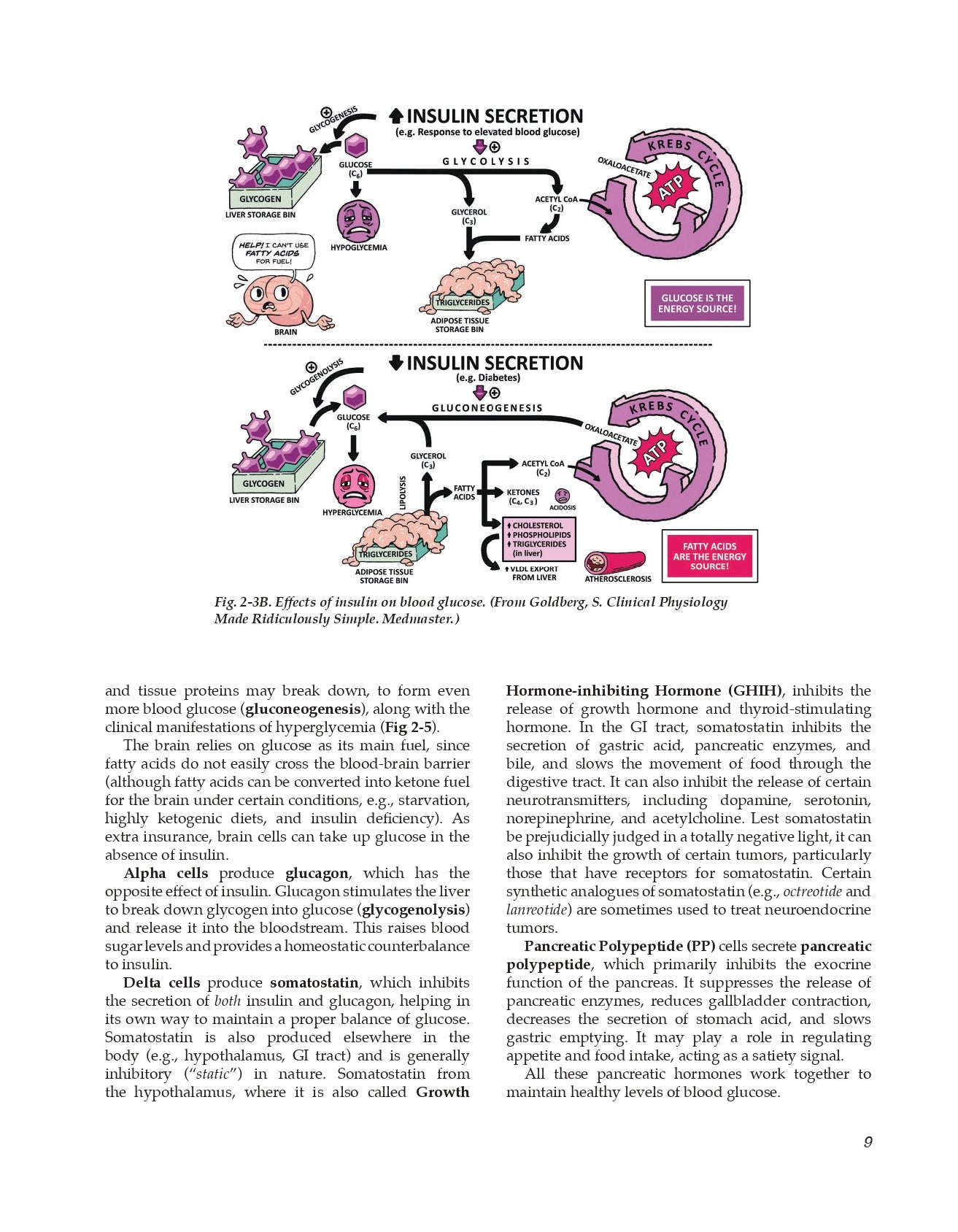
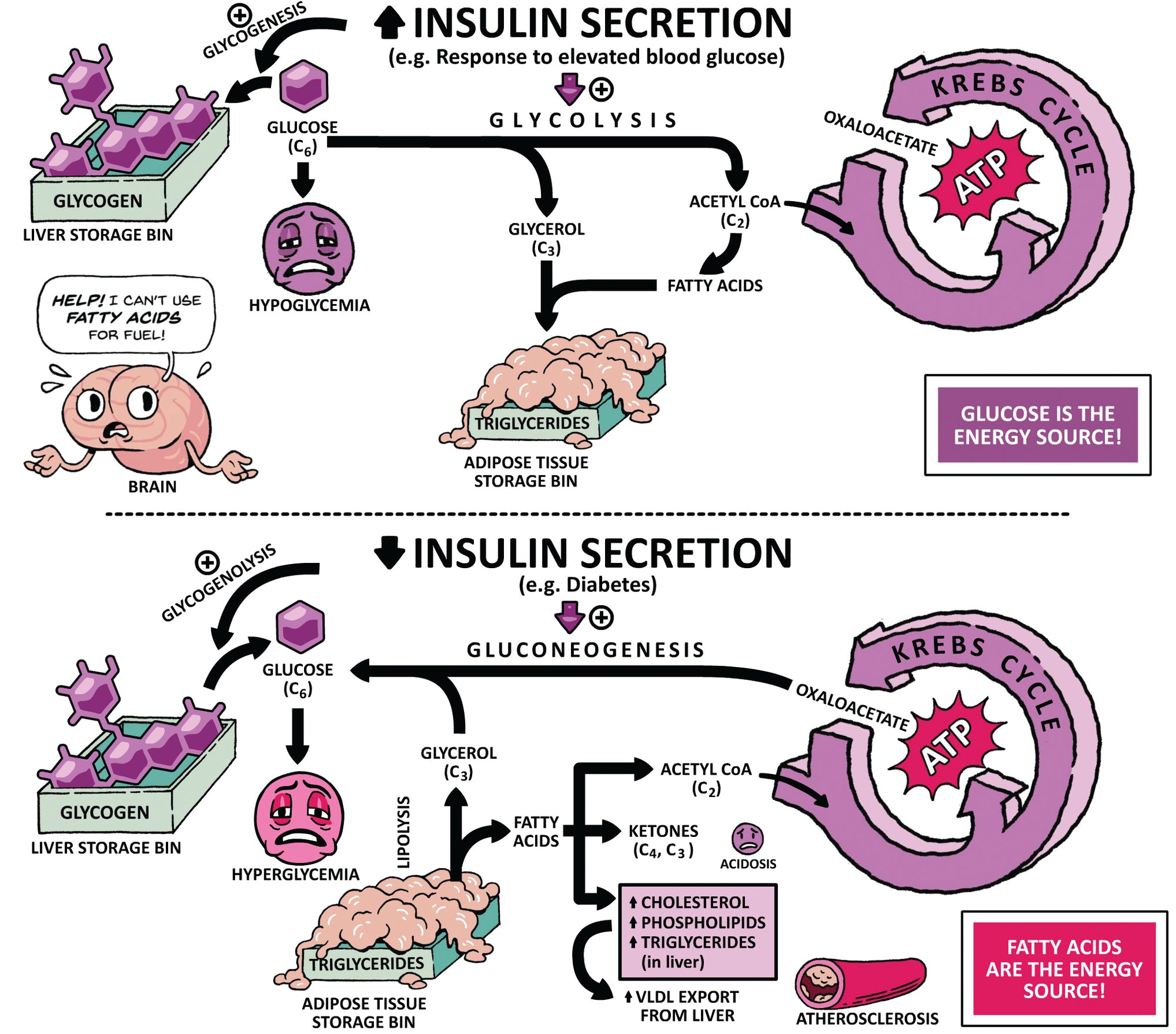
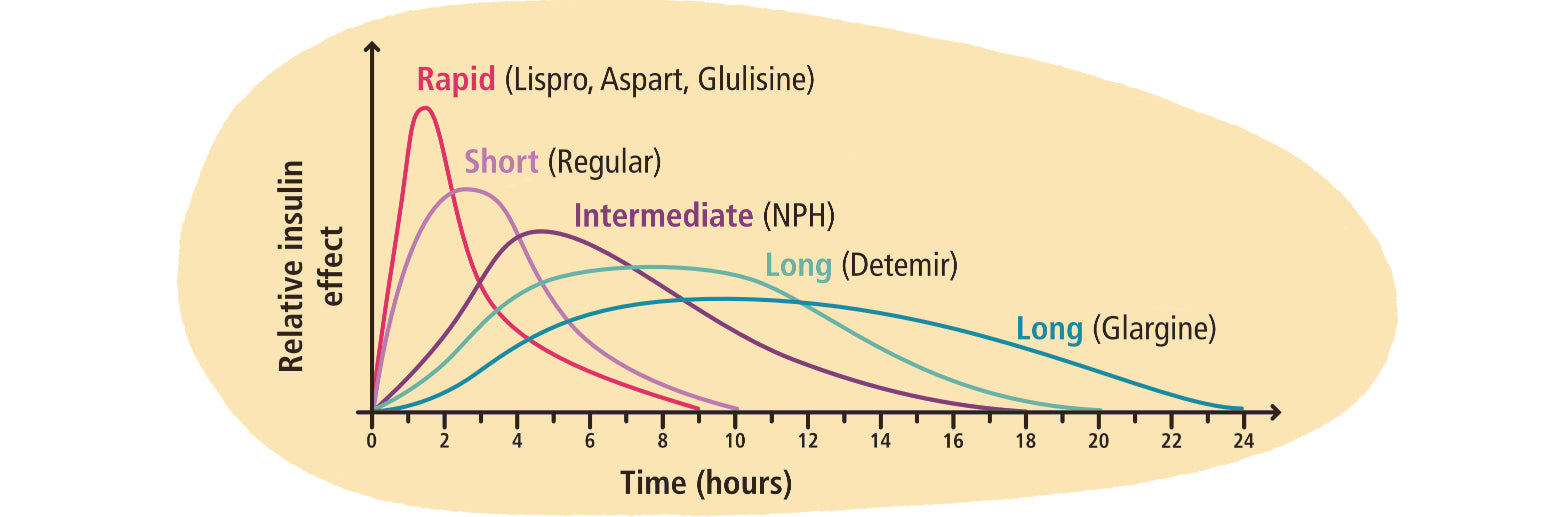
Insulin
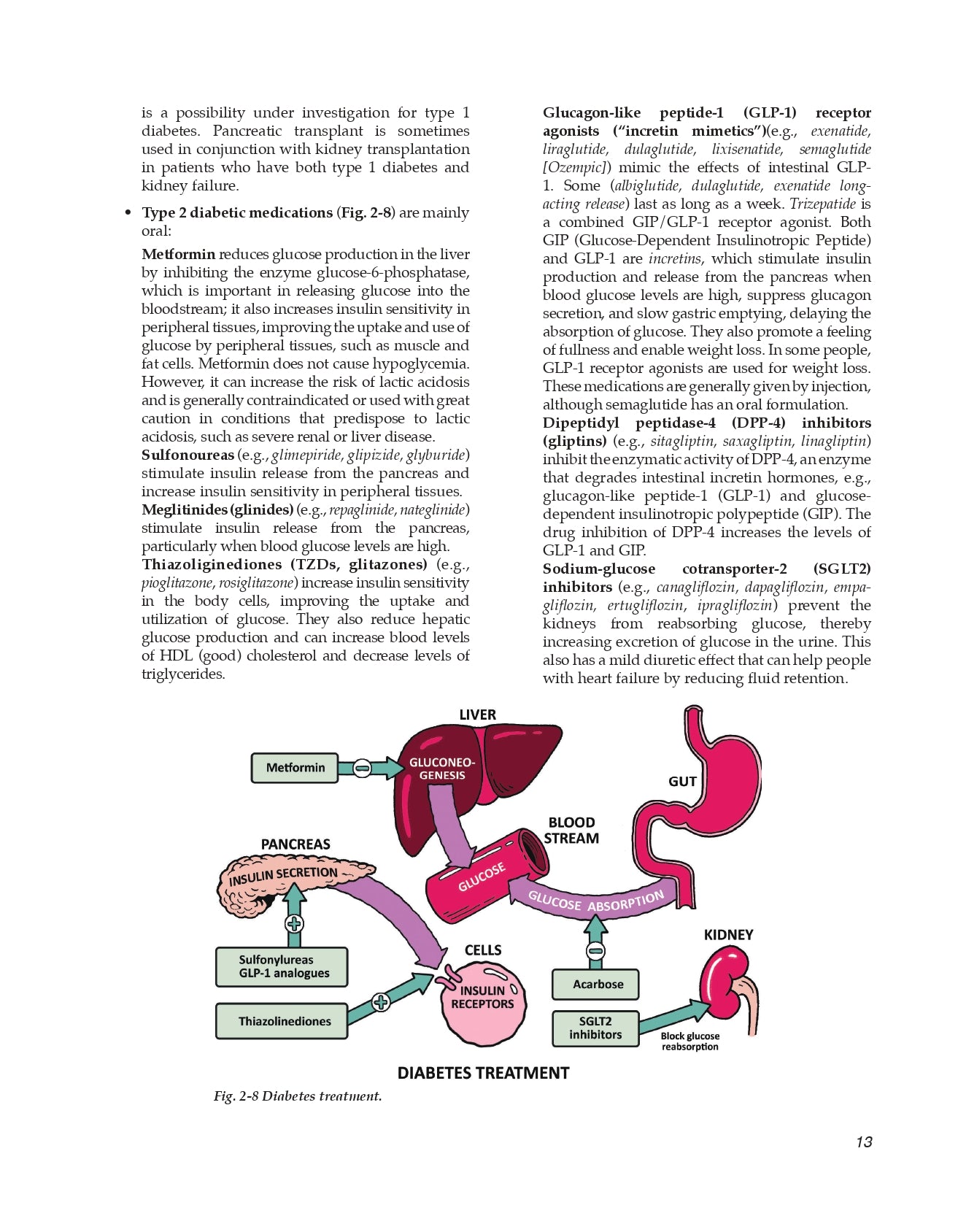
Diabetes and Hyperglycemia
Diabetic Ketoacidosis
Hyperosmolar Nonketotic Coma
Hypoglycemia
Glucagon
Hyperglucagonemia
Hypoglucagonemia
Somatostatin
Pancreatic Polypeptide
Which hormones increase blood glucose?
Which hormones decrease blood glucose?
Chapter 3. Thyroid Gland
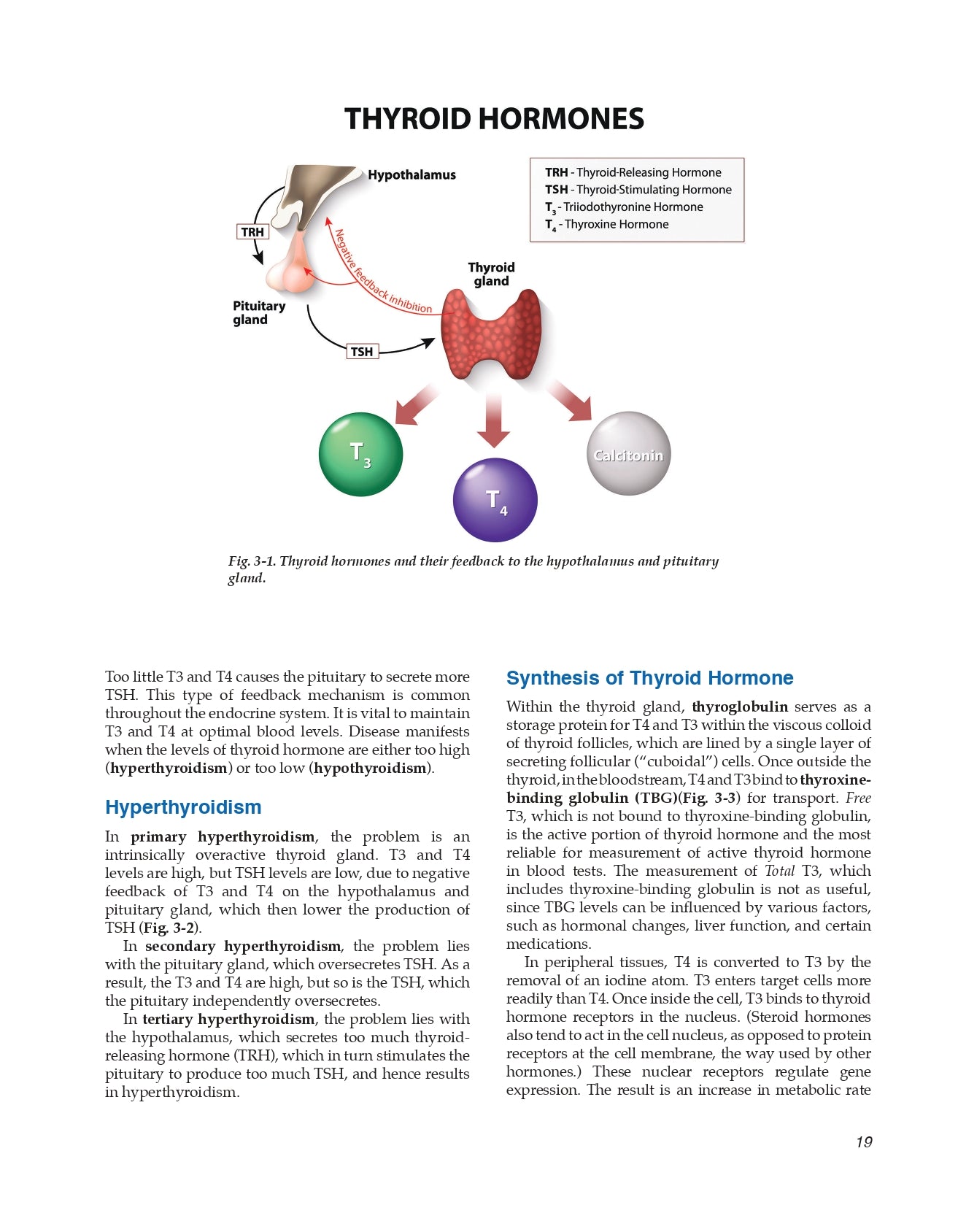
Thyroid Hormone
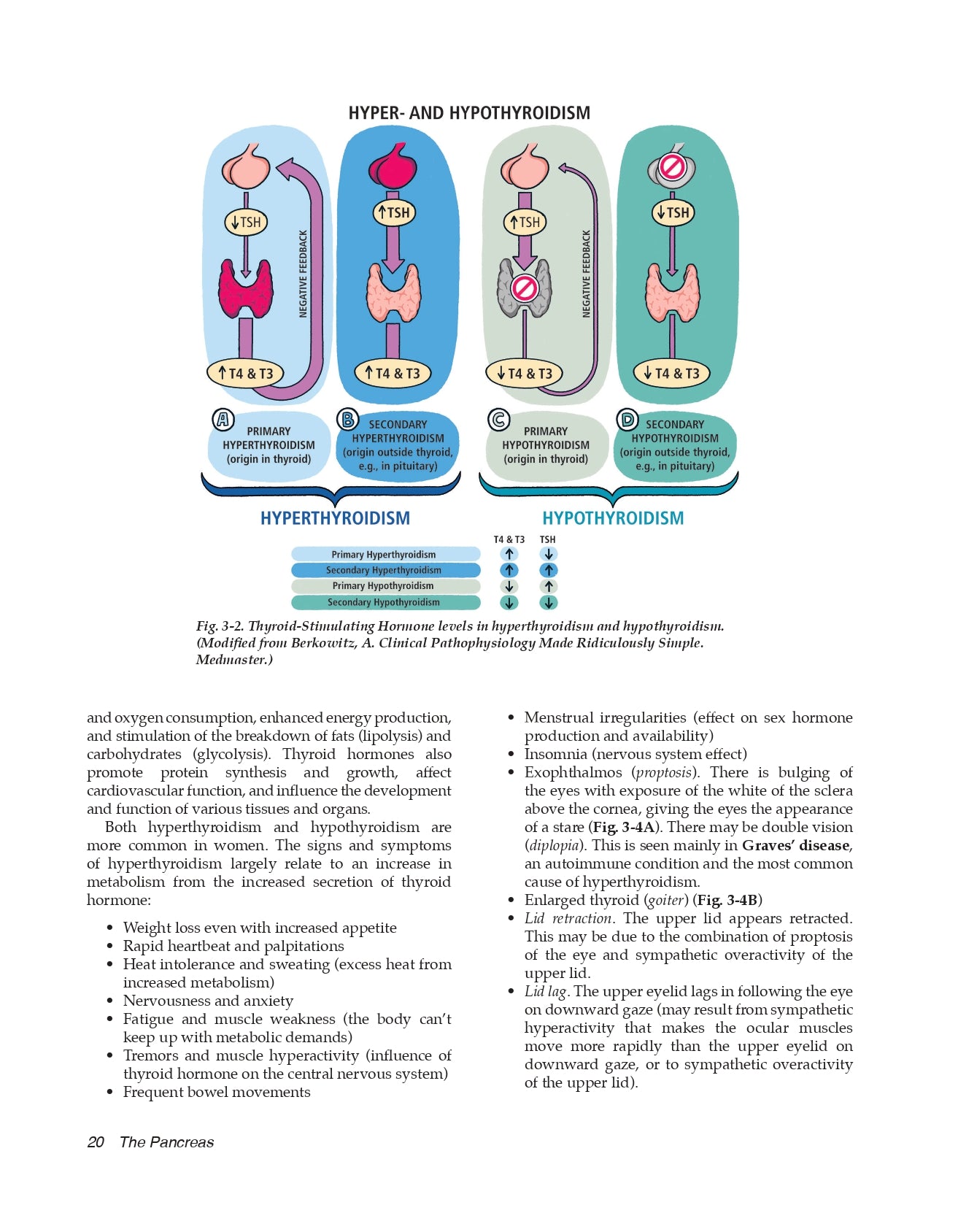
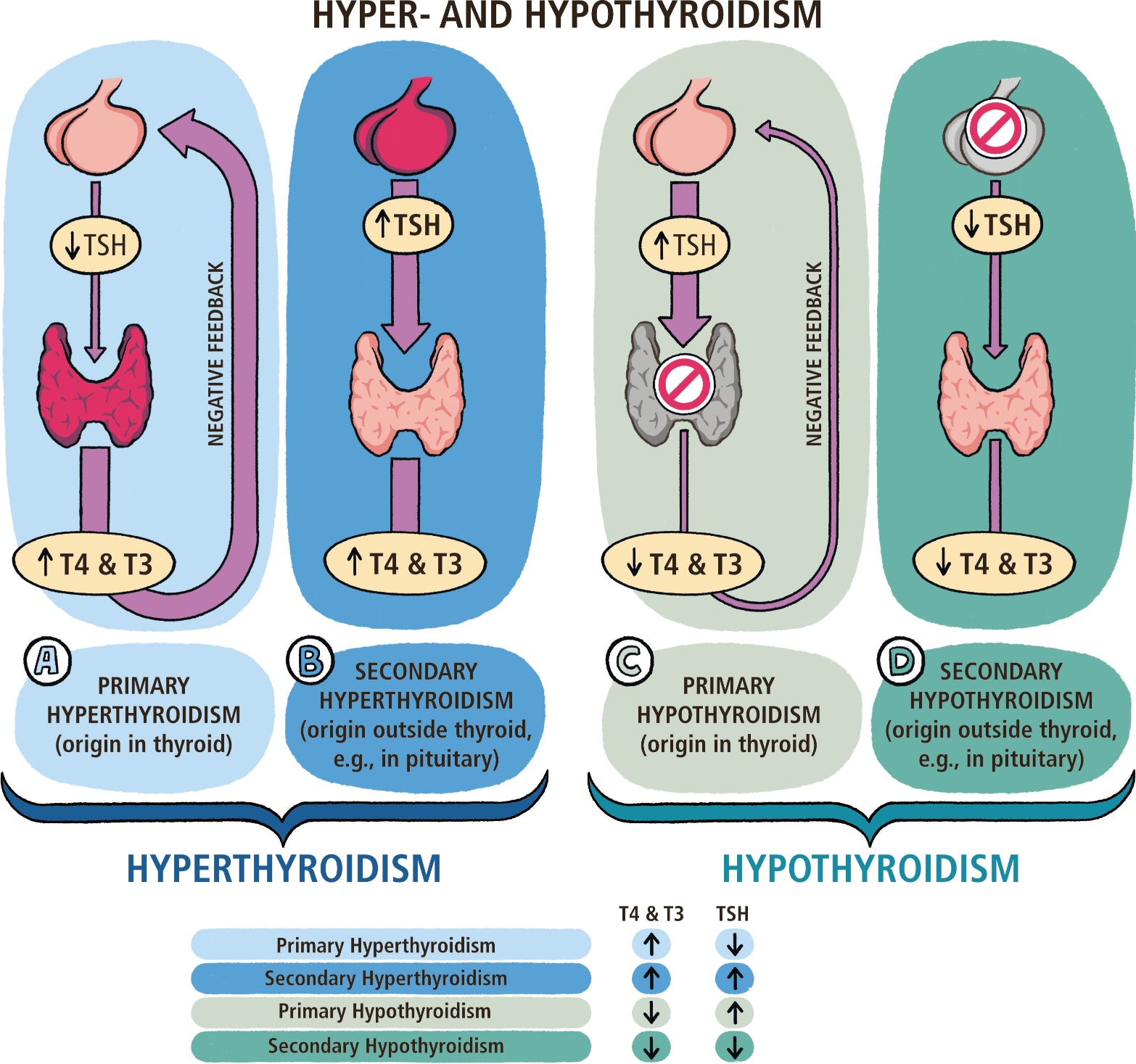
Hyperthyroidism
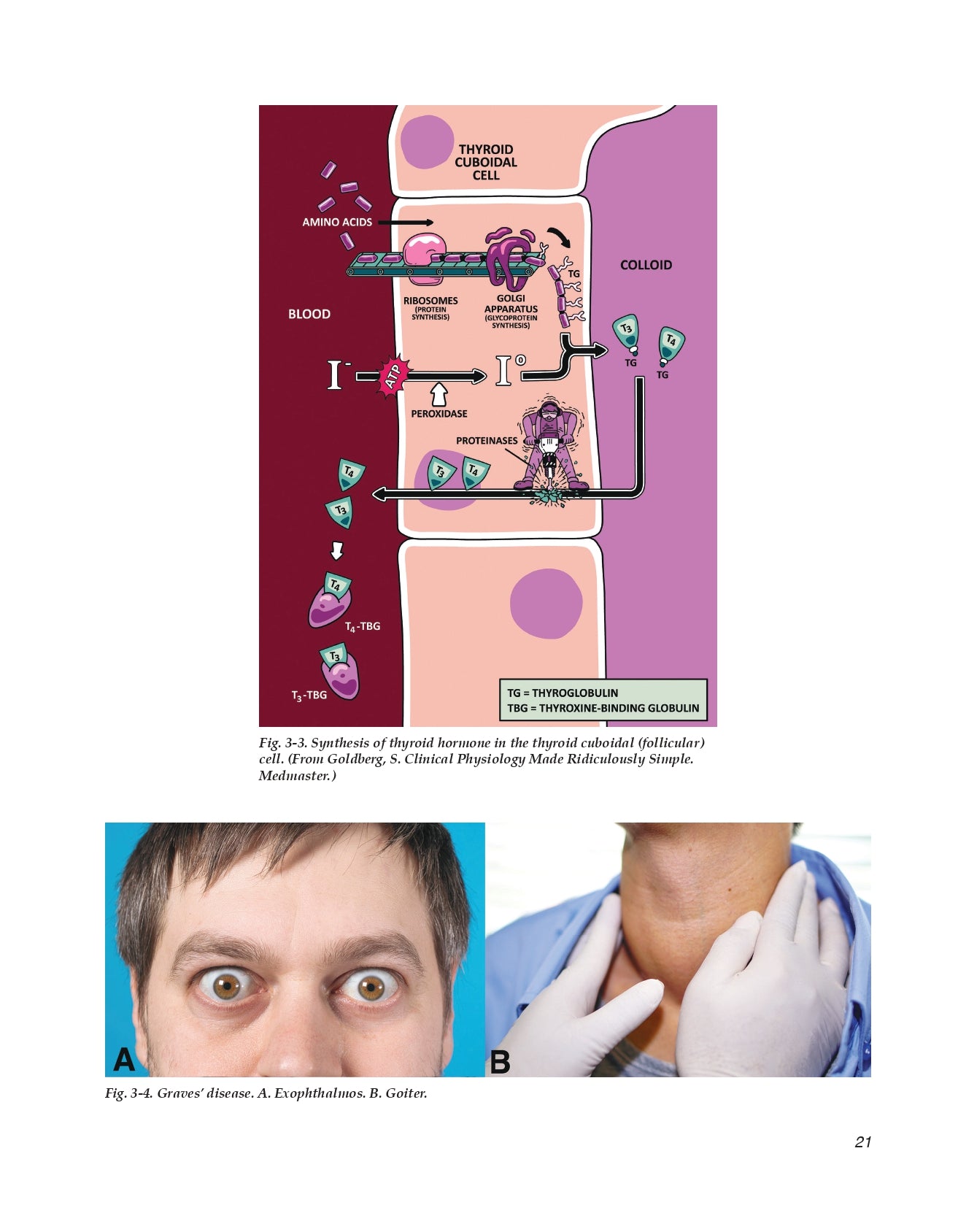
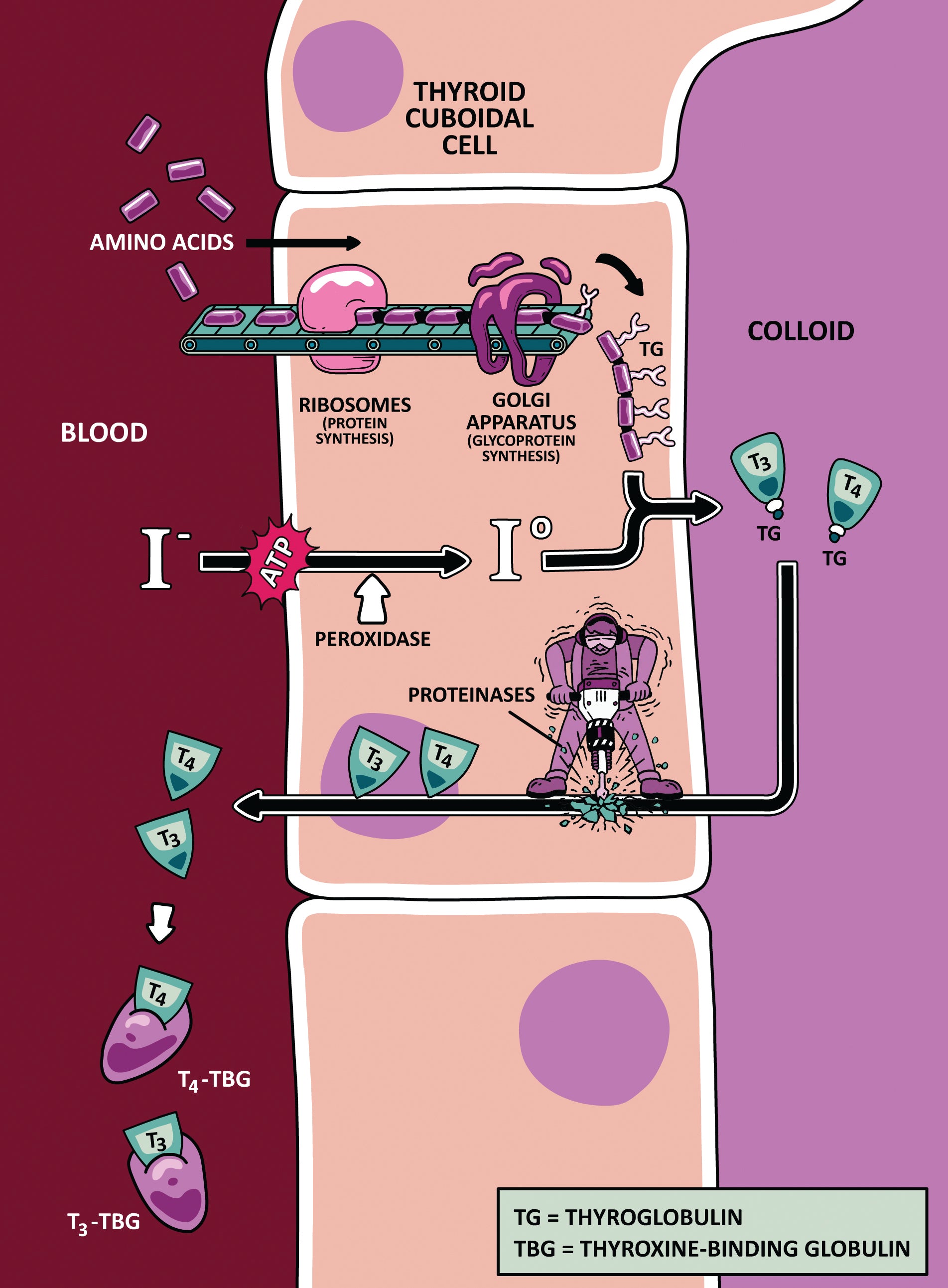
Synthesis of Thyroid Hormone
Hypothyroidism
Goiter
Thyroiditis
Thyroid Cancer
Euthyroid Sick Syndrome
Calcitonin
Chapter 4. Parathyroid Glands
Parathyroid Hormone (PTH)
Hyperparathyroidism
Hypoparathyroidism
Hypercalcemia
Hypocalcemia
Hungry Bone Syndrome
Parathyroid Hormone-related Protein (PTHrP)
Vitamin D
Vitamin D Synthesis
Hypervitaminosis D
Hypovitaminosis D
Rickets
Osteomalacia
Osteoporosis
Paget’s Disease
Chapter 5. Adrenal Glands
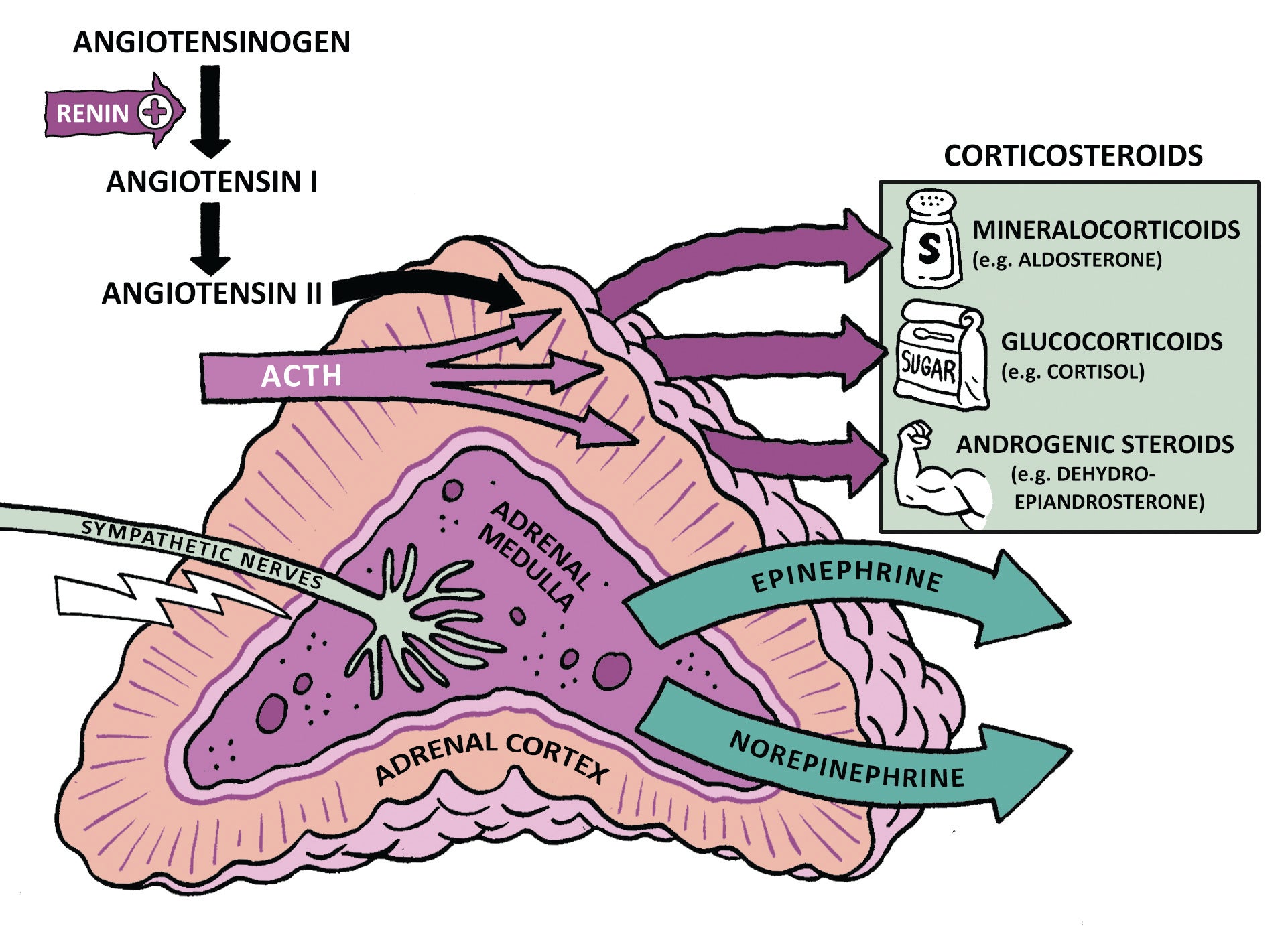
ADRENAL CORTEX
Mineralocorticoids (Aldosterone)
Glucocorticoids (Cortisol)
Androgens (Dehydroepiandrosterone; DHEA)
Cushing’s Syndrome
Addison’s Disease (Primary Adrenal Insufficiency)
Hyperaldosteronism
Hypoaldosteronism
Addison’s Disease vs Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia
Adrenal Crisis
DHEAExcess
DHEA Deficiency
ADRENAL MEDULLA
Epinephrine and Norepinephrine
Excess Epinephrine and Norepinephrine
Incidentalomas
Chapter 6. Hypertension
What Controls Blood Pressure?
What Causes High Blood Pressure?
Evaluating the Cause of Hypertension
Treatment of Hypertension
Chapter 7. Ovaries
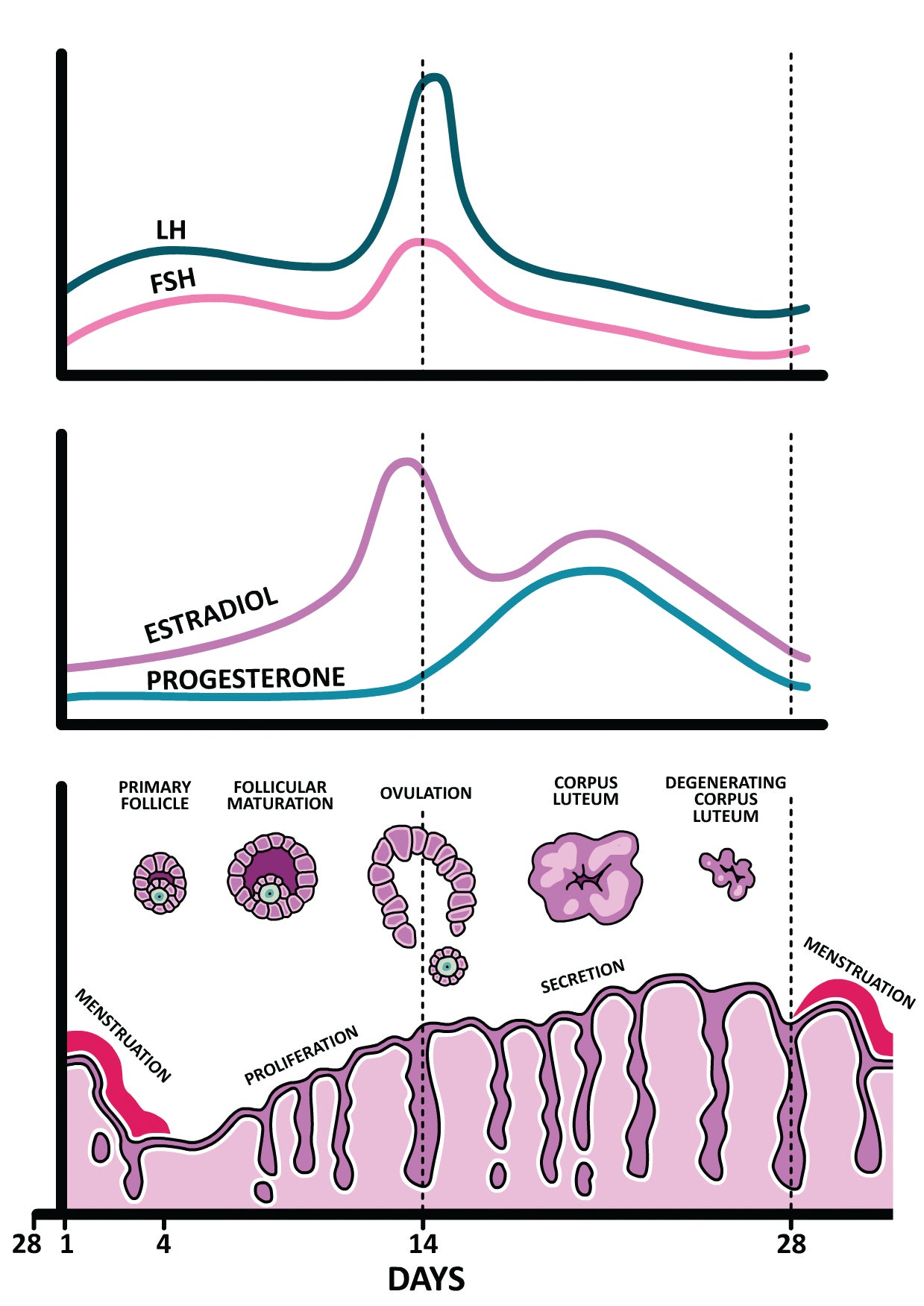
Estrogen and Progesterone
The Menstrual Cycle and Pregnancy
How Do Birth Control Pills Work?
Hyperestrogenism
Estrogen Deficiency
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
Premenstrual Syndrome (PMS)
Amenorrhea
Chapter 8. Testes
Testosterone
Hyperandrogenism
Hypoandrogenism
Chapter 9. Pituitary Gland and Hypothalamus
Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone
Growth Hormone
Growth Hormone Excess
Growth Hormone Deficiency
Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH) and Luteinizing Hormone (LH)
FSH and LH Deficiency
Prolactin
Hyperprolactinemia
Prolactin Deficiency
Antidiuretic Hormone
Syndrome of Inappropriate Antidiuretic Hormone Secretion
Diabetes Insipidus
Hypothalamic Releasing Hormones
Pineal Gland
Chapter 10. Heart
Atrial Natriuretic Peptide (ANP)
B-type Natriuretic Peptide (BNP)
Chapter 11. Liver
Insulin-like Growth Factor 1 (IGF-1)
Thrombopoietin
Hepcidin
Angiotensinogen
Chapter 12. Kidney
Renin
Hyperreninemia
Hyporeninemia
Erythropoietin (EPO)
Polycythemia
Chapter 13. Stomach and Intestines
Peptide YY (PYY)
Gastrin
Pernicious Anemia
Serotonin
Cholecystokinin (CCK)
Secretin
Gastric Inhibitory Peptide (GIP)
Motilin
Ghrelin
Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 (GLP-1)
Chapter 14. Placenta
Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (hCG)
Relaxin
Human Placental Lactogen (hPL)
Chapter 15. Adipose Tissue
Leptin
Adiponectin
Hormones That Decrease Appetite
Hormones That Increase Appetite
Chapter 16. Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia (MEN)
MEN1, MEN2A, and MEN2B
Neuroendocrine Tumors
Autoimmune Polyendocrine Syndromes
Chapter 17. Disorders of Sexual Development (DSD)
Genetic Disorders
Disorders of Puberty
Delayed Puberty
Precocious Puberty
Gynecomastia
Chapter 18. Infertility
Causes of Infertility
Infertility Workup
Infertility Treatment
Chapter 19. Gender Identity Dysphoria
Chapter 20. Dyslipidemia and Metabolic Syndrome
Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity
Medications for Obesity
Weight Loss Diets
Weight Loss Surgery