Introduction
Contributors
The Illustrator
The Consultant for Point of Care Ultrasound (POCUS)
Chapter 1 The Art of the Patient Presentation
1.1 Welcome to Acute Hospital Medicine
1.2 How to Summarize Your Patient
1.3 Structure Those Random Thoughts
1.4 Think DataDiagnosisDirection
1.5 A Sample Presentation
Chapter 2 Acute Care Chest Radiology
2.1 Basics of Reading Portable Chest Radiographs
- Is the Radiograph Worth Reading?
- Ignore the Most Interesting Findings
- Get to the Heart of the Matter
- The Pleural Space and Costophrenic Angles
- Finally, the Lungs!
2.2 Our Top Ten X-Ray Bad Guys
- #10 Mediastinal and Hilar Masses
- #9 Pericardial Effusion and Tamponade
- #8 Pulmonary Hypertension and Pulmonary Emboli
- #7 Tube Mishaps
- #6 Pneumothorax and Barotrauma
- #5 Effusions, Empyema, and Hemothorax
- #4 Atelectasis and Lobar Collapse
- #3 Congestive Heart Failure
- #2 Pneumonia
- #1 Adult Respiratory Distress Syndrome
-- Suggested Reading
Chapter 3 Point of Care Ultrasound (Pocus)
3.1 The Three Goals of POCUS
- Procedural Guidance
- Diagnosis
- Shock Management
3.2 POCUS Lingo
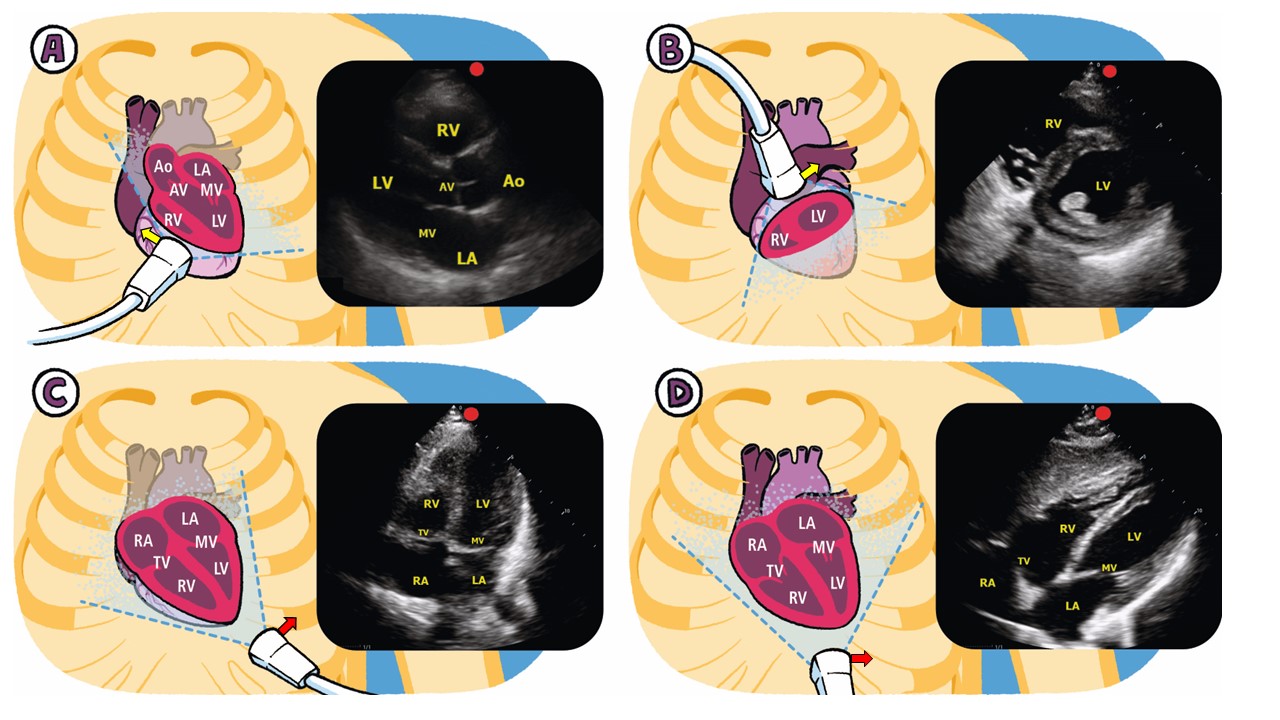
3.3 Our Top Ten POCUS Findings in the ICU
- Vessel Location for Catheter Placement
- Pneumothorax
- Pleural Fluid
- Lung Patterns
- Left Ventricle and Right Ventricle Dysfunction
- Valvular Vegetation
- Inferior Vena Cava (IVC) Size
- Distended Bladder
- Peritoneal Fluid
- Deep Venous Thrombosis (DVT)
3.4 POCUS Focus
Chapter 4 Sepsis and Resuscitation
4.1 Sepsis Defined
4.2 Sepsis and Shock
4.3 Initial Sepsis Management
- Reverse Hypoxemia and Limited Ventilation
- Reverse Hypotension and Support Organ Perfusion
4.4 Fluid Administration in Sepsis
- Crystalloids vs. Colloids
4.5 Vasopressors and Inotropes
4.6 Assessment of Tissue Oxygenation
- Mixed Venous Oxygen Saturation
- Blood Lactate
4.7 Hydrocortisone and Septic Shock
4.8 Antibiotics and Source Control
- Suggested Reading
Chapter 5 Management of Tachyarrythmias
5.1 Do I Have Time to Think?
5.2 What is the Diagnosis?
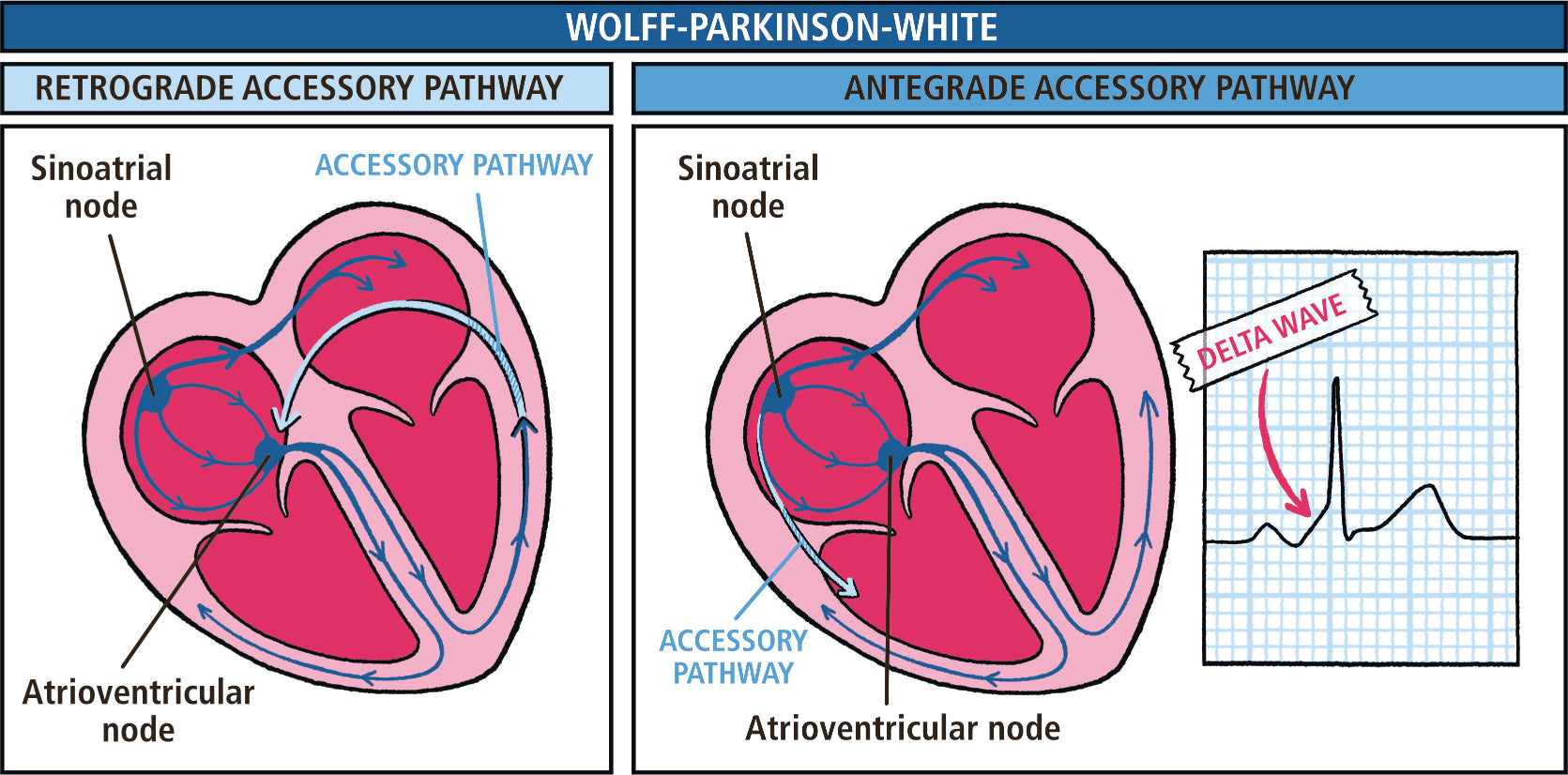
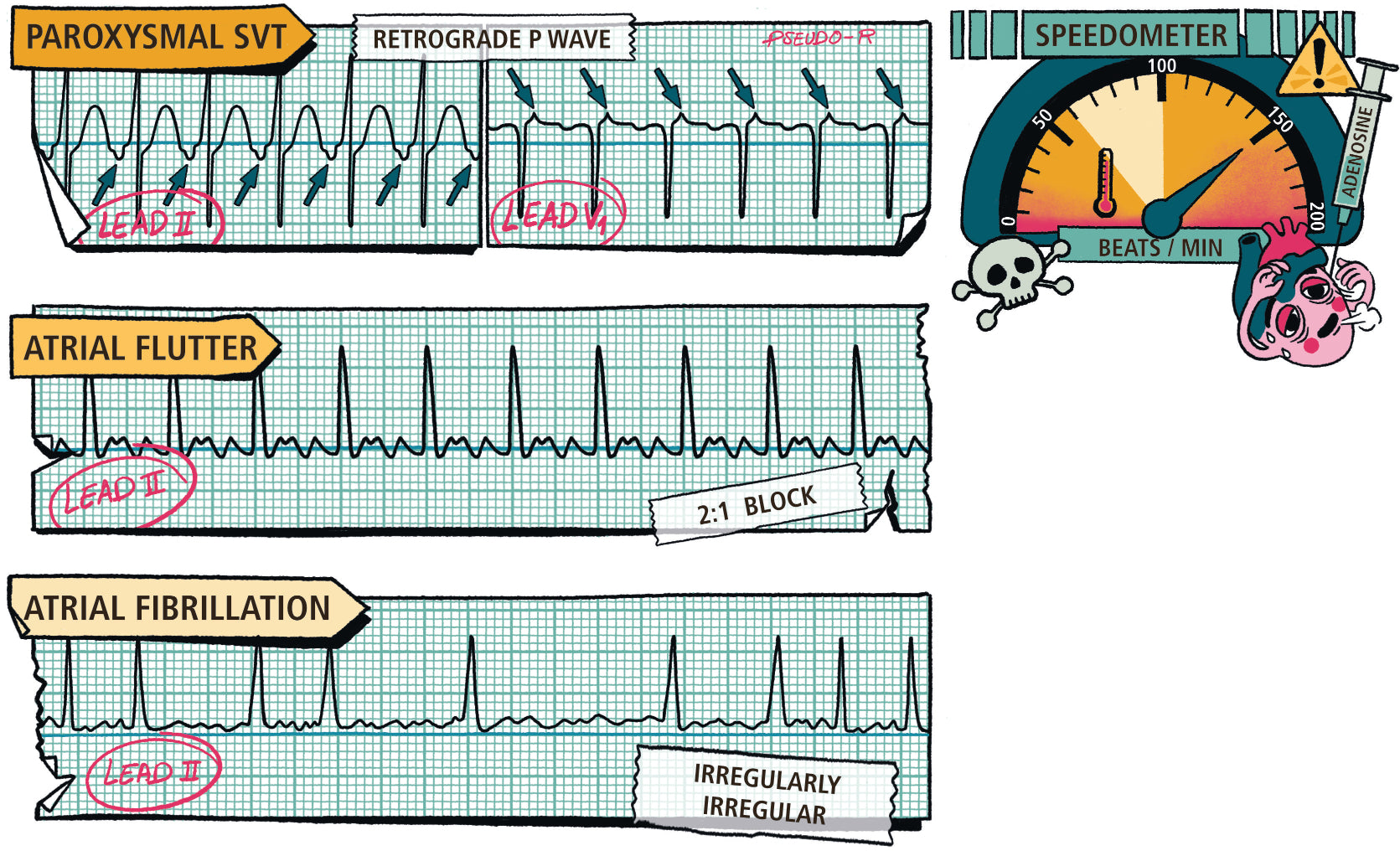
- Narrow Complex Tachycardia
- Wide Complex Tachycardia
5.3 How Do I Stop the Arrhythmia?
- Sinus Tachycardia
- Atrial Fibrillation and Flutter
- Multi-focal Atrial Tachycardia
- Paroxysmal Supraventricular Tachycardia (PSVT)
- Ventricular Tachycardia
5.4 What is the Rhythm Trying to Tell Me?
5.5 Do I Need to Anticoagulate?
- Suggested Reading
Chapter 6 Running a Code
6.1 Chest Compressions
6.2 Circulation: Take Charge and Shock
- Defibrillators
- Pulseless and a Shockable Rhythm
- Pulseless Electrical Activity (PEA)
- Pulseless and Asystole (Flat Line)
6.3 Breathing and Airway
6.4 Post-Arrest Care
- Suggested Reading
Chapter 7 Hemodynamic Monitoring
7.1 Arterial Blood Pressure
- The Arterial Catheter
7.2 Pressure Transducers
7.3 Vascular Pressures and the Pulmonary Artery Catheter
- Atrial Pressures and Waveforms
- Ventricular Pressures and Waveforms
- Pulmonary Artery Pressure and Waveforms
7.4 Cardiac Chamber Pressures and Pericardial Disease
7.5 Cardiac Output
7.6 Vascular Resistance
7.7 Shock and Hemodynamic Assessment
- Hypovolemic Shock
- Cardiogenic Shock
- Distributive Shock
7.8 Limitations of the Pulmonary Artery (PA) Catheter
7.9 Hemodynamic Assessment without the PA Catheter
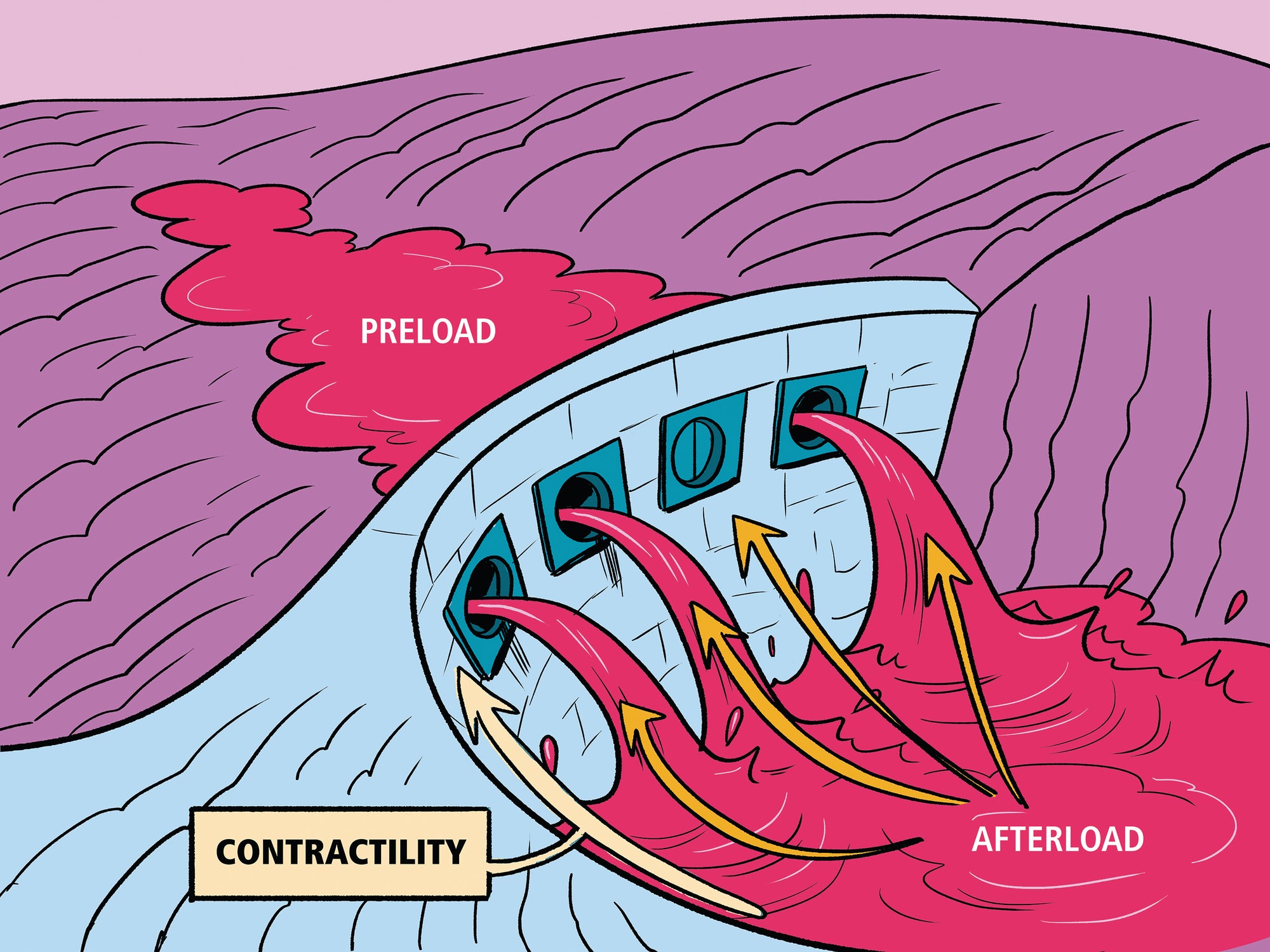
- Techniques to Change Preload
- Techniques to Assess Stroke Volume
- Inferior Vena Cava Diameter
- Miscellaneous Methods for Preload Assessment
7.10 Hemodynamic Approach to Your ICU Patient
- Suggested Reading
Chapter 8 Acute coronary syndromes
8.1 Step 1: Cool down the Heart
8.2 Step 2: Classify the ACS Syndrome (STEMI, Unstable Angina, NSTEMI)
- The ECG
- Cardiac Biomarkers
- ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction (STEMI)
- Non-ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction (NSTEMI) and Unstable Angina (UA)
8.3 Step 3: Crush the Platelets
8.4 Step 4: Bash the Coagulation System for UA and NSTEMI
8.5 Step 5: Blast Open the Obstruction for STEMI and High-Risk NSTEMI
- Treatment at a PCI-Capable Hospital
- Pharmacologic Therapy for Non-PCI-Capable Hospital
- Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG)
8.6 Wrapping it up
- Suggested Reading
Chapter 9 Acute Decompensated Heart Failure
9.1 Diagnosis of Decompensated Left Heart Failure
- Imaging
- Brain Natriuretic Peptide
- Echocardiography
9.2 Treatment of Acute Decompensated Left Heart Failure
- Reduce Left Ventricular Filling Pressure (Preload)
- Reduce Systemic Vascular Resistance (Afterload)
- Fix the Broken Heart (Dam)Increase Cardiac Output
- Find the Cause
- Arrythmia Management
- Hypertension Management
9.3 Diagnosis of Pulmonary Hypertension and Right Heart Failure
- Pulmonary Hypertension Classification
- Pulmonary Hypertension Diagnosis
- Why Pulmonary Hypertension Matters
9.4 Treatment of Pulmonary Hypertension in the Hospital
- Nitric Oxide
- Endothelin A and B Receptor Blockers
- Prostanoids
- Inotropes
- Heroics
9.5 Pulmonary Hypertension with Shock
- Suggested Reading
Chapter 10 High Systemic Arterial Blood Pressure
10.1 Pathophysiology of Hypertensive Urgency
10.2 Patient Assessment
10.3 Drug Therapy
- Calcium Channel Blockers
- Nitric Oxide Vasodilators
- Beta-Blockers
- Miscellaneous Medications
10.4 Hypertensive Emergency Clinical Syndromes
- Cardiovascular Disease
- Cerebrovascular Disease
- Subarachnoid Hemorrhage (SAH)
- Renovascular Disease
- Excess Catecholamine States
- Miscellaneous Conditions
Chapter 11 Pulmonary Thromboembolic Disease
11.1 Pathophysiology
- Right Heart Failure in PE
- Gas Exchange in PE
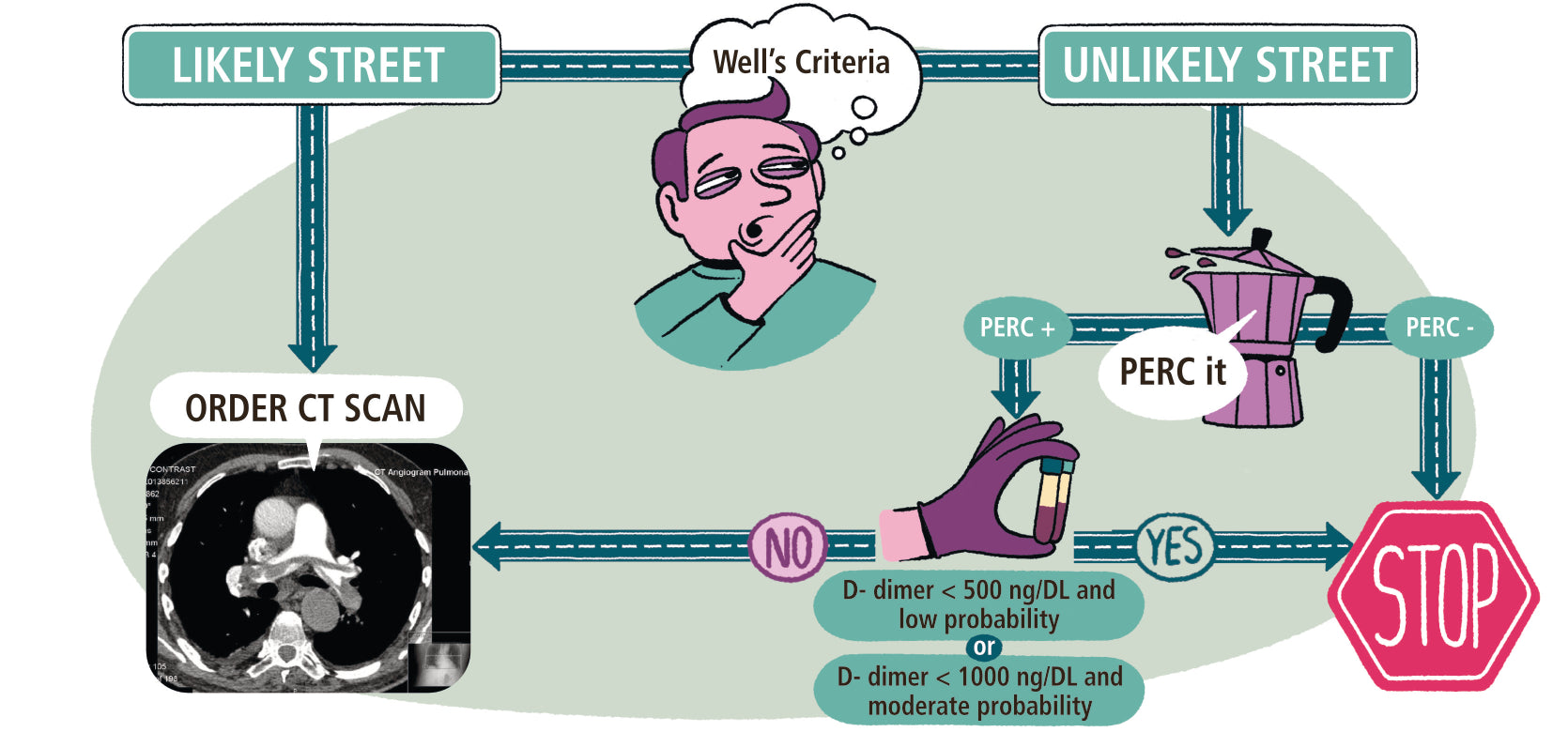
11.2 Diagnosis and Risk Stratification
- Diagnostic Risk PE Clinical Decision Rules
- Mortality Risk
11.3 Treatment of Massive PE
- Oxygenate and Ventilate
- Optimize RV Cardiac Output
- Reduce RV Afterload with Anticoagulation
- To Lyse or Not to Lyse
11.4 Treatment of Submassive PE
- Suggested Reading
Chapter 12 Basic Airway Management
12.1 Establish a Patent Airway with Ventilation
12.2 Clinical Clues for a Difficult Intubation
12.3 Key Steps to a Successful Airway
12.4 Endotracheal Intubation
- The Tools
- Pre-oxygenation
- Intubation Pharmacology
- Post-intubation Hemodynamics
12.5 The Difficult Airway
12.6 Changing the Endotracheal Tube
- Suggested Reading
Chapter 13 Acute Respiratory Failure
13.1 Assessment of Arterial Blood Oxygenation
- Partial Pressure of Oxygen (PaO2)
- Pathophysiology of Hypoxemia
- Non-invasive Oxygen Saturation (SpO2)
- Assessment of Tissue Oxygen Delivery (DO2)
13.2 Supplemental Oxygen and Hypoxemic Respiratory Failure
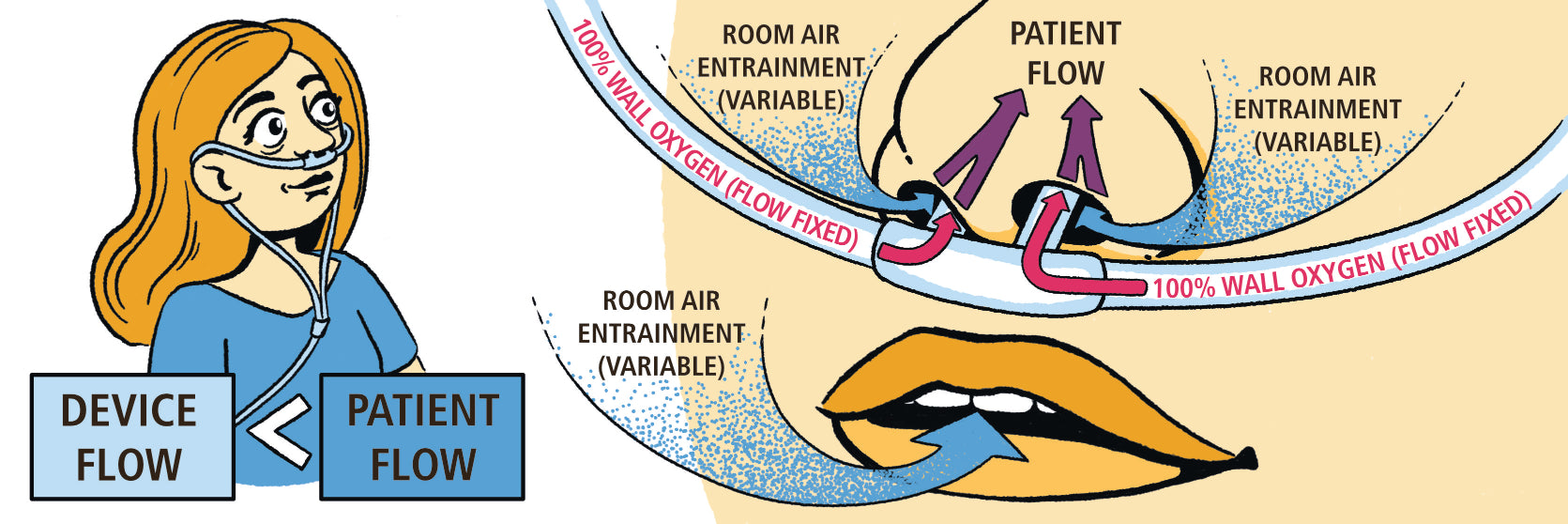
- Low-Flow Oxygen Systems
- High-Flow Oxygen Systems
- High-Flow Nasal Cannula
- Fixing Hypoxemia
13.3 Assessment of Ventilation (PaCO2)
- Non-Invasive Assessment of Carbon Dioxide
13.4 Hypercapnic Respiratory Failure
- Primary and Secondary Compensation
- Etiology of Ventilation Disorders in the ICU
- Suggested Reading
Chapter 14 Mechanics of Respiratory Failure
14.1 Simple Mechanics of Lung Inflation the EOM
14.2 Compliance/Elastance and Pleural Pressure
- Measurement of Compliance
14.3 Resistance and Time Constants
- Measurement of Airways Resistance
14.4 Lets Put it Together
- Suggested Reading
Chapter 15 Mechanical Ventilation
15.1 Ventilator Components
15.2 Setting the Breath Rate (Triggering)
- Pressure-Based Triggering
- Flow-Based Triggering
15.3 Setting the Breath Type
- Control Breaths
- Support Breaths
15.4 Modes of Mechanical VentilationThe Full Monty
- Control (Assist Control) Ventilation
- Intermittent Mandatory Ventilation (IMV)
- Spontaneous Mode of Ventilation
- APRV and BiLevel Ventilation
15.5 Mode summary
15.6 Positive End-Expiratory PressurePEEP, CPAP, and EPAP
- Adverse Effects of End-Expiratory Pressure
15.7 How to Set Your Best PEEP on the Ventilator
15.8 Extrinsic vs. Intrinsic PEEP
15.9 Mean Airway Pressure and Oxygenation
- Suggested Reading
Chapter 16 Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (Ards)
16.1 ARDS Ridiculously Simple Overview
16.2 Berlin Definition
16.3 Causes of ARDS
16.4 Pathophysiology of ARDS
- ARDS as a Heterogeneous Lung Disease
16.5 Airway Management in ARDS
16.6 ARDS and the Ventilator First Do No Harm
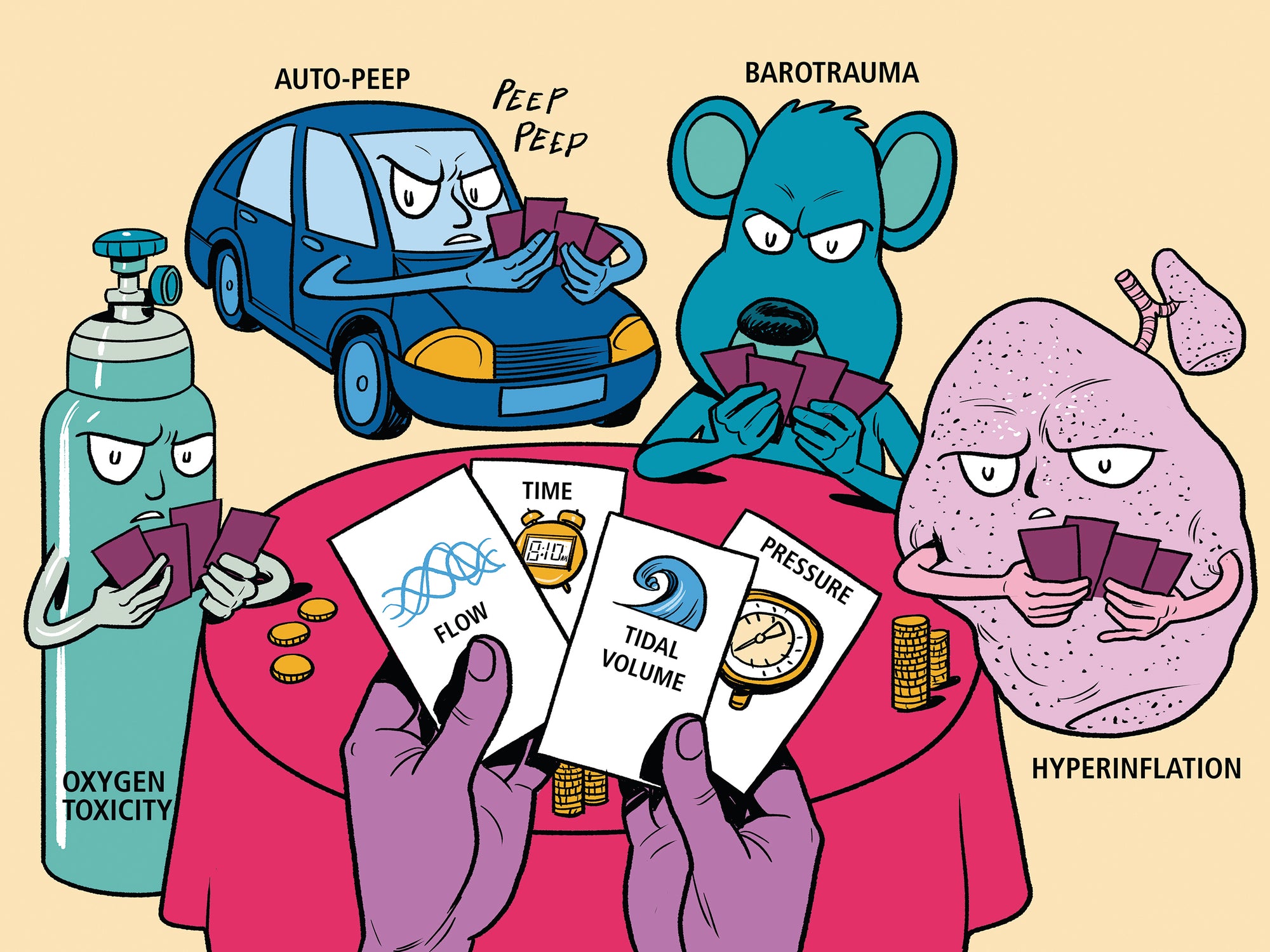
- Oxygen Toxicity: Hyperoxic Lung Injury
- BarotraumaNo Pressure!
- Volutrauma Turn Down the Volume!
- Atelectrauma The Elusive Best Peep!
16.7 Mechanical Ventilation in ARDS
- Control Breaths
- PEEP Management
- Alveolar Recruitment Maneuvers
16.8 Fluid Management in ARDSWet or dry?
16.9 Approach to Intractable Hypoxemia in ARDS
- Pharmacologic Paralysis
- Prone Ventilation
- Inhaled Vasodilators
- High-frequency Oscillation
- APRV and Bilevel Ventilation
- Extracorporeal Support
- Hypoxemia Overview
16.10 The Little Things
16.11 Prognosis
- Suggested Reading
Chapter 17 Obstructive Lung Disease (Old) and Respiratory Failure
17.1 Pathophysiology of Airflow Obstruction
17.2 Intrinsic PEEP (PEEPi) in OLD
- Intrinsic PEEP Assessment
- Complications of Intrinsic PEEP
- Limiting Intrinsic PEEP in OLD
17.3 Mechanical Ventilation in OLD
- Non-Invasive Mechanical Ventilation in OLD
- Invasive Mechanical Ventilation in OLD
- Ventilator Management in OLD
17.4 Drug Therapy in OLD
- Antibiotics
- Bronchodilators
- Corticosteroids
- Miscellaneous Interventions
17.5 Patient Outcome
- Suggested Reading
Chapter 18 Weaning From Mechanical Ventilation
18.1 Control That SOB
18.2 Spontaneous Breathing Trial (SBT)
- Spontaneous Breathing Trial Intolerance
- Removing the Tube
18.3 Non-invasive Ventilation (NIV) and Weaning
18.4 Alternatives to the SBT Trial
18.5 Beyond the SBT Trial Pain, Sedation, and Delirium
- Sedation Management: Less Is More
- Pain Management
- Delirium
- Early Mobility in the ICU
18.6 Coordination of Ventilator Care Know Your Alphabet?
18.7 When Is a Tracheostomy Indicated?
- Timing and Technique of Tracheostomy
- Type and Size of the Tracheotomy Tube
- Care of the Tracheotomy Tube
- Swallowing
- Decannulation
- Suggested Reading
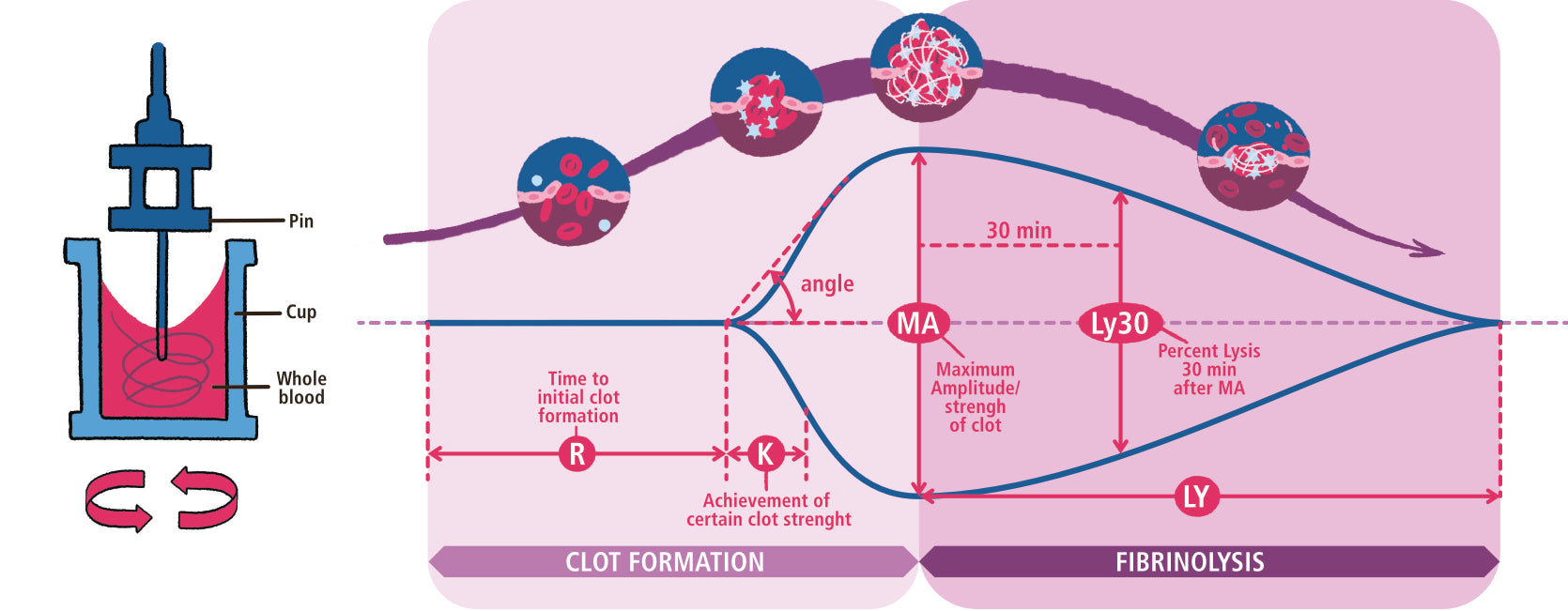
Chapter 19 Bleeding, Clotting and Hematological Emergencies
19.1 Clotting Cascade: Help Me Memorize! ! !
- Extrinsic or Tissue Factor Pathway
- Intrinsic or Contact (collagen) Activation Pathway
- Anti-Clotting Pathways
19.2 Overview of Bleeding and Clotting disorders
- Things that Elevate the PT-INR
- Things that Elevate the PTT
- Things that Elevate both PT-INR and PTT
19.3 Top four Bad Boys of ICU Hematology
- Public Enemy #1: Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia (HIT)
- Public Enemy #2: Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC)
- Public Enemy #3: Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura (and HELLP! and HUS! )
- Public Enemy #4: Catastrophic Antiphospholipid Antibody Syndrome (CAPS)
- Suggested Reading
Chapter 20 Transfusion Medicine
20.1 Quick-Thinking Rapid Transfusion
20.2 Red Blood Cell Transfusions
- When to Transfuse?
- Complications of Red Blood Cell Transfusion
20.3 Platelets
20.4 Fresh Frozen Plasma (FFP)
20.5 Cryoprecipitate
20.6 Recombinant Factor VIIa (Novo-Seven)
20.7 Four-Factor Prothrombin Complex Concentrate
- Suggested Reading
Chapter 21 Acute Kidney Injury
21.1 Classification of Acute Kidney Injury
21.2 Drug-induced Acute Kidney Injury
21.3 Prevention of Acute Kidney Injury
- Hypoperfusion
- Contrast-Induced AKI
- Aminoglycoside Nephropathy
21.4 Management of Acute Kidney Injury
- Diuretic Use in AKI
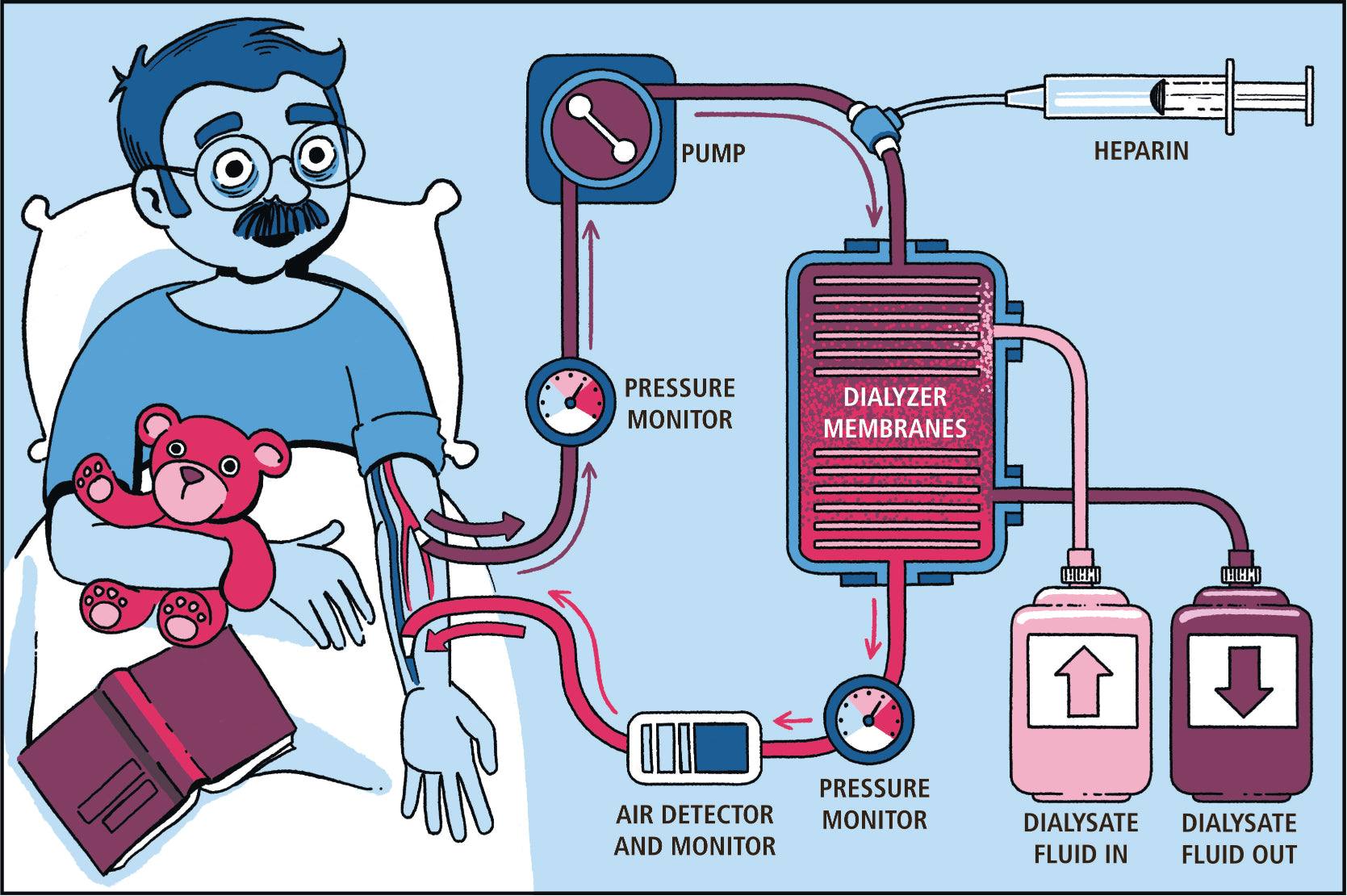
- Dialysis Therapy
- Dialysis Methods
- Dialysis Dose
- Suggested Reading
Chapter 22 Gastrointestinal Bleeding
22.1 ABCs (and D) of GI Bleeding
- Access
- Blood and Blood Products
- Call for Help
- Diagnose the Bleeding Source
- Suggested Reading
Chapter 23 Acid-Base Disorders
23.1 Simple Acid-Base
23.2 Primary Disturbance and Secondary Compensation
23.3 The Four Steps of Acid-Base Analysis
- STEP 1: Define the Primary Disorder
- STEP 2: Assess the Compensation
- STEP 3: Calculate the Anion Gap
- STEP 4: Calculate the Delta Gap
23.4 Respiratory Acid-Base Disorders
- Respiratory Acidosis
- Respiratory Alkalosis
23.5 Metabolic Acid-Base Disorders
- Metabolic Acidosis and the Anion Gap
- Metabolic Acidosis and the Osmolar Gap
- Anion Gap Metabolic Acidosis and Management
- Non-Anion Gap Acidosis
23.6 Metabolic Alkalosis
- Contraction Alkalosis
- Post-Hypercapnic Metabolic Alkalosis
- Mineralocorticoid Excess
- Suggested Reading
Chapter 24 Drug Overdose
24.1 The Basics
- Resuscitate and Stabilize
- Confirm Diagnosis and Toxin
- Antidotes and Toxin Elimination
- The Overdose Booby Traps
24.2 Specific Overdoses
- Acetaminophen
- Alcohols
- Benzodiazepines
- Slow it Down: Beta Blockers and Calcium Channel Blockers
- Speed it Up: Cocaine and Cathinones
- Hypoglycemia Secondary to Insulin and Oral Hypoglycemic Agents
- Antidepressants and the Abnormal ECG
- Salicylates and the Pseudosepsis Syndrome
- Serotonin Syndrome
- Opioids
- Suggested Reading
Chapter 25 Neurologic Emergencies
25.1 Acute Ischemic Stroke
25.2 Acute Intracerebral Hemorrhage
- Blood Pressure Control
- Reversal of Coagulopathy
- Elevated Intracranial Pressure
25.3 Status Epilepticus
25.4 Acute Myasthenic Crisis
Chapter 26 SARS-CoV-2 Infection and COVID-19 Disease
26.1 Epidemiology of the Pandemic
26.2 SARS-CoV-2 Virus
- SARS-CoV-2 Infectivity
26.3 COVID-19: Clinical Features
- COVID-19 Clinical Phenotypes
- COVID-19 Timeline
- COVID-19 Risk factors
26.4 The Diagnosis of COVID-19
- Laboratory Testing in COVID-19
- Radiology Findings in COVID-19
- PCR and Antibody Testing
- Pre-Test Probability and PCR Testing
26.5 Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
26.6 The Clinical Management of COVID-19
- Hypoxemic Respiratory Failure in the Non-Intubated Patient
- Airway Management
- Hypoxemic Respiratory Failure in the Intubated Patient
- Cardiovascular Management of the Patient with COVID-19
- Cytokine Release Syndrome (CRS)
- Coagulation Disorders
- Gastrointestinal Manifestations of COVID-19
- Renal Manifestations of COVID-19
26.7 Treatment of COVID-19
- Empiric Antibiotics for Secondary Infection
- Antiviral therapy
- Corticosteroid Therapy
- Convalescent plasma (CP)
- Monoclonal Antibody Therapy
- Anticoagulant and antiplatelet therapy
- Anti-inflammatory therapy
- Treatment for Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19
26.8 Vaccine for COVID-19
26.9 Goals of Care and Resource Limitations
- Suggested Reading
References
Index