Clinical Biostatistics and Epidemiology Made Ridiculously Simple
Also available on
Description
The most important points in clinical biostatistics, presented intuitively with clinical examples. Because intuitive concepts are the easiest to learn and retain, this book minimizes math and emphasizes concepts. From terminology to research design to various statistical testing, this text provides a lasting clear approach to interpreting medical research reports. Valuable for biostatistics courses.
Excellent USMLE Board Review.
Author(s)
Ann Weaver, Ph.D.
Ann Weaver, PhD, Professor, Statistics and Research, Program Chair of Research and Statistics, Argosy University, Sarasota FL.
Stephen Goldberg, M.D.
Stephen Goldberg, M.D., a graduate of the Albert Einstein College of Medicine, is a researcher, physician, teacher, computer programmer, writer, musician/composer, and past President of the Medmaster Publishing Company for 40 years. Dr. Goldberg has published numerous medical and scientific papers through research at the Albert Einstein College of Medicine, National Institutes of Health, New York Medical College and the University of Miami School of Medicine. He has authored 20 books in a diversity of medical areas, including textbooks of Anatomy, Physiology, Biochemistry, Genetics, Biostatistics and Epidemiology, Neurology, Consciousness, Ophthalmology, Hematology, and Computer Programming, as well as many interactive computer programs on various medical topics, including Atlas of Microbiology and Atlas of Human Diseases. He is Professor Emeritus at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine, where he taught medical students for 25 years. His reputation is that of an educator who can simplify complex topics. He received the George Paff Most Outstanding Professor Teaching Award11 times at the U of M and was invited in 2004 to be the keynote speaker at the medical school graduation commencement at the Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis for his work in medical education. He is currently Editor-in-Chief of the Medmaster Publishing Company.
Details
Pages: 104
Publication: Edition 1 (April 1, 2012)
Language: English
ISBN: 9781935660026 eISBN: 9781935660118
Table of contents
PART I. INTRODUCTION
CHAPTER 1. TERMINOLOGY
- Population, Sample, and Element
- Descriptive vs. Inferential Statistics
- Parameter vs. Statistic Sampling
- Error vs. Selection
- Bias Imprecision vs. Bias (Inaccuracy)
- Validity vs. Reliability
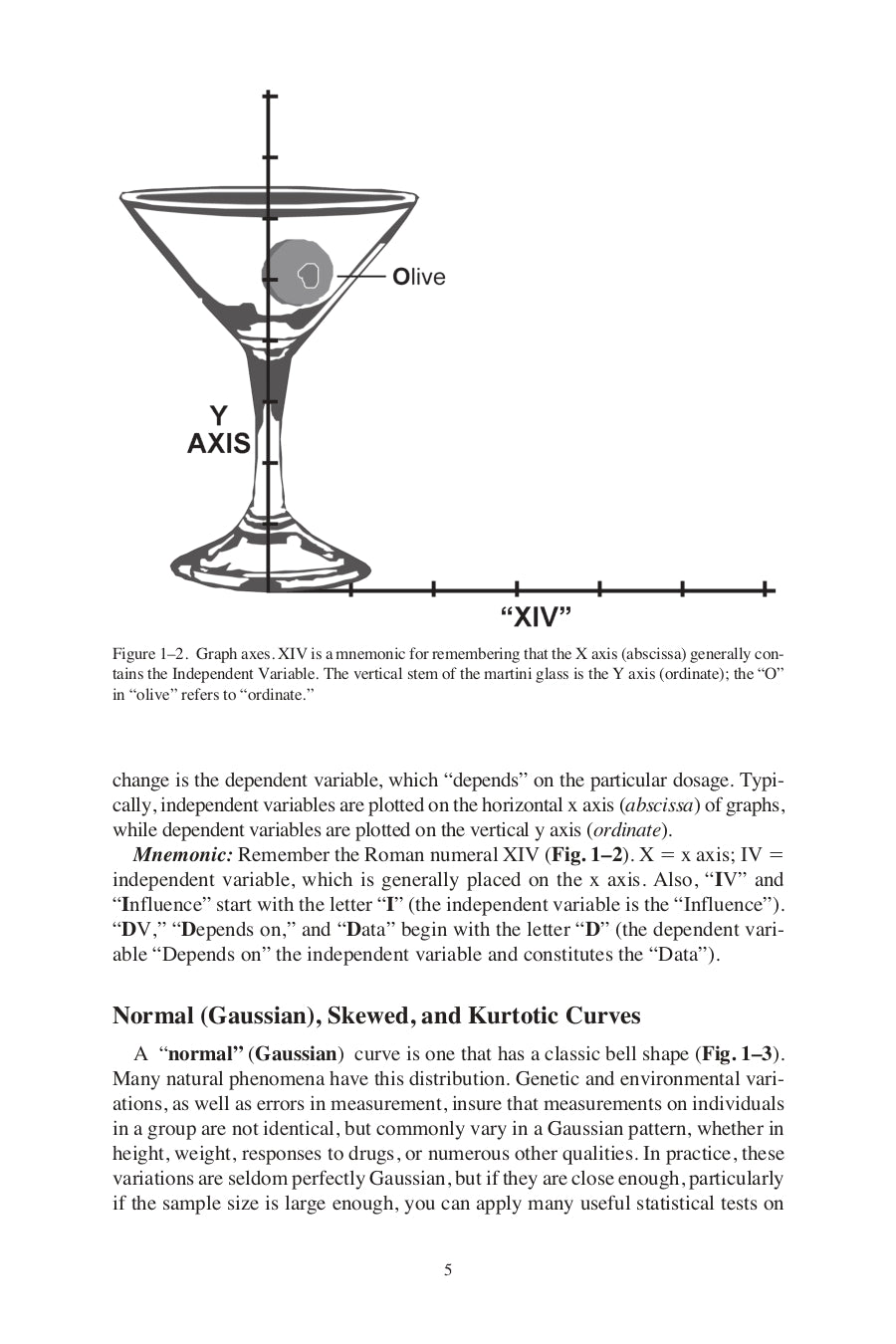
- Independent vs. Dependent Variables
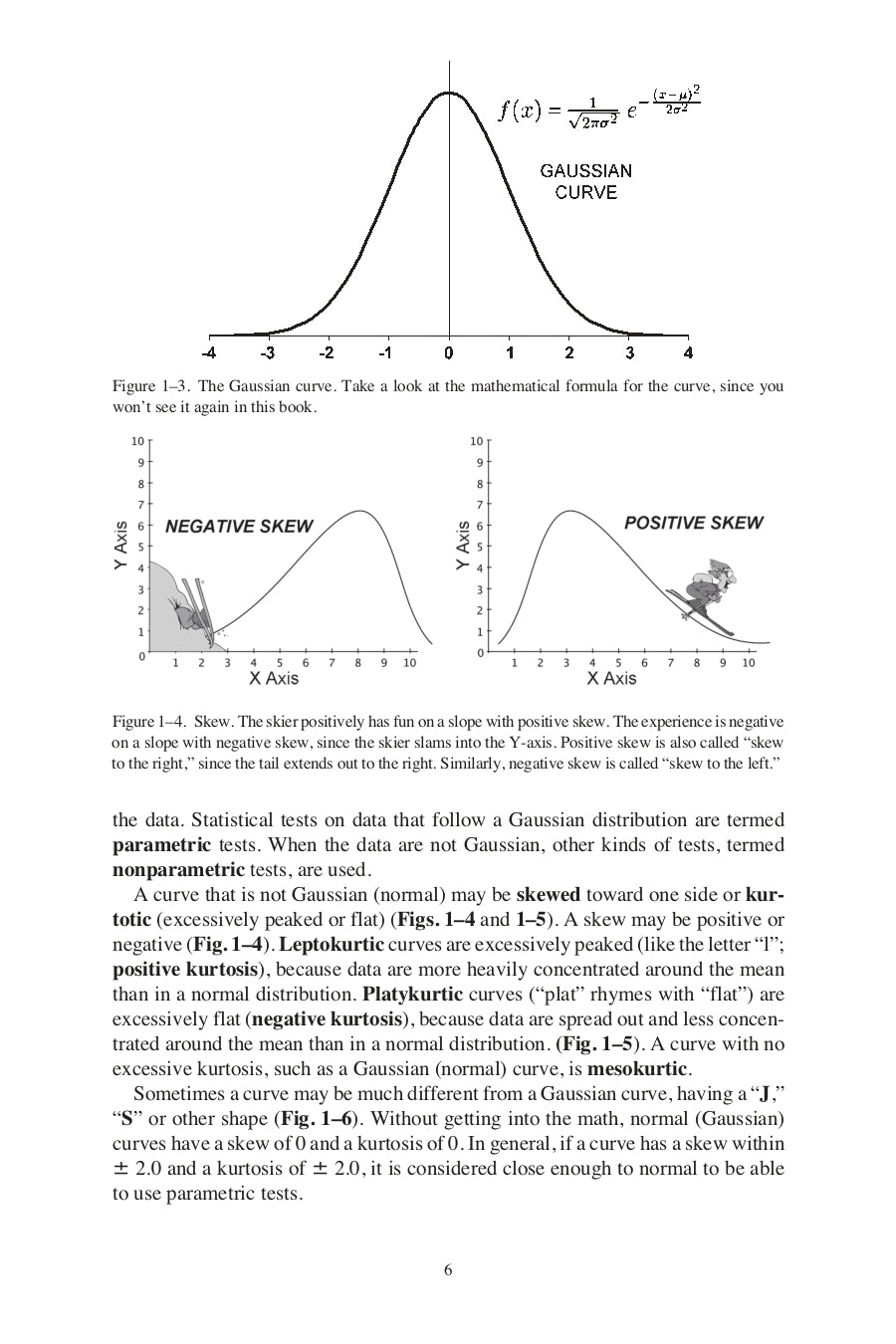
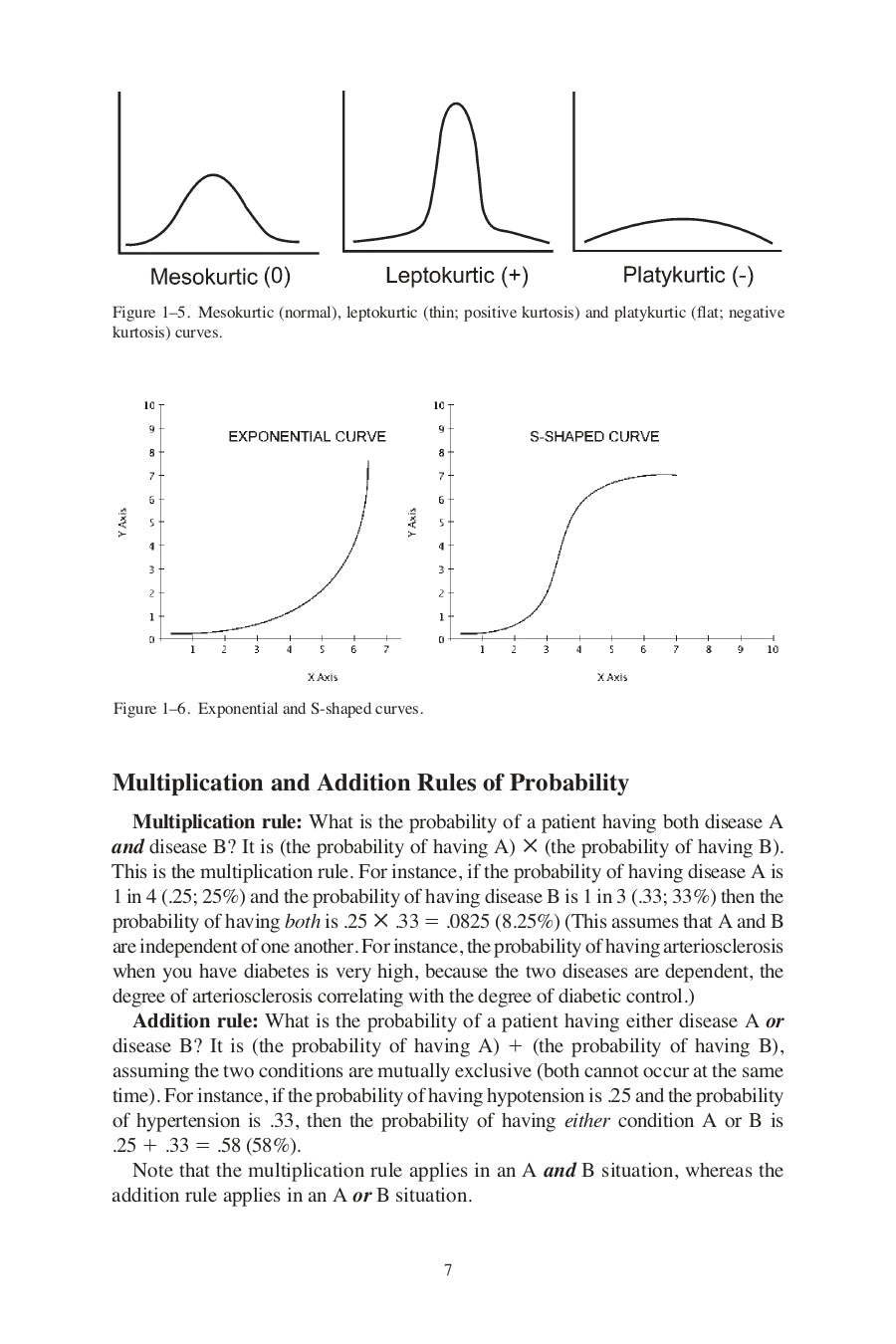
- Normal (Gaussian), Skewed and Kurtotic curves
- Multiplication and Addition Rules of Probability
- Statistical Significance vs. Clinical Significance
- Statistical Abnormality vs. Clinical Abnormality
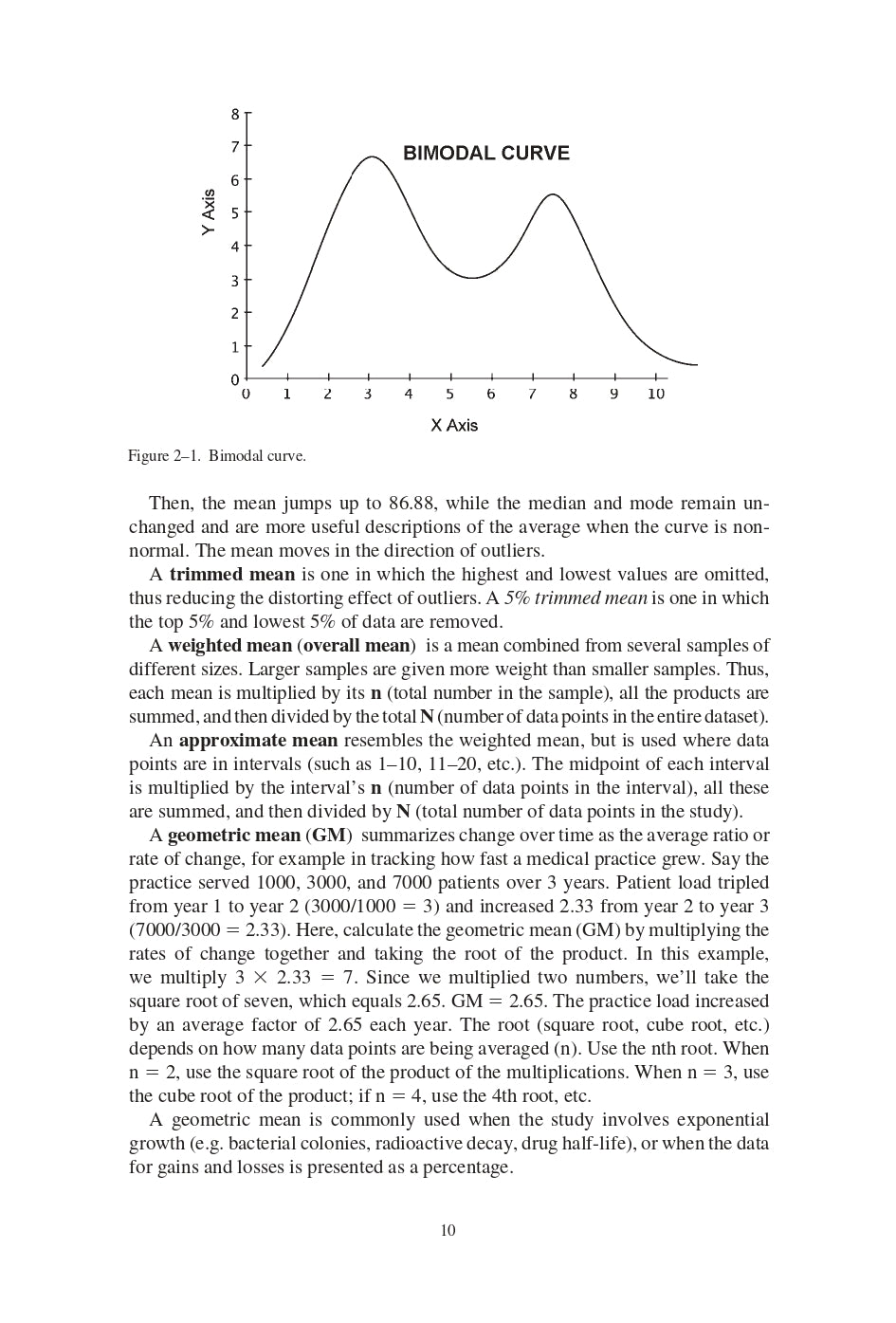
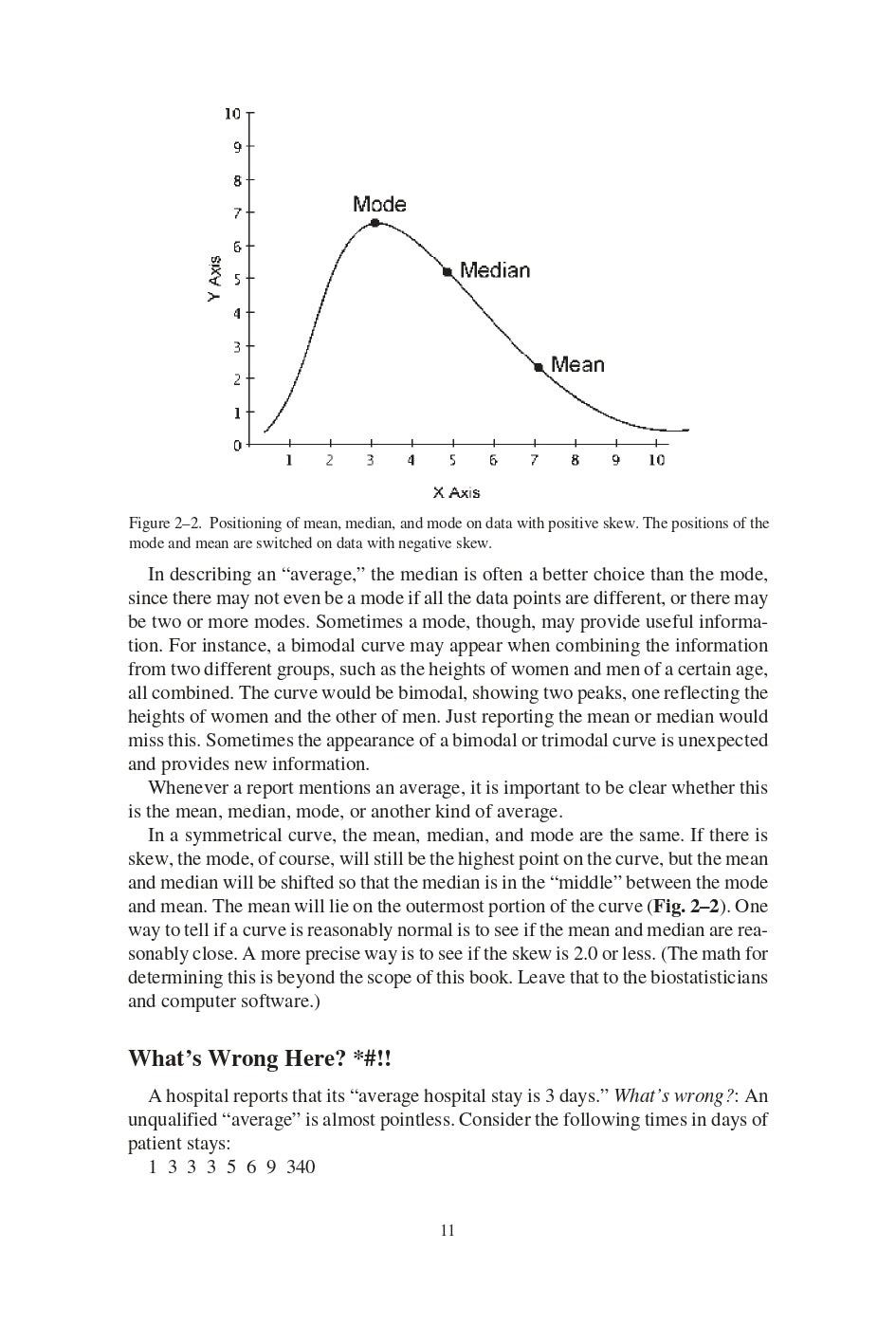
CHAPTER 2. MEAN, MEDIAN, AND MODE
- Mean
- Median
- Mode
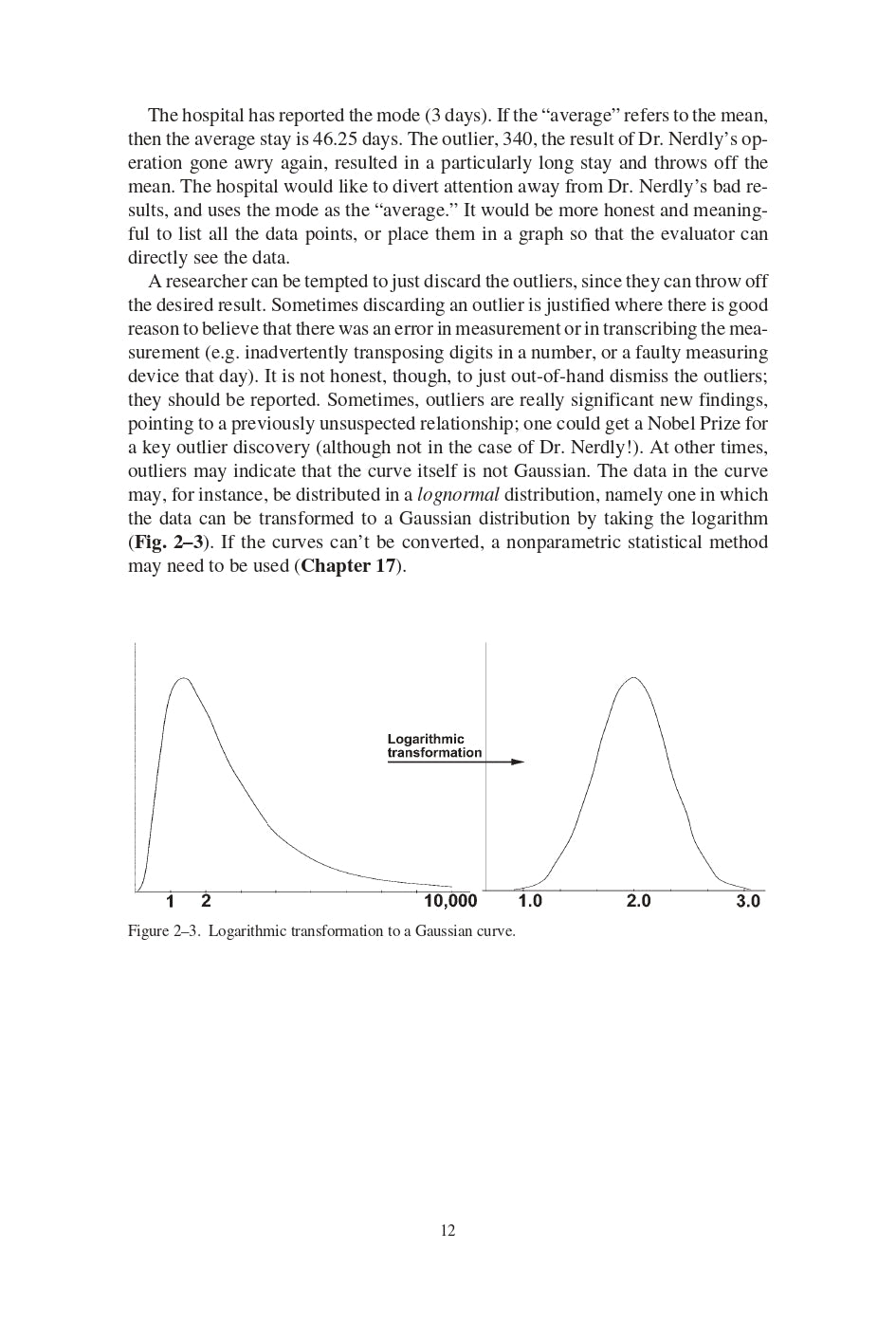
- What’s Wrong Here? *#!!
CHAPTER 3. RANGE, VARIATION, AND STANDARD DEVIATION
- Range
- Variance
- Standard Deviation
- Coefficient of Variation
CHAPTER 4. KINDS OF DATA
- Nominal Data
- Ordinal Data
- Interval Data
- Ratio Data
PART II. RESEARCH DESIGN
CHAPTER 5. KINDS OF STUDIES
- Randomized Control Studies
- Matching Studies
- Stratified Randomization Studies
- Blind Studies
- Prospective (Cohort; Longitudinal) Studies
- Retrospective (Case-control) Studies
- Cross-sectional (Prevalence) Studies
- Experimental vs. Observational Studies
- Case Series and Case Reports
- Meta-analysis
- Crossover, Between-subjects, and Within-subjects Studies
- Therapeutic Trials
CHAPTER 6. GRAPHING
- Bar Graphs (Bar Charts)
- Tables
- Histograms
- Line Graphs
- Cumulative Frequency Curves
- Box-and-Whiskers Plots
- Stem-and-Leaf Plots
- Scattergrams
- Survival Curves
CHAPTER 7. HYPOTHESIS TESTING
- The Null and Alternative Hypotheses
- Rejecting the Null Hypothesis
PART III. STATISTICAL TESTS
- Parametric vs. Nonparametric Tests
CHAPTER 8. DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS
- The Z-score
CHAPTER 9. INFERENTIAL STATISTICS
- Confidence Intervals vs. Hypothesis Testing and P-values
CHAPTER 10. STANDARD ERROR OF THE MEAN
- The Central Limit Theorem
- Standard Error of the Mean (SEM)
CHAPTER 11. THE T-TEST
- The Meaning of the T-Test
- Comparing Two Samples
CHAPTER 12. ONE-TAILED VS. TWO-TAILED STUDIES
- The two-tailed test
- The one-tailed test
CHAPTER 13. P-ING (PEE-ING) ALL OVER THE PLACE
CHAPTER 14. TYPE I AND TYPE II ERRORS AND POWER
- Type I and Type II Errors
- Power
- Effect Size
- Bayesian Thinking
- Calculation of Sample Size
CHAPTER 15. ANOVA (ANALYSIS OF VARIANCE)
- ANOVA and F-ratio
- MANOVA and ANCOVA
CHAPTER 16. CORRELATION AND REGRESSION
- Correlation Techniques
- Correlation Coefficient
- Coefficient of Determination
- Correlation Does Not Mean Causation
- Criteria of Causality
- Regression
- Kinds of Regression Analysis
- Regression to the Mean
CHAPTER 17. NONPARAMETRIC TESTS
- Chi Square Goodness-of-Fit Test
- Nonparametric Tests That Use Ranking
- Nonparametric Tests That Do Not Use Ranking
CHAPTER 18. EPIDEMIOLOGICAL TESTS
- Incidence vs. Prevalence
- Mortality, Morbidity, and Case Fatality
- Absolute Risk vs. Relative Risk (RR)
- Odds and Odds Ratio (Relative Odds)
- Absolute Risk Reduction (Attributable Risk) vs. Relative Risk Reduction
- Number Needed to Treat (NNT)
- Number Needed to Harm (NNH)
- Sensitivity vs. Specificity
- Positive and Negative Predictive Values
PART IV. ARE THE RESEARCH CONCLUSIONS CORRECT?
CHAPTER 19. WHAT'S WRONG HERE?
- Who Says So?
- How Does the Researcher Know?
- What's Missing?
- Did Someone Change the Subject?
- Does It Make Sense?
Appendix A. The Z table
Appendix B. The T table
Appendix C. The Chi-square Table
References
INDEX